
1. Acid, Mefenamic
2. Apo Mefenamic
3. Apo-mefenamic
4. Contraflam
5. Coslan
6. Dysman
7. Mefac
8. Mefacit
9. Mefenaminic Acid
10. Mefic
11. Nu Mefenamic
12. Nu-mefenamic
13. Parkemed
14. Pinalgesic
15. Pms Mefenamic Acid
16. Pms-mefenamic Acid
17. Ponalar
18. Ponalgic
19. Ponmel
20. Ponstan
21. Ponstan Forte
22. Ponstel
23. Ponsyl
24. Pontal
1. 61-68-7
2. Ponstel
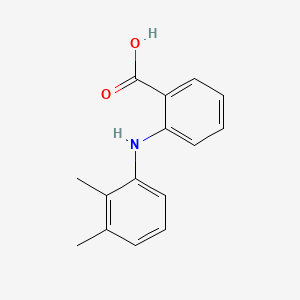
3. 2-[(2,3-dimethylphenyl)amino]benzoic Acid
4. Mephenamic Acid
5. Mephenaminic Acid
6. Ponstan
7. 2-((2,3-dimethylphenyl)amino)benzoic Acid
8. Parkemed
9. Coslan
10. Mefacit
11. Ponalar
12. Methenamic Acid
13. Mefenaminsaeure
14. Bonabol
15. Lysalgo
16. Tanston
17. Vialidon
18. Bafameritin-m
19. Tamany Bonsan
20. Ponstan Forte
21. Acide Mefenamique
22. Namphen
23. Pontal
24. Mefanamic Acid
25. Bafhameritin-m
26. Cn-35355
27. N-2,3-xylylanthranilic Acid
28. 2-(2,3-dimethylanilino)benzoic Acid
29. Mefenamate
30. Mefenacid
31. Ponstil
32. Ponstyl
33. Mefenaminic Acid
34. Hl 1
35. Inf-3355
36. Inf 3355
37. Acido Mefenamico
38. Ci-473
39. N-(2,3-xylyl)anthranilic Acid
40. Acidum Mefenamicum
41. N-(2,3-xylyl)-2-aminobenzoic Acid
42. N-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)anthranilic Acid
43. Agn-1255
44. Cl 473
45. Gardan
46. Benzoic Acid, 2-[(2,3-dimethylphenyl)amino]-
47. 2-(2,3-dimethylphenylamino)benzoic Acid
48. Anthranilic Acid, N-2,3-xylyl-
49. Cn 35355
50. Nsc 94437
51. Benzoic Acid, 2-((2,3-dimethylphenyl)amino)-
52. Ci 473
53. Nsc-94437
54. 2-diphenylaminecarboxylic Acid, 2',3'-dimethyl-
55. Chembl686
56. Mls000069709
57. Chebi:6717
58. Benzoic Acid, 2-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)amino-
59. M01ag01
60. Nsc94437
61. 367589pj2c
62. J2.344b
63. Cas-61-68-7
64. Ncgc00016278-07
65. Smr000058188
66. Dsstox_cid_3243
67. Mefenaminsaeure [german]
68. Dsstox_rid_76938
69. Dsstox_gsid_23243
70. Ac. Mefenamico [italian]
71. In-m
72. Acide Mefenamique [french]
73. Acide Mefenamique [inn-french]
74. Acido Mefenamico [inn-spanish]
75. Acidum Mefenamicum [inn-latin]
76. 2-(2,3-xylidino)benzoic Acid
77. Hsdb 3115
78. Sr-01000000216
79. Einecs 200-513-1
80. Mfcd00051721
81. Brn 2216243
82. Mefenamic-acid
83. Unii-367589pj2c
84. Prestwick_506
85. Anthranilic Acid, N-(2,3-xylyl)-
86. Mefenamic Acid,(s)
87. Spectrum_000174
88. Cpd000058188
89. Opera_id_542
90. Mefenamic Acid [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
91. Prestwick0_000054
92. Prestwick1_000054
93. Prestwick2_000054
94. Prestwick3_000054
95. Spectrum2_001941
96. Spectrum3_001082
97. Spectrum4_001235
98. Spectrum5_001341
99. M1782
100. Anthranilic Acid,3-xylyl-
101. Cid_4044
102. Schembl3544
103. Mefenamic Acid [mi]
104. Oprea1_193889
105. Bspbio_000207
106. Bspbio_002724
107. Kbiogr_001730
108. Kbioss_000654
109. Mefenamic Acid [inn]
110. Mefenamic Acid [jan]
111. Mls001074162
112. Divk1c_000298
113. Mefenamic Acid [hsdb]
114. Mefenamic Acid [usan]
115. Spectrum1501103
116. Spbio_002001
117. Spbio_002128
118. Mefenamic Acid [vandf]
119. Bpbio1_000229
120. F0850-6853
121. Gtpl2593
122. Sgcut00005
123. Wln: Qvr Bmr B1 C1
124. Mefenamic Acid [mart.]
125. Dtxsid5023243
126. Mefenamic Acid [usp-rs]
127. Mefenamic Acid [who-dd]
128. Hms500o20
129. Kbio1_000298
130. Kbio2_000654
131. Kbio2_003222
132. Kbio2_005790
133. Kbio3_001944
134. Zinc20241
135. Brd8217
136. Ninds_000298
137. Hms1568k09
138. Hms1921d13
139. Hms2090b07
140. Hms2092b17
141. Hms2095k09
142. Hms2232p18
143. Hms3259m19
144. Hms3370k18
145. Hms3652a10
146. Hms3712k09
147. Hms3885o22
148. Pharmakon1600-01501103
149. Mefenamic Acid (jp17/usp/inn)
150. Mefenamic Acid, Analytical Standard
151. Albb-025759
152. Bcp08499
153. Brd-8217
154. Hy-b0574
155. To_000071
156. Tox21_110344
157. Tox21_301983
158. Bbl003564
159. Bdbm50134036
160. Ccg-39434
161. Mefenamic Acid [orange Book]
162. Nsc757834
163. S4078
164. Stk666691
165. Mefenamic Acid [ep Monograph]
166. Akos001025551
167. Akos002388313
168. Benzoic Acid,3-dimethylphenyl)amino]-
169. Mefenamic Acid [usp Monograph]
170. Tox21_110344_1
171. Db00784
172. Nc00517
173. Nsc-757834
174. Idi1_000298
175. Smp2_000141
176. 2-(2,3-dimethylanilino)benzoic Acid #
177. 2-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)aminobenzoic Acid
178. Ncgc00016278-01
179. Ncgc00016278-02
180. Ncgc00016278-03
181. Ncgc00016278-04
182. Ncgc00016278-05
183. Ncgc00016278-06
184. Ncgc00016278-10
185. Ncgc00022393-03
186. Ncgc00022393-04
187. Ncgc00022393-05
188. Ncgc00255401-01
189. Ac-11160
190. As-12677
191. Sbi-0051636.p002
192. 2-(2,3-dimethyl-phenylamino)-benzoic Acid
193. 2-[(2,3-dimethylphenyl) Amino]benzoic Acid
194. 2-diphenylaminecarboxylic Acid,3'-dimethyl-
195. Ab00052200
196. Am20060688
197. Ft-0628184
198. Sw196700-3
199. Unm000001233403
200. 1-methyl-3-benzylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate
201. C02168
202. D00151
203. Ab00052200-17
204. Ab00052200_18
205. Ab00052200_19
206. A833367
207. Q284321
208. 2-(2,3-dimethylanilino)benzoic Acid;mefenamic Acid
209. Sr-01000000216-2
210. Sr-01000000216-4
211. W-105113
212. Brd-k92778217-001-06-1
213. Z56755828
214. 2-(2,3-dimethyl-phenylamino)-benzoic Acid(mefenamic Acid)
215. Mefenamic Acid, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
216. Mefenamic Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
217. 4-methyl-n-(3-{3-[(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl)carbonyl]imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]thiazol-6-yl}phenyl)benzenesulfonamide
| Molecular Weight | 241.28 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H15NO2 |
| XLogP3 | 5.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 241.110278721 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 241.110278721 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 49.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 292 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mefenamic acid |
| PubMed Health | Mefenamic Acid (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Analgesic, Antimigraine, Central Nervous System Agent |
| Drug Label | Mefenamic acid is a member of the fenamate group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Each Size 1 Yellow-Yellow capsule, with PAD imprinted on the cap & 195 imprinted on the body, contains 250 mg of mefenamic acid for o... |
| Active Ingredient | Mefenamic acid |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Vintage Pharms; Breckenridge Pharm; Lupin; Micro Labs |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ponstel |
| PubMed Health | Mefenamic Acid (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Analgesic, Antimigraine, Central Nervous System Agent |
| Drug Label | PONSTEL (mefenamic acid) is a member of the fenamate group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Each blue-banded, ivory capsule contains 250 mg of mefenamic acid for oral administration. Mefenamic acid is a white to greyish-white, odor... |
| Active Ingredient | Mefenamic acid |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Shionogi |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mefenamic acid |
| PubMed Health | Mefenamic Acid (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Analgesic, Antimigraine, Central Nervous System Agent |
| Drug Label | Mefenamic acid is a member of the fenamate group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Each Size 1 Yellow-Yellow capsule, with PAD imprinted on the cap & 195 imprinted on the body, contains 250 mg of mefenamic acid for o... |
| Active Ingredient | Mefenamic acid |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Vintage Pharms; Breckenridge Pharm; Lupin; Micro Labs |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ponstel |
| PubMed Health | Mefenamic Acid (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Analgesic, Antimigraine, Central Nervous System Agent |
| Drug Label | PONSTEL (mefenamic acid) is a member of the fenamate group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Each blue-banded, ivory capsule contains 250 mg of mefenamic acid for oral administration. Mefenamic acid is a white to greyish-white, odor... |
| Active Ingredient | Mefenamic acid |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Shionogi |
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal; Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
MEFENAMIC ACID (PONSTEL) ... PROVIDES ANALGESIA IN MAN SIMILAR TO THAT PRODUCED BY ASPIRIN.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 343
...INDICATED FOR RELIEF OF PAIN RESULTING FROM DENTAL EXTRACTIONS.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1050
DRUG PREFERABLY SHOULD BE TAKEN WITH FOOD.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 349
MEFENAMIC ACID SHOWED FAVORABLE RESULTS RELATIVE TO SOME ANALGESICS.
ANDERSON ET AL; TRIAL OF PROSTAGLANDIN SYNTHETASE INHIBITORS IN PRIMARY DYSMENORRHEA; LANCET 1(FEB 18) 345-348 (1978)
SINCE IT IS NOT SUPERIOR TO ESTABLISHED ANALGESICS & CAN CAUSE SERIOUS TOXICITY, USE OF MEFENAMIC ACID IS NOT RECOMMENDED. IF IT IS USED, ADMIN SHOULD NOT BE EXTENDED BEYOND 7 DAYS. IF DIARRHEA OCCURS, DRUG MUST BE DISCONTINUED & NOT USED AGAIN. IT SHOULD NOT BE USED IN CHILDREN OR IN WOMEN OF CHILDBEARING AGE.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 343
IT IS CONTRAINDICATED IN PT WITH ULCERATION OF UPPER OR LOWER INTESTINAL TRACT...& PT KNOWN TO BE HYPERSENSITIVE TO DRUG. ...CONSIDER ITS USE ONLY IN CASES WHICH EITHER CAN NOT TOLERATE OR DO NOT RESPOND TO LESS TOXIC AGENTS.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1050
MEFENAMIC ACID IS CONTRAINDICATED IN PT...WITH IMPAIRED RENAL FUNCTION, & SHOULD BE USED WITH CAUTION IN ASTHMATICS BECAUSE IT MAY EXACERBATE CONDITION.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 349
Maternal Medication usually Compatible with Breast-Feeding: Mefenamic acid: Reported Sign or Symptom in Infant or Effect on Lactation: None. /from Table 6/
Report of the American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Drugs in Pediatrics 93 (1): 141 (1994)
For the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, dysmenorrhea, and mild to moderate pain, inflammation, and fever.
