


1. Amd 070
2. Amd 11070
3. Amd-070
4. Amd-11070
5. Amd070
6. Amd11070
7. Mavorixafor
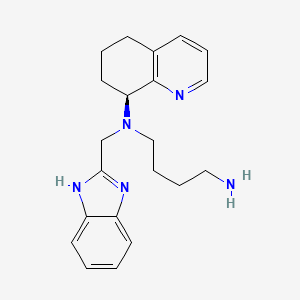
8. N'-((1h-benzo(d)imidazol-2-yl)methyl)-n'-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl)butane-1,4-diamine
9. X 4p-001
10. X4p-001
11. X4p001
1. 558447-26-0
2. Amd-070
3. Mavorixafor
4. Amd070
5. Amd11070
6. Amd 070
7. Amd-11070
8. X4p-001
9. Mavorixafor [usan]
10. X4p001
11. Cxcr4 Inhibitor X4p-001
12. 0g9lgb5o2w
13. X 4p-001
14. Chembl518924
15. Mavorixafor (usan)
16. N'-(1h-benzimidazol-2-ylmethyl)-n'-[(8s)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl]butane-1,4-diamine
17. Amd-070 (amd11070)
18. Unii-0g9lgb5o2w
19. Amd 11070
20. Compound 2 [pmid: 20297846]
21. Amd-070; Mavorixafor
22. Mavorixafor [inn]
23. Mavorixafor [who-dd]
24. Gtpl8580
25. Schembl2511950
26. Dtxsid60971247
27. Chebi:138865
28. X4p-001-io
29. X4p-001-ld
30. Bcp07108
31. Ex-a2661
32. Bdbm50315305
33. Mfcd11977316
34. Nsc775637
35. Who 10724
36. Zinc33359232
37. Amd-070 Hcl 75%(w/w%)
38. Cs-0352
39. Cs-1257
40. Db05501
41. Nsc-775637
42. Ncgc00378947-01
43. Ncgc00378947-02
44. Ncgc00378947-03
45. Hy-50101
46. N~1~-[(1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl]-n~1~-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl)butane-1,4-diamine
47. C20266
48. D11510
49. F31237
50. Q27074430
51. (s)-n-((1h-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)-n-(4-aminobutyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-amine
52. 1,4-butanediamine, N-(1h-benzimidazol-2-ylmethyl)-n-((8s)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-8-quinolinyl)-
53. 1,4-butanediamine, N1-(1h-benzimidazol-2-ylmethyl)-n1-((8s)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-8-quinolinyl)-
54. 690656-53-2
55. N'-((1h-benzo(d)imidazol-2-yl)methyl)-n'-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl)butane-1,4-diamine
56. N-(1h-benzimidazol-2-ylmethyl)-n-[(8s)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl]butane-1,4-diamine
57. N1-(1h-benzimidazol-2-ylmethyl)-n1-((s)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl)-butane-1,4-diamine
| Molecular Weight | 349.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H27N5 |
| XLogP3 | 2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 349.22664588 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 349.22664588 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 70.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 431 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Investigated for use/treatment in HIV infection.
AMD-070 is a small molecule drug candidate that belongs to a new investigational class of anti-HIV drugs known as entry (fusion) inhibitors. Approximately 76% of HIV-patients with measurable viral load are infected with a strain of virus that is resistant to one or more classes of antiretroviral agents, thus reducing treatment options. Unlike many existing HIV drugs that target the virus after it has infected a healthy cell, AMD-070 blocks the virus from entering a healthy cell, thus preventing the replication process. AMD-070 targets the CXCR4 receptor on HIV and prevents the virus from entering and infecting healthy cells. * AMD-070 is specific for the CXCR4 receptor and does not interact with any other chemokine receptors in vitro * AMD-070 strongly inhibits viral infection by all CXCR4 using virus (including virus using CXCR4 alone and/or virus using CXCR4 and CCR5) in vitro * AMD-070 is orally bioavailable in animals * Suitable PK and toxicity profile for oral dosing * AMD-070 shows additive or synergistic effects in vitro in combination with other known anti-HIV agents * AMD-070 is active against CXCR4 using HIV strains that are resistant to existing antiretroviral therapies in vitro * Potent anti-HIV activity against CXCR4-using laboratory strains and clinical isolates
Chemokine receptors expressed on the surface of immune cells are known to play a critical role in virus infection and transmission. CXCR4, and another chemokine receptor CCR5, are involved in HIV infection. The process of HIV entry begins with binding of the viral envelope glycoprotein to both the CD4 receptor and one of only two chemokine receptors, and ends with fusion of viral and cell membranes. Viral entry provides novel therapeutic targets against HIV. To date, at least 3 sub classes of HIV viral entry/fusion inhibitors have emerged: 1. CD4 binding or attachment - targets initial recognition and binding of the viral glycoprotein gp120 to the cell-surface CD4 antigen. 2. Chemokine co-receptor binding - targets binding of virus to the CCR5 or CXCR4 co-receptor. 3. Fusion Inhibition - targets the viral glycoprotein gp41 inhibiting the fusion of virus with the cell. Different strains of HIV prefer one receptor or the other, or may use either receptor to infect cells. * 35% of strains use both CXCR4 and CCR5 * 5% of strains are pure CXCR4 using * 60% of strains are pure CCR5 using * An infected individual may harbor different levels of both CXCR4 and CCR5 using virus * CXCR4 using virus independently predicts CD4 decline and HIV clinical progression and is associated with earlier mortality
