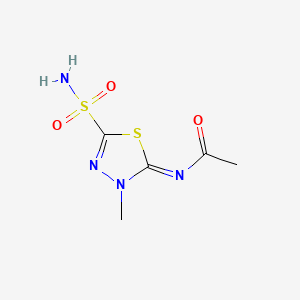

1. N Methylacetazolamide
2. N-methylacetazolamide
1. 554-57-4
2. Methenamide
3. Neptazaneat
4. Neptazane
5. Naptazane
6. N-(3-methyl-5-sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-ylidene)acetamide
7. Chebi:6822
8. L584601
9. Methazolamide, (z)-
10. Nsc-758426
11. Acetamide, N-(5-(aminosulfonyl)-3-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3h)-ylidene)-
12. Acetamide, N-[5-(aminosulfonyl)-3-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3h)-ylidene]-
13. Mls000028532
14. Chembl288100
15. Da43gw06p1
16. Vvp808
17. W733b0s9sd
18. Vvp-808
19. N-(3-methyl-5-sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3h)-ylidene)acetamide
20. Ncgc00016508-01
21. Metazolamide
22. Cas-554-57-4
23. Smr000058287
24. N-[(2e)-3-methyl-5-sulfamoyl-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-ylidene]acetamide
25. L-584601
26. Metazolamide [dcit]
27. Metazolamida
28. Methazolamidum
29. (ne)-n-(3-methyl-5-sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-ylidene)acetamide
