
1. Amethopterin
2. Dicesium Salt Methotrexate
3. Hydrate, Methotrexate
4. Methotrexate Hydrate
5. Methotrexate Sodium
6. Methotrexate, (d)-isomer
7. Methotrexate, (dl)-isomer
8. Methotrexate, Dicesium Salt
9. Methotrexate, Disodium Salt
10. Methotrexate, Sodium Salt
11. Mexate
12. Sodium, Methotrexate
1. 59-05-2
2. Amethopterin
3. Rheumatrex
4. Methylaminopterin
5. Abitrexate
6. Trexall
7. Mexate
8. Metatrexan
9. Hdmtx
10. Methylaminopterinum
11. Mtx
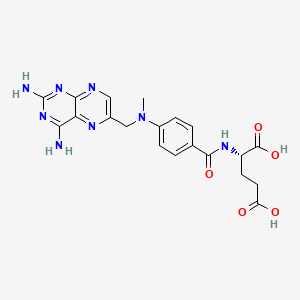
12. (s)-2-(4-(((2,4-diaminopteridin-6-yl)methyl)(methyl)amino)benzamido)pentanedioic Acid
13. Methotrexatum
14. Rasuvo
15. 4-amino-10-methylfolic Acid
16. Metotrexato
17. Maxtrex
18. Nsc-740
19. Mexate-aq
20. N-bismethylpteroylglutamic Acid
21. Folex
22. Nci-c04671
23. Cl-14377
24. Antifolan
25. Methotrexate Lpf
26. Xatmep
27. 133073-73-1
28. Amethopterine
29. Farmitrexat
30. Emt 25,299
31. L-amethopterin
32. Cl 14377
33. Methotrexat-ebewe
34. Tcmdc-125858
35. (2s)-2-[[4-[(2,4-diaminopteridin-6-yl)methyl-methylamino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic Acid
36. Abitrexate (methotrexate)
37. R 9985
38. Yl5fz2y5u1
39. Methotextrate
40. Methotrexat
41. Chembl34259
42. Nsc740
43. Chebi:44185
44. Adx-2191
45. N-[4-[[(2,4-diamino-6-pteridinyl)methyl]methylamino]benzoyl]-l-glutamic Acid
46. N-[(4-{[(2,4-diaminopteridin-6-yl)methyl](methyl)amino}phenyl)carbonyl]-l-glutamic Acid
47. Cl14377
48. Ncgc00025060-04
49. Nsc 740
50. 4-amino-n(10)-methylpteroylglutamic Acid
51. A-methopterin
52. Dsstox_cid_822
53. A-methpterin
54. Amethopterin L-
55. Folex-pfs
56. R-9985
57. (2s)-2-[(4-{[(2,4-diaminopteridin-6-yl)methyl](methyl)amino}phenyl)formamido]pentanedioic Acid
58. Dsstox_rid_75810
59. Methotrexate, L-
60. Dsstox_gsid_20822
61. X 133
62. Metotressato [dcit]
63. Methotrexate, D-
64. Fauldexato
65. Medsatrexate
66. Methoblastin
67. Metotressato
68. Brimexate
69. Emthexat
70. Emthexate
71. Lantarel
72. Lumexon
73. Metrotex
74. Novatrex
75. Otrexup
76. Tremetex
77. Trexeron
78. Trixilem
79. Metex
80. Texate
81. Mls001401431
82. Methotrexatum [inn-latin]
83. Metotrexato [inn-spanish]
84. [3h]methotrexate
85. Smr000112001
86. [3h]-methotrexate
87. Folic Acid Antagonist
88. Ccris 1109
89. 4-aminomethylpteroylglutamic Acid
90. Hsdb 3123
91. L-(+)-n-(p-(((2,4-diamino-6-pteridinyl)methyl)methylamino)benzoyl)glutamic Acid
92. N-(p-(((2,4-diamino-6-pteridinyl)methyl)methylamino)benzoyl)-l-(+)-glutamic Acid
93. Sr-01000075682
94. Smr000449324
95. Einecs 200-413-8
96. Unii-yl5fz2y5u1
97. Metolate
98. Nordimet
99. Ai3-25299
100. Intradose-mtx
101. 4-amino-n(sup 10)-methylpteroylglutamic Acid
102. 1dhi
103. 1dhj
104. 2drc
105. 4ocx
106. (2s)-2-[[4-[(2,4-diaminopteridin-6-yl)methyl-methyl-amino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic Acid
