

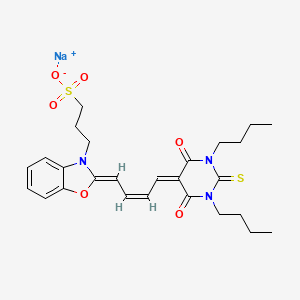

1. Mc 540
2. Merocyanine 540
3. Merocyanine Dye
1. Merocyanine 540
2. 62796-23-0
3. Schembl611112
4. E78227
| Molecular Weight | 569.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H32N3NaO6S2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 |
| Exact Mass | 569.16302238 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 569.16302238 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 151 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 38 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1020 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Antiviral Agents
Agents used in the prophylaxis or therapy of VIRUS DISEASES. Some of the ways they may act include preventing viral replication by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase; binding to specific cell-surface receptors and inhibiting viral penetration or uncoating; inhibiting viral protein synthesis; or blocking late stages of virus assembly. (See all compounds classified as Antiviral Agents.)
Fluorescent Dyes
Chemicals that emit light after excitation by light. The wave length of the emitted light is usually longer than that of the incident light. Fluorochromes are substances that cause fluorescence in other substances, i.e., dyes used to mark or label other compounds with fluorescent tags. (See all compounds classified as Fluorescent Dyes.)
Photosensitizing Agents
Drugs that are pharmacologically inactive but when exposed to ultraviolet radiation or sunlight are converted to their active metabolite to produce a beneficial reaction affecting the diseased tissue. These compounds can be administered topically or systemically and have been used therapeutically to treat psoriasis and various types of neoplasms. (See all compounds classified as Photosensitizing Agents.)
Radiation-Sensitizing Agents
Drugs used to potentiate the effectiveness of radiation therapy in destroying unwanted cells. (See all compounds classified as Radiation-Sensitizing Agents.)