30. Acetamide, N-(5-(aminosulfonyl)-3-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3h)-ylidene)-, (n(z))-
31. Metazolamida [inn-spanish]
32. Methazolamidum [inn-latin]
33. 1164547-86-7
34. Hsdb 3269
35. Sr-05000001844
36. Einecs 209-066-7
37. Brn 0232387
38. Unii-w733b0s9sd
39. 2-acetylimino-3-methyl-.delta.(4)-1,3,4-thiadiazoline-5-sulfonamide
40. 5-acetylimino-4-methyl-.delta.(2)-1,3,4-thiadiazoline-2-sulfonamide
41. N-(4-methyl-2-sulfamoyl-.delta.2-1,3,4-thiadiazolin-5-ylidene)acetamide
42. N-(5-(aminosulfonyl)-3-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3h)-ylidene)acetamide #
43. Acetamide, N-(4-methyl-2-sulfamoyl-.delta.2-1,3,4-thiadiazolin-5-ylidene)-
44. (z)-methazolamide
45. Neptazane (tn)
46. Methazolamide,(s)
47. Methazolamide [usp:inn:ban:jan]
48. Methazolamide, Mza
49. Prestwick_1007
50. Methazolamide (mza)
51. Noname_433
52. Spectrum_001615
53. Opera_id_717
54. Chembl19
55. Mza3
56. Prestwick0_000802
57. Prestwick1_000802
58. Prestwick2_000802
59. Prestwick3_000802
60. Spectrum2_001543
61. Spectrum3_001914
62. Spectrum4_000190
63. Spectrum5_001006
64. 2-acetylimino-3-methyl-delta(sup 4)-1,3,4-thiadiazoline-5-sulfonamide
65. 5-acetylimino-4-methyl-delta(sup 2)-1,3,4-thiadiazoline-2-sulfonamide
66. Dsstox_cid_3281
67. Methazolamide [mi]
68. Methazolamide [inn]
69. Methazolamide [jan]
70. N-(4-methyl-2-sulfamoyl-delta(sup 2)-1,3,4-thiadiazolin-5-ylidene)acetamide
71. Cid_4100
72. Dsstox_rid_76956
73. Methazolamide [hsdb]
74. Unii-da43gw06p1
75. Dsstox_gsid_23281
76. Oprea1_161738
77. Schembl24686
78. Schembl24687
79. Bspbio_000663
80. Bspbio_003508
81. Kbiogr_000739
82. Kbioss_002095
83. Methazolamide [vandf]
84. 4-27-00-08221 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
85. Mls001146905
86. Divk1c_000582
87. Methazolamide [mart.]
88. Spectrum1503252
89. Spbio_001386
90. Spbio_002584
91. Methazolamide [usp-rs]
92. Methazolamide [who-dd]
93. Bpbio1_000731
94. Gtpl6828
95. Methazolamide (jan/usp/inn)
96. Us10172837, Methazolamide
97. Chembl1335656
98. Dtxsid1023281
99. Schembl13825893
100. Bdbm10881
101. Chebi:94513
102. Hms501n04
103. Kbio1_000582
104. Kbio2_002095
105. Kbio2_004663
106. Kbio2_007231
107. Kbio3_003013
108. Dtxsid50901331
109. Methazolamide, >=98% (hplc)
110. Ninds_000582
111. Bdbm315269
112. Hms1570b05
113. Hms1922m19
114. Hms2093a05
115. Hms2097b05
116. Hms2234l03
117. Hms3259h05
118. Hms3372g12
119. Hms3652e21
120. Hms3714b05
121. Hms3747o09
122. Pharmakon1600-01503252
123. Methazolamide [orange Book]
124. Hy-b0553
125. Tox21_110464
126. Bdbm50013792
127. Ccg-39321
128. Methazolamide [usp Monograph]
129. Mfcd00083416
130. Nsc758426
131. Zinc12503151
132. Akos015897587
133. Akos024464790
134. Akos026749792
135. N-(3-methyl-5-sulfamoyl-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-ylidene)acetamide
136. Zinc100019188
137. Zinc253917094
138. Ccg-266836
139. Cl 8490
140. Db00703
141. Ks-5328
142. Nc00618
143. Nsc 758426
144. Sb17307
145. Acetamide, N-(4-methyl-2-sulfamoyl-delta(sup 2)-1,3,4-thiadiazolin-5-ylidene)-
146. Idi1_000582
147. N-[(2e)-5-(aminosulfonyl)-3-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3h)-ylidene]acetamide
148. Ncgc00016508-03
149. Ncgc00016508-04
150. Ncgc00016508-18
151. Ncgc00018188-01
152. Ncgc00018188-02
153. Ncgc00018188-03
154. Ncgc00018188-04
155. Ncgc00018188-05
156. Ncgc00018188-06
157. Ncgc00018188-07
158. Ncgc00022950-03
159. Ncgc00022950-04
160. Ncgc00178022-01
161. Ncgc00178022-02
162. Ac-32472
163. As-13272
164. Sbi-0051804.p002
165. Db-052736
166. A4364
167. Ab00490015
168. S4039
169. Sw197085-3
170. C07764
171. D00655
172. D81966
173. Ab00052336_04
174. 554m574
175. A830656
176. Methazolamide, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
177. Q1149099
178. Sr-05000001844-1
179. Sr-05000001844-2
180. Sr-05000001844-3
181. Brd-k13356952-001-15-2
182. Brd-k71053238-001-03-6
183. Brd-k71053238-001-04-4
184. Q27276292
185. (e)-n-(3-methyl-5-sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3h)-ylidene
186. N-(3-methyl-5-sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-ylidene)ethanamide
187. (nz)-n-(3-methyl-5-sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-ylidene)acetamide
188. Methazolamide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
189. (e)-n-(3-methyl-5-sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3h)-ylidene)acetamide
190. N-(4-methyl-2-sulfamoyl-.delta.(sup 2)-1,3,4-thiadiazolin-5-ylidene)acetamide
191. N-[(2z)-3-methyl-5-sulfamoyl-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-ylidene]acetamide
192. 2101958-72-7
