
1. An-448
2. An448
3. Diestet
4. Mazanor
5. Mazindole
6. Sanjorex
7. Sanorex
8. Solucaps
9. Teronac
10. Teronak
1. Mazanor
2. Sanorex
3. 22232-71-9
4. Mazildene
5. Teronac
6. Magrilon
7. Terenac
8. An 448
9. An-448
10. Mazindol Civ
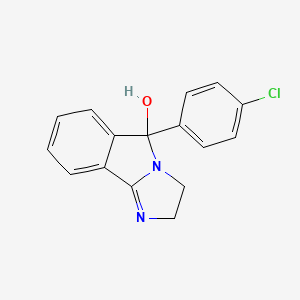
11. 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydroimidazo[1,2-b]isoindol-5-ol
12. 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3,5-dihydro-2h-imidazo[2,1-a]isoindol-5-ol
13. 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-5-hydroxy-5h-imidazo[2,1-a]isoindole
14. Sah-42548
15. Dimagrir
16. 5-p-chlorophenyl-2,3-dihydro-5h-imidazo(2,1-a)isoindol-5-ol
17. Chembl781
18. 3h-imidazo(2,1-a)isoindol-5-ol, 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-
19. Mazindole
20. 5-(p-chlorophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-3h-imidazo(2,1-a)isoindol-5-ol
21. 3h-imidazo[2,1-a]isoindol-5-ol, 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-
22. C56709m5nh
23. 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-5-hydroxy-5h-imidazo(2,1-a)isoindole
24. Mazindolum [inn-latin]
25. Mazindolum
26. 3h-imidazo(2,1-a)isoindol-5-ol, 5-(p-chlorophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-
27. Sah 42548
28. 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2h,3h,5h-imidazo[2,1-a]isoindol-5-ol
29. 3h-imidazo[2,1-a]isoindol-5-ol, 5-(p-chlorophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-
30. [3h]-mazindol
31. Ccris 3152
32. Dea No. 1605
33. 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-3h-imidazo[2,1-a]isoindol-5-ol
34. Hsdb 3112
35. Sa 42-548
36. [3h]mazindol
37. Sanorex (tn)
38. Einecs 244-857-0
39. S 42548
40. Mazindol (jan/usp/inn)
41. Brn 0546547
42. Unii-c56709m5nh
43. 5-(p-chlorophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-3h-imidazo[2,1-a]isoindol-5-ol
44. Mazindol [usan:usp:inn:ban]
45. 5h-imidazo(2,1-a)isoindol-5-ol, 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro
46. Mazindol [hsdb]
47. Mazindol [usan]
48. Mazindol [inn]
49. Mazindol [jan]
50. Mazindol [mi]
51. Mazindol [vandf]
52. (+-)-5-(p-chlorophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-3h-imidazo(2,1-a)isoindol-5-ol
53. 3h-imidazo(2,1-a)isoindol-5-ol, 2,5-dihydro-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-
54. Mazindol [mart.]
55. Mazindol [who-dd]
56. Schembl27849
57. Mls003899228
58. Mazindol [orange Book]
59. Chebi:6702
60. Gtpl4591
61. Gtpl4797
62. Mazindol [usp Impurity]
63. Dtxsid1023237
64. Mazindol, >=98% (tlc), Powder
65. Bdbm50005536
66. 3h-imidazo(2,1-a)isoindol-5-ol, 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-, (+-)-
67. Akos015895573
68. Db00579
69. Ncgc00378886-01
70. Hy-15279
71. Smr000238174
72. Ft-0670955
73. D00367
74. 232m719
75. A816031
76. Q255680
77. Mazindol, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
78. 5-(4-chloro-phenyl)-2,5-dihydro-3h-imidazo[2,1-a]isoindol-5-ol
79. 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-5h-imidazo [2,1-a]isoindol-5-ol
80. 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-5h-imidazo[2,1-a]isoindol-5-ol
81. 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-3h-imidazo[2,1-a]isoindol-5-ol #
82. 5h-imidazo(2,1-a)isoindol-5-ol, 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-
83. 5-thiophen-2-yl-2,3,5,6-tetrahydro-imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinolin-5-ol
84. (+/-)-5-(p-chlorophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-3h-imidazo(2,1-a)isoindol-5-ol
85. 3h-imidazo(2,1-a)isoindol-5-ol, 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-, (+/-)-
| Molecular Weight | 284.74 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H13ClN2O |
| XLogP3 | 2.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 284.0716407 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 284.0716407 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 35.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 419 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Appetite Depressants; Dopamine Uptake Inhibitors; Adrenergic Uptake Inhibitors; Central Nervous System Stimulants
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
The primary Medication Classification of the US Veterans Administration is GA751: Centrally-acting Appetite Suppressants.