FDA Label
Mefenamic acid, an anthranilic acid derivative, is a member of the fenamate group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activities. Similar to other NSAIDs, mefenamic acid inhibits prostaglandin synthetase.
Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with cyclooxygenase (PROSTAGLANDIN-ENDOPEROXIDE SYNTHASES) and thereby prevent its substrate-enzyme combination with arachidonic acid and the formation of eicosanoids, prostaglandins, and thromboxanes. (See all compounds classified as Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors.)
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M01 - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products
M01A - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids
M01AG - Fenamates
M01AG01 - Mefenamic acid
Absorption
Mefenamic acid is rapidly absorbed after oral administration.
Route of Elimination
The fecal route of elimination accounts for up to 20% of the dose, mainly in the form of unconjugated 3-carboxymefenamic acid.3 The elimination half-life of mefenamic acid is approximately two hours. Mefenamic acid, its metabolites and conjugates are primarily excreted by the kidneys. Both renal and hepatic excretion are significant pathways of elimination.
Volume of Distribution
1.06 L/kg [Normal Healthy Adults (18-45 yr)]
Clearance
Oral cl=21.23 L/hr [Healthy adults (18-45 yrs)]
CROSSES PLACENTAL BARRIER IN MONKEYS...EXCRETED IN URINE, BILE &/OR FECES...
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Data supplied on contract from American Hospital Formulary Service and other current ASHP sources., p. 1967
ABSORBED SLOWLY FROM GI TRACT...HIGH PERCENTAGE...BOUND TO PLASMA PROTEINS. PEAK PLASMA LEVELS APPEAR IN 2 TO 4 HR...ANALGESIA MAY PERSIST FOR UP TO 6 HR...ABOUT 50%...IS EXCRETED IN URINE WITHIN 24 HR /HUMAN, ORAL/
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Data supplied on contract from American Hospital Formulary Service and other current ASHP sources., p. 1967
Mefenamic acid undergoes metabolism by CYP2C9 to 3-hydroxymethyl mefenamic acid, and further oxidation to a 3-carboxymefenamic acid may occur. The activity of these metabolites has not been studied. Mefenamic acid is also glucuronidated directly.
MEFENAMIC ACID...IS TRANSFORMED TO HYDROXYMETHYL DERIVATIVE & TO ACID BY MAJOR, IF NOT ONLY, METABOLIC PATHWAY IN DOG, MONKEY, & HUMAN.
Testa, B. and P. Jenner. Drug Metabolism: Chemical & Biochemical Aspects. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc., 1976., p. 12
Mefenamic acid has known human metabolites that include 3-hydroxymethyl mefenamic aci.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
2 hours
...ABOUT 50%...IS EXCRETED IN URINE WITHIN 24 HR /HUMAN, ORAL/
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Data supplied on contract from American Hospital Formulary Service and other current ASHP sources., p. 1967
Mefenamic acid binds the prostaglandin synthetase receptors COX-1 and COX-2, inhibiting the action of prostaglandin synthetase. As these receptors have a role as a major mediator of inflammation and/or a role for prostanoid signaling in activity-dependent plasticity, the symptoms of pain are temporarily reduced.