| Molecular Weight | 236.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C5H8N4O3S2 |
| XLogP3 | 0.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 236.00378248 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 236.00378248 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 139 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 419 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Methazolamide |
| PubMed Health | Methazolamide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiglaucoma, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Methazolamide, a sulfonamide derivative, is a white crystalline powder, weakly acidic, slightly soluble in water, alcohol and acetone. The chemical name for methazolamide is: N-[5-(aminosulfonyl)-3-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazo1-2(3H)-ylidene]-acetamide and... |
| Active Ingredient | Methazolamide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ani Pharms; Sandoz; Mikart |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Methazolamide |
| PubMed Health | Methazolamide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiglaucoma, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Methazolamide, a sulfonamide derivative, is a white crystalline powder, weakly acidic, slightly soluble in water, alcohol and acetone. The chemical name for methazolamide is: N-[5-(aminosulfonyl)-3-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazo1-2(3H)-ylidene]-acetamide and... |
| Active Ingredient | Methazolamide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ani Pharms; Sandoz; Mikart |
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors; Diuretics
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITOR CHEMICALLY RELATED TO ACETAZOLAMIDE & HAVING SAME PROFILE OF CLINICAL INDICATIONS. ... IT IS INDICATED IN PATIENTS WHO DO NOT RESPOND TO ACETAZOLAMIDE OR IN THOSE WHO ARE INTOLERANT TO IT.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 867
ALTHOUGH UNDOUBTEDLY EFFECTIVE IN EVOKING DIURESIS, CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS ARE RELATIVELY INEFFECTIVE COMPARED TO NEWER & MORE EFFICACIOUS AGENTS. /CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 828
ACETAZOLAMIDE HAS BEEN GIVEN TO REDUCE INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE IN MGMNT OF GLAUCOMA. IT MAY...BE EMPLOYED FOR ITS ANTICONVULSANT ACTION FOR BOTH GRAND MAL & PARTICULARLY PETIT MAL EPILEPSY. ...ACETAZOLAMIDE APPEARS TO HAVE BENEFICIAL EFFECT IN MGMNT OF PERIODIC PARALYSIS EVEN WHEN ASSOCIATED WITH HYPOKALEMIA. /ACETAZOLAMIDE/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 828
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for METHAZOLAMIDE (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
CONTRAINDICATIONS, PRECAUTIONS, & ADVERSE REACTIONS ARE SIMILAR TO THOSE OBSERVED WITH ACETAZOLAMIDE & OTHER CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS...
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 867
SAFE USE OF THESE AGENTS DURING PREGNANCY HAS NOT BEEN ESTABLISHED. THESE AGENTS ARE CONTRAINDICATED IN PATIENTS WITH IDIOPATHIC RENAL HYPERCHLOREMIC ACIDOSIS, RENAL FAILURE, KNOWN DEPLETION OF SODIUM & OF POTASSIUM, ADDISON'S DISEASE, & PATIENTS KNOWN TO BE SENSITIVE TO THIS CLASS OF DRUGS. /CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 866
IN EDEMATOUS PATIENT, DAILY ADMIN OF ACETAZOLAMIDE LEADS TO METABOLIC TYPE OF ACIDOSIS THAT IS ACCOMPANIED BY LOSS OF DIURETIC RESPONSE TO CONTINUED DRUG THERAPY. /ACETAZOLAMIDE/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 826
CAUTION IS EMPHASIZED IN USE OF CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS IN PATIENTS WITH OBSTRUCTIVE AIRWAY DISEASE.
PMID:1244265 COUDON WL, BLOCK AJ; CHEST 69 (1): 112-113 (1976)
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for METHAZOLAMIDE (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For treatment of chronic open-angle glaucoma and acute angle-closure glaucoma
Methazolamide is topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Methazolamide is indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension who are insufficiently responsive to beta-blockers. Methazolamide is a sulfonamide derivative; however, it does not have any clinically significant antimicrobial properties. Although methazolamide achieves a high concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid, it is not-considered an effective anticonvulsant. Methazolamide has a weak and transient diuretic effect, therefore use results in an increase in urinary volume, with excretion of sodium, potassium and chloride.