107. Cas-59-05-2
108. Glutamic Acid, N-(p-(((2,4-diamino-6-pteridinyl)methyl)methylamino)benzoyl)-, L-
109. Kyselina N-(p-((2,4-diamino-6-pteridinylmethyl)methylamino)benzoyl)-l-glutamova
110. Mpi-2505
111. Prestwick_322
112. Otrexup (tn)
113. Xatmep (tn)
114. Reditrex
115. Kyselina 4-amino-n(sup 10)-methylpteroylglutamova [czech]
116. Methylaminopterin; Mtx
117. Methotrexate [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
118. Spectrum_001836
119. Tocris-1230
120. 4kn0
121. Wr-19039
122. Prestwick0_000135
123. Prestwick1_000135
124. Prestwick2_000135
125. Spectrum2_001077
126. Spectrum3_000497
127. Spectrum4_000616
128. Spectrum5_000958
129. Methotrexate - Abitrexate
130. Methotrexate [mi]
131. N-(p-(((2,4-diamino-6-pteridyl)methyl)methylamino)benzoyl)glutamic Acid
132. Methotrexate [inn]
133. Methotrexate [jan]
134. L(+)-amethopterin Hydrate
135. Methotrexate [hsdb]
136. Methotrexate [iarc]
137. Methotrexate [inci]
138. Methotrexate [usan]
139. N-(4-(((2,4-diamino-6-pteridinyl)methyl)methylamino)benzoyl)-l-glutamicacid
140. Ncimech_000767
141. Schembl3711
142. Kyselina N-(p-((2,4-diamino-6-pteridinylmethyl)methylamino)benzoyl)-l-glutamova [czech]
143. Methotrexate [vandf]
144. Bidd:pxr0175
145. Lopac0_000020
146. Kbiogr_001172
147. Kbioss_002341
148. Methotrexate [mart.]
149. Kyselina 4-amino-n(sup 10)-methylpteroylglutamova
150. Mls000049968
151. Mls002154208
152. Divk1c_000114
153. Methotrexate [usp-rs]
154. Methotrexate [who-dd]
155. Methotrexate [who-ip]
156. Spbio_001094
157. Spbio_002149
158. Amy235
159. Cid_126941
160. Cid_165528
161. Gtpl4674
162. Gtpl4815
163. Dtxsid4020822
164. Schembl12421860
165. Schembl23111732
166. Bdbm18050
167. Bdbm66082
168. Hms500f16
169. Kbio1_000114
170. Kbio2_002338
171. Kbio2_004906
172. Kbio2_007474
173. Kbio3_001493
174. Methotrexate (jp17/usp/inn)
175. G301
176. Ninds_000114
177. Bio1_000486
178. Bio1_000975
179. Bio1_001464
180. Hms1568k12
181. Hms2095k12
182. Hms2233o18
183. Hms3260c21
184. Hms3414l09
185. Hms3678l07
186. Hms3712k12
187. Methotrexate [orange Book]
188. Methotrexate [ep Monograph]
189. Methotrexate [usp Impurity]
190. Act03341
191. Apc-2002
192. Bcp13701
193. Mpi-5004
194. Zinc1529323
195. Methotrexate [usp Monograph]
196. Tox21_110944
197. Tox21_300269
198. Tox21_500020
199. Ccg-35800
200. Emt-25299
201. Methotrexatum [who-ip Latin]
202. Mfcd00064370
203. S1210
204. Stl535338
205. (4-(((2,4-diaminopteridin-6-yl)methyl)(methyl)amino)benzoyl)-l-glutamic Acid
206. Akos016340329
207. Tox21_110944_1
208. Cs-1732
209. Db00563
210. Ks-5093
211. Lp00020
212. Sdccgsbi-0050009.p003
213. Wr19039
214. Idi1_000114
215. N-(4-{[(2,4-diaminopteridin-6-yl)methyl](methyl)amino}benzoyl)-l-glutamic Acid
216. Smp2_000020
217. (methyl)amino)benzamido)pentanedioic Acid
218. Ncgc00025060-01
219. Ncgc00025060-02
220. Ncgc00025060-03
221. Ncgc00025060-05
222. Ncgc00025060-06
223. Ncgc00025060-07
224. Ncgc00025060-08
225. Ncgc00025060-09
226. Ncgc00025060-10
227. Ncgc00025060-11
228. Ncgc00025060-12
229. Ncgc00025060-13
230. Ncgc00025060-15
231. Ncgc00025060-16
232. Ncgc00254216-01
233. Ncgc00260705-01
234. Hy-14519
235. Eu-0100020
236. G-301
237. Sw198601-3
238. Methotrexate 1.0 Mg/ml In Dimethyl Sulfoxide
239. 73m731
240. A10021
241. C01937
242. D00142
243. Q422232
244. Sr-01000597411
245. W-60383
246. (s)-2-(4-(((2,4-diaminopteridin-6-yl)methyl)
247. Q-201366
248. Sr-01000075682-1
249. Sr-01000075682-2
250. Sr-01000075682-6
251. Sr-01000597411-1
252. W-105347
253. Brd-k59456551-001-09-3
254. Brd-k59456551-001-11-9
255. Wln: T66 Bn Dn Gn Jnj Cz Ez H1n1&r Dvmyvq2vq
256. Z1541638527
257. N,n,n,n-ethylenediaminetetra(methylenephosphonicacid)
258. Methotrexate, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
259. Methotrexate, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
260. Glutamic Acid,4-diamino-6-pteridinyl)methyl] Methylamino]benzoyl]-, L-(+)-
261. L-glutamic Acid,4-diamino-6-pteridinyl)methyl]- Methylamino]benzoyl]-
262. (s)-2-(4-(((2,4-diaminopteridin-6-yl)methyl)-(methyl)amino)benzamido)pentanedioic Acid
263. L-glutamic Acid,n-[4-[[(2,4-diamino-6-pteridinyl)methyl]methylamino]benzoyl]-,hydrate(9ci)
264. Methotrexate For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
265. Methotrexate For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
266. Methotrexate, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
267. N-[4-[[(2,4-diamino-6-pteridinyl)methyl] Methylamino]benzoyl]-l-glutamic Acid
268. (2s)-2-((4-(((2,4-diaminopteridin-6-yl)methyl)(methyl)amino)benzoyl)amino)pentanedioic Acid
269. (2s)-2-[[[4-[(2,4-diamino-6-pteridinyl)methