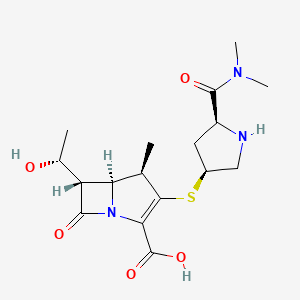

1. 3-(5-dimethylcarbamoylpyrrolidin-3-ylthio)-6-(1-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
2. Merrem
3. Penem
4. Ronem
5. Sm 7338
6. Sm-7338
7. Sm7338
1. 96036-03-2
2. Merrem
3. Meropenem Anhydrous
4. Meropenemum
5. Antibiotic Sm 7338
6. Meronem
7. Meropenem [inn]
8. 119478-56-7
9. Mepm
10. Sm 7338
11. Chebi:43968
12. Sm-7338
13. Meropenemum [inn-latin]
14. Merrem I.v.
15. Meropenem (inn)
16. Meropenem, Anhydrous
17. (4r,5s,6s)-3-{[(3s,5s)-5-(dimethylcarbamoyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]sulfanyl}-6-[(1r)-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
18. Meropenem Hydrate
19. Yop6px0bao
20. (4r,5s,6s)-3-[(3s,5s)-5-(dimethylcarbamoyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]sulfanyl-6-[(1r)-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
21. Ici-194660
22. (4r,5s,6s)-3-{[(3s,5s)-5-(dimethylcarbamoyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]thio}-6-[(1r)-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
23. Ncgc00016962-01
24. Ici 194660
25. Dsstox_cid_25526
26. Dsstox_rid_80930
27. Dsstox_gsid_45526
28. Ici 194,660
29. Meropenem (as Trihydrate)
30. Meropen
31. (1r,5s,6s)-2-[(3s,5s)-5-dimethylaminocarbonylpyrrolidin-3-ylthio]-6-[(r)-1-hydroxyethyl]-1-methylcarbapen-2-em-3-carboxylic Acid
32. (4r,5s,6s)-3-(((3s,5s)-5-(dimethylcarbamoyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)thio)-6-((r)-1-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
33. (4r,5s,6s)-3-[[(3s,5s)-5-[(dimethylamino)carbonyl]-3-pyrrolidinyl]thio]-6-[(1r)-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
34. Meronem (tn)
35. Cas-96036-03-2
36. Nsc-759621
37. Merrem I.v. (tn)
38. Sr-01000762894
39. Unii-yop6px0bao
40. Hsdb 8019
41. Merrem Iv
42. Meropenem,(s)
43. M2279
44. Brn 6940582
45. Meropenem (closed Form)
46. Meropenem [mi]
47. Prestwick0_001106
48. Prestwick1_001106
49. Prestwick2_001106
50. Prestwick3_001106
51. Chembl127
52. Epitope Id:195064
53. Meropenem [who-dd]
54. Schembl34442
55. Bspbio_001212
56. Mls001401437
57. Bidd:gt0851
58. 4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo
59. Spbio_003086
60. Bpbio1_001334
61. Meropenem With Sodium Carbonate
62. Dtxsid7045526
63. Gtpl10829
64. Hms1571m14
65. Hms2051g08
66. Hms2090c05
67. Hms2098m14
68. Hms3715m14
69. Meropenem Aslo Known As Meropenemum
70. (4r,5s,6s)-3-[(3s,5s)-5-(dimethylcarbamoyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]sulfanyl-6-[(1s)-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
71. 1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 3-(((3s,5s)-5-((dimethylamino)carbonyl)-3-pyrrolidinyl)thio)-6-((1r)-1-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-7-oxo-, (4r,5s,6s)-
72. Amy22192
73. Zinc3808779
74. Tox21_110715
75. Tox21_113794
76. Bdbm50129062
77. Mfcd00864966
78. Akos015920140
79. Tox21_110715_1
80. Ccg-100850
81. Cs-1865
82. Db00760
83. Ks-5224
84. Nc00100
85. [3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
86. Ncgc00179259-01
87. Ncgc00179259-06
88. Ncgc00179259-17
89. Ncgc00253670-01
90. Ncgc00262579-02
91. (6s)-2-{[(3s,5s)-5-(dimethylcarbamoyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]sulfanyl}-6-[(1r)-1-hydroxyethyl]-1beta-methyl-2,3-didehydro-1-carbapenam-3-carboxylic Acid
92. Hy-13678
93. Smr000469184
94. Ab00514051
95. D08185
96. M-2780
97. M05727
98. Ab00514051-02
99. Ab00698370-05
100. Pyrrolidin-3-ylthio)-6-((r)-1-hydroxyethyl)-
101. 036m032
102. Q421670
103. (4r,5s,6s)-3-((3s,5s)-5-(dimethylcarbamoyl)
104. Sr-01000762894-3
105. Sr-01000762894-4
106. Meropenem Trihydrate, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
107. (1r,5s,6s)-2-[(3s,5s)-5-(dimethylaminocarbonyl)pyrrolidin-3-ylthio]-6-[(r)-1-hydroxyethyl]-1-methylcarbapen-2-em-3-carboxylic Acid
108. (4r,5s,6s)-3-(((3s,5s)-5-(dimethylcarbamoyl)-3-pyrrolidinyl)thio)-6-((1r)-1-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
109. (4r,5s,6s)-3-(((3s,5s)-5-(dimethylcarbamoyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)thio)-6-((r)-1-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylicacid
110. (4r,5s,6s)-3-((3s,5s)-5-(dimethylcarbamoyl)pyrrolidin-3-ylthio)-6-((r)-1-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
111. (4r,5s,6s)-3-[[(3s,5s)-5-(dimethylaminocarbonyl)-3-pyrrolidinyl]thio]-6-[(1r)-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
112. (4r,6s)-3-((3s,5s)-5-(dimethylcarbamoyl)pyrrolidin-3-ylthio)-6-((r)-1-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
113. 1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 3-((5-((dimethylamino)carbonyl)-3-pyrrolidinyl)thio)-6-(1-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-7-oxo-, (4r-(3(s*,5s*),4-alpha,5-beta,6-beta(r*)))-
| Molecular Weight | 383.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H25N3O5S |
| XLogP3 | -2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 383.15149208 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 383.15149208 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 136 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 679 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 6 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Meropenem |
| PubMed Health | Meropenem (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | Meropenem for Injection, USP (I.V.) is a sterile, pyrogen-free, synthetic, broad-spectrum, carbapenem antibiotic for intravenous administration. It is (4R,5S,6S)-3-[[(3S,5S)-5-(Dimethylcarbamoyl)-3-pyrrolidinyl]thio]-6-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-methyl-... |
| Active Ingredient | Meropenem |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 500mg/vial; 1gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira; Sandoz; Acs Dobfar |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Merrem |
| PubMed Health | Meropenem (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | MERREM I.V. (meropenem for injection) is a sterile, pyrogen-free, synthetic, broad-spectrum, carbapenem antibiotic for intravenous administration. It is (4R,5S,6S)-3- [[(3S,5S)-5-(Dimethylcarbamoyl)-3-pyrrolidinyl]thio]-6- [(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-m... |
| Active Ingredient | Meropenem |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 500mg/vial; 1gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Meropenem |
| PubMed Health | Meropenem (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | Meropenem for Injection, USP (I.V.) is a sterile, pyrogen-free, synthetic, broad-spectrum, carbapenem antibiotic for intravenous administration. It is (4R,5S,6S)-3-[[(3S,5S)-5-(Dimethylcarbamoyl)-3-pyrrolidinyl]thio]-6-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-methyl-... |
| Active Ingredient | Meropenem |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 500mg/vial; 1gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira; Sandoz; Acs Dobfar |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Merrem |
| PubMed Health | Meropenem (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | MERREM I.V. (meropenem for injection) is a sterile, pyrogen-free, synthetic, broad-spectrum, carbapenem antibiotic for intravenous administration. It is (4R,5S,6S)-3- [[(3S,5S)-5-(Dimethylcarbamoyl)-3-pyrrolidinyl]thio]-6- [(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-m... |
| Active Ingredient | Meropenem |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 500mg/vial; 1gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
Anti-Bacterial Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2012)
Meropenem is used for the treatment of intra-abdominal infections, including complicated appendicitis and peritonitis, caused by susceptible bacteria. The drug may be used as monotherapy for the treatment of intra-abdominal infections caused by susceptible viridans streptococci, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacteroides fragilis, B. thetaiotaomicron, or Peptostreptococcus. Because meropenem has a broad spectrum of antibacterial activity, the drug may be used empirically to treat intra-abdominal infections before identification of the causative organism. /Included in US product labeling/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 186
Meropenem is used for the treatment of bacterial meningitis caused by susceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae (including beta-lactamase-producing strains), or Neisseria meningitidis in children 3 months of age and older. /Included in US product labeling/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 187
The drug also is used in the treatment of meningitis in adults. /NOT included in US product labeling/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 187
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Meropenem (20 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis) reported with beta-lactams. If hypersensitivity occurs, discontinue meropenem and institute appropriate therapy as indicated (e.g., epinephrine, corticosteroids, and maintenance of an adequate airway and oxygen).