Diuretics
Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. (See all compounds classified as Diuretics.)
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
A class of compounds that reduces the secretion of H+ ions by the proximal kidney tubule through inhibition of CARBONIC ANHYDRASES. (See all compounds classified as Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors.)
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01E - Antiglaucoma preparations and miotics
S01EC - Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
S01EC05 - Methazolamide
Absorption
Methazolamide is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Volume of Distribution
17 to 23 L
.../CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS/...READILY ABSORBED FROM GI TRACT. PEAK PLASMA CONCN...WITHIN 2 HR. ... EXCRETED BY KIDNEY, BOTH ACTIVE TUBULAR SECRETION & PASSIVE REABSORPTION ARE INVOLVED. /CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 827
.../CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS/ ARE TIGHTLY BOUND TO CARBONIC ANHYDRASE &... PRESENT IN GREATER AMT IN THOSE TISSUES IN WHICH ENZYME IS PRESENT IN HIGH CONCN...ERYTHROCYTES & RENAL CORTEX. /CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 828
SOME CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS DO NOT PENETRATE ERYTHROCYTE. /CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 828
Methazolamide is absorbed more slowly from the GI tract and disappears more slowly from the plasma than does acetazolamide.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2312
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for METHAZOLAMIDE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
AZETAZOLAMIDE DOES NOT UNDERGO METABOLIC ALTERATION. .../SOME CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS/ HAVE BEEN FOUND TO BE INACTIVE IN VITRO BUT ACTIVE IN VIVO, AS RESULT OF N-DEALKYLATION TO FORM AN ACTIVE METABOLITE. /CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 828
14 hours
Half-life is ~14 hours. /From table/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 693
Methazolamide is a potent inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase. Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase in the ciliary processes of the eye decreases aqueous humor secretion, presumably by slowing the formation of bicarbonate ions with subsequent reduction in sodium and fluid transport.
ANTICONVULSANT PROPERTIES...RESEMBLE THOSE OF CARBON DIOXIDE. IN ANIMALS, THEY ABOLISH THE TONIC EXTENSOR COMPONENT OF MAXIMAL ELECTROSHOCK CONVULSIONS, ELEVATE SEIZURE THRESHOLD, & PROTECT AGAINST AUDIOGENIC SEIZURES & THOSE PRODUCED BY WITHDRAWAL FROM HIGH CONCN OF CARBON DIOXIDE. /CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 218
MAJOR PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTION...IS INHIBITION OF ENZYME CARBONIC ANHYDRASE. STUDIES WITH PURIFIED ENZYME HAVE SHOWN THAT INHIBITION IS NONCOMPETITIVE. NONCATALYZED HYDRATION OR DEHYDRATION REACTION CAN TAKE PLACE...IN ABSENCE OF ENZYME. /CARBONIC ANHYDRAS INHIBITORS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 826
MORE THAN 99% OF ENZYME ACTIVITY IN THE KIDNEY MUST BE INHIBITED BEFORE PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS BECOME APPARENT. THE ENZYME ITSELF IS DOMINANT TISSUE COMPONENT TO WHICH THE INHIBITORS BECOME BOUND. /CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 826
FOLLOWING ADMIN OF ACETAZOLAMIDE, THE URINE VOLUME PROMPTLY INCR. NORMALLY ACIDIC PH BECOMES ALKALINE. URINARY CONCN OF BICARBONATE ANION INCR AND IS MATCHED BY SODIUM AND SUBSTANTIAL AMT OF POTASSIUM. /CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 826
...THE DRUG HAS BEEN FOUND TO INHIBIT EPILEPTIC SEIZURES & TO DECR RATE OF SPINAL FLUID FORMATION. EXACT MECHANISMS BY WHICH CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITION IS RELATED TO THESE CHANGES IN FUNCTION ARE NOT CLEAR, & MULTIPLE FACTORS MAY BE INVOLVED. /CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 827