United States Pharmacopeial Convention; USP Dispensing Information 12th ed Vol IA p. 525 (1992)
Anorexic. Central nervous system stimulant.
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 1029
... Mazindol /is/ indicated in the short-term (a few weeks) treatment of exogenous obesity in conjunction with a regimen of weight reduction based on caloric restriction, exercise, and behavior modification in patients with a body mass index of > or = 30 kg of body weight per height in meters squared (kg/sq m) or in patients with a body mass index of > or = 27 kg/sq m in the presence of risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, or hyperlipidemia. /Included in US product labeling /
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 438
An increased prevalence of abnormal cardiac valve function, primarily aortic regurgitation, was found on echocardiographic evaluation in patients receiving phentermine in combination with either dexfenfluramine or fenfluramine, both of which act to suppress appetite by increasing serotonergic function; however, an increased prevalence of abnormal cardiac valve function also has been found in patients receiving dexfenfluramine or fenfluramine alone, and the role of phentermine in producing the cardiotoxic effect is uncertain; because of the severity of these cardiovascular effects and because the safety and efficacy of other appetite suppressant combinations have not been established, combined use is not recommended; also, the safety and efficacy of combining as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), which enhances serotonergic function, with a sympathomimetic appetite suppressant have not been established and combined use is not recommended. /Appetite suppressants, sympathomimetic/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 439
When appetite suppressants and the concurrent dietary regimen are used in the treatment of obesity, blood glucose concentrations may be altered in patients with diabetes mellitus; dosage adjustment of the hypoglycemic agent may be necessary during and after concurrent therapy. /Appetite suppressants, sympathomimetic/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 439
Although only cardiovascular action attributed to mazindol is increase of 10 beats/min in orthostatic heart rate, use of this drug in patients with severe cardiovascular disease, including marked hypertension, is inadvisable.
American Medical Association. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1991. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1991., p. 2000
Extreme care is needed during concomitant use of pressor amines.
American Medical Association. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1991. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1991., p. 2000
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for MAZINDOL (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Used in short-term (a few weeks) treatment of exogenous obesity in conjunction with a regimen of weight reduction based on caloric restriction, exercise, and behavior modification in patients with a body mass index of 30 kg of body weight per height in meters squared (kg/m2) or in patients with a body mass index of 27 kg/m2 in the presence of risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, or hyperlipidemia.
Mazindol is a sympathomimetic amine that stimulates the central nervous system (nerves and brain), leading to increased your heart rate and blood pressure, and decreased appetite. Since the appetite-suppressing effect of the drug tends to decrease after few weeks of treatment, sympathomimetic appetite suppressants are typically used short-term weight-loss program.
Adrenergic Uptake Inhibitors
Drugs that block the transport of adrenergic transmitters into axon terminals or into storage vesicles within terminals. The tricyclic antidepressants (ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS, TRICYCLIC) and amphetamines are among the therapeutically important drugs that may act via inhibition of adrenergic transport. Many of these drugs also block transport of serotonin. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic Uptake Inhibitors.)
Central Nervous System Stimulants
A loosely defined group of drugs that tend to increase behavioral alertness, agitation, or excitation. They work by a variety of mechanisms, but usually not by direct excitation of neurons. The many drugs that have such actions as side effects to their main therapeutic use are not included here. (See all compounds classified as Central Nervous System Stimulants.)