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 189
Adverse effects reported in 1% or more of patients receiving meropenem including GI effects (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, constipation), local reactions (pain and inflammation at injection site, phlebitis/thrombophlebitis), headache, anemia, rash, pruritus, sepsis, apnea, shock, glossitis, and oral candidiasis.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 190
Seizures and other adverse CNS effects reported during meropenem therapy, especially in those with underlying CNS disorders (e.g., brain lesions, history of seizures), bacterial meningitis, or compromised renal function. Do not exceed recommended dosage, especially in those with known factors that predispose to seizures. Anticonvulsant therapy should be continued in those with known seizure disorders. If focal tremors, myoclonus, or seizures occur, evaluate the patient neurologically, initiate anticonvulsant therapy if necessary, and determine whether meropenem dosage should be decreased or the drug discontinued.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 189
Partial cross-allergenicity among beta-lactam antibiotics, including penicillins, cephalosporins, and other beta-lactams. Prior to initiation of meropenem therapy, make careful inquiry concerning previous hypersensitivity reactions to meropenem, cephalosporins, penicillins, or other drugs.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 189
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Meropenem (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For use as single agent therapy for the treatment of the following infections when caused by susceptible isolates of the designated microorganisms: complicated skin and skin structure infections due to Staphylococcus aureus (b-lactamase and non-b-lactamase producing, methicillin-susceptible isolates only), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, viridans group streptococci, Enterococcus faecalis (excluding vancomycin-resistant isolates), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Bacteroides fragilis and Peptostreptococcus species; complicated appendicitis and peritonitis caused by viridans group streptococci, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacteroides fragilis, B. thetaiotaomicron, and Peptostreptococcus species. Also for use in the treatment of bacterial meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae (b-lactamase and non-b-lactamase-producing isolates), and Neisseria meningitidis.
FDA Label
Treatment of bacterial sepsis, Treatment of bacterial meningitis
Meropenem is a broad-spectrum carbapenem antibiotic. It is active against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Meropenem exerts its action by penetrating bacterial cells readily and interfering with the synthesis of vital cell wall components, which leads to cell death.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
J01DH02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01D - Other beta-lactam antibacterials
J01DH - Carbapenems
J01DH02 - Meropenem
Route of Elimination
Approximately 70% of the intravenously administered dose is recovered as unchanged meropenem in the urine over 12 hours, after which little further urinary excretion is detectable.
Approximately 70% of the intravenously administered dose is recovered as unchanged meropenem in the urine over 12 hours, after which little further urinary excretion is detectable. Urinary concentrations of meropenem in excess of 10 ug/mL are maintained for up to 5 hours after a 500 mg dose.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for MEROPENEM injection, powder, for solution (October 2011). Available from, as of February 8, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=meropenem
Meropenem is distributed into most body tissues and fluids, including bronchial mucosa, lung, bile, gynecologic tissue (endometrium, myometrium, ovary, cervix, fallopian tube), muscle, heart valves, skin, interstitial and peritoneal fluid, and CSF. Plasma protein binding is approximately 2%. The drug is partially metabolized to at least one microbiologically inactive metabolite. About 70% of an IV dose is eliminated in urine as unchanged drug by tubular secretion and glomerular filtration.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 190
At the end of a 30 minute intravenous infusion of a single dose of Meropenem for injection (IV) in healthy volunteers, mean peak plasma concentrations of meropenem are approximately 23 ug/mL (range 14-26) for the 500 mg dose and 49 ug/mL (range 39-58) for the 1 g dose. A 5-minute intravenous bolus injection of Meropenem for injection (IV) in healthy volunteers results in mean peak plasma concentrations of approximately 45 ug/mL (range 18-65) for the 500 mg dose and 112 ug/mL (range 83-140) for the 1 g dose. Following intravenous doses of 500 mg, mean plasma concentrations of meropenem usually decline to approximately 1 ug/mL at 6 hours after administration. No accumulation of meropenem in plasma was observed with regimens using 500 mg administered every 8 hours or 1 g administered every 6 hours in healthy volunteers with normal renal function.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for MEROPENEM injection, powder, for solution (October 2011).
Primarily excreted unchanged. There is one metabolite which is microbiologically inactive.
There is one metabolite of meropenem that is microbiologically inactive.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for MEROPENEM injection, powder, for solution (October 2011). Available from, as of February 8, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=meropenem
Approximately 1 hour in adults and children 2 years of age and older with normal renal function. Approximately 1.5 hours in children 3 months to 2 years of age.
The plasma half-life of meropenem is approximately 1 hour in adults with normal renal function and 1.5 hours in children 3 months to 2 years of age. Plasma half-life is increased and clearance of the drug is decreased in patients with renal impairment.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 190
The bactericidal activity of meropenem results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis. Meropenem readily penetrates the cell wall of most Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria to reach penicillin-binding- protein (PBP) targets. Its strongest affinities are toward PBPs 2, 3 and 4 of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa; and PBPs 1, 2 and 4 of Staphylococcus aureus.
The bactericidal activity of meropenem results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis. Meropenem readily penetrates the cell wall of most Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria to reach penicillin-binding-protein (PBP) targets. Its strongest affinities are toward PBPs 2, 3 and 4 of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa; and PBPs 1, 2, and 4 of Staphylococcus aureus. Bactericidal concentrations (defined as a 3 log10 reduction in cell counts within 12 to 24 hours) are typically 1-2 times the bacteriostatic concentrations of meropenem, with the exception of Listeria monocytogenes, against which lethal activity is not observed.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for MEROPENEM injection, powder, for solution (October 2011). Available from, as of February 8, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=meropenem