Dopamine Uptake Inhibitors
Drugs that block the transport of DOPAMINE into axon terminals or into storage vesicles within terminals. Most of the ADRENERGIC UPTAKE INHIBITORS also inhibit dopamine uptake. (See all compounds classified as Dopamine Uptake Inhibitors.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A08 - Antiobesity preparations, excl. diet products
A08A - Antiobesity preparations, excl. diet products
A08AA - Centrally acting antiobesity products
A08AA05 - Mazindol
Single oral dose of 2-mg produced peak blood level of 2.5 ng/mL, for 6 hr. Multiple doses 2-mg 3/day for 4 days caused max concentration of 10.8 ng/mL 2 hr following last dose on day 4.
PMID:38081 Dugger HA et al; Drug Metab Dispos 7 (3): 129-31 (1979)
Excreted primarily in the urine as unchanged drug and conjugated metabolites.
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Data supplied on contract from American Hospital Formulary Service and other current ASHP sources., p. 1974
Following oral administration, mazindol is readily absorbed from the GI tract. The drug has an onset of action of 30-60 minutes and a duration of action of 8-15 hours. Therapeutically effective blood concentrations reportedly are 3-12 ng/mL, and blood concentrations achieved with recommended dosage are 2-4 ng/mL. Mazindol is excreted primarily in urine as unchanged drug and conjugated metabolites.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 97. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1997 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1772
Hepatic.
Major metabolite in urine in rat, dog, and human: 5-(para-chlorophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-5-hydroxy-(3)h-imidazo(2,1-alpha)isoindol-3-o.
Dugger HA et al; Drug Metabs Dispos 7 (3): 132-7 (1979)
10-13 hours
Half-life is 10-13 hours. Duration of action is 8 to 15 hours.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 438
12 to 24 hr
Reynolds, J.E.F., Prasad, A.B. (eds.) Martindale-The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 28th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press, 1982., p. 68
Unlike other sympathomimetic appetite suppressants such as phentermine, mazindol is thought to inhibit the reuptake of norepinephrine rather than to cause its release.
Mechanism of anorexiant & other central actions is unknown, but lowering of brain 5-hydroxytryptamine & elevation of dopamine levels both may be involved. Also mazindol interferes with neuronal reuptake of both brain & peripheral norepinephrine.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 823
The mechanism of action of mazindol has not been clearly defined. Although mazindol is used in the treatment of obesity as an anorexigenic, it has not been firmly established that the pharmacologic action is primarily one of appetite suppression; other CNS actions and/or metabolic effects may be involved. Results in animal studies show that mazindol exerts its effects primarily on the septal area of the brain, specifically the limbic system. The drug appears to alter norepinephrine metabolism by inhibiting the normal neuronal uptake mechanism.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 97. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1997 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1771
Saturable low-affinity binding sites for (3)H mazindol have been demonstrated in crude synaptosomal membranes from rat brain using both a centrifugation and a filtion assay. Studies on the regional distribution of these binding sites revealed that the hypothalamus and brainstem had the highest density of sites. Kinetic analysis of the binding of (3)H mazindol to hypothalamic membranes demonstrated a single class of noninteracting binding sites with an apparent affinity constant (KD) of 10.2 +/- 0.7 microM and maximal number of binding sites (Bmax) of 786 + or - 94 pmol/mg of protein. Specific (3)H mazindol binding was rapidly reversible, temperature sensitive, labile to pretreatment with proteolytic enzymes, and inhibited by physiological concn of sodium. In most peripheral tissues, such as the liver and kidney, very low levels of binding were observed; however, the adrenal gland had a relatively high density of sites. The potency of a series of anorectic drugs in inhibiting specific (3)H mazindol binding to hypothalamic membranes was highly correlated with their anorectic potencies in rats, but not with their motor stimulatory effects. These results suggest the presence of a specific drug recognition site in the hypothalamus that may mediate the anorectic activity of mazindol and related phenylethylamines.
PMID:3467029 Angel I et al; J Neurochem 48 (2): 491-7 (1987)
The action of an anorexiant, mazindol was investigated, and found that it reduced food intake by directly suppressing neurons in the lateral hypothalamus, inhibited gastric acid secretion, increased motor activity, decreased glucose absorption, and inhibited insulin secretion. It thus appears that the main effect of mazindol is to decrease food intake through suppressing feeding centers in the hypothalamus.
Inoue S et al; Am J Clin Nutr 55 (1 Suppl): 199S-202S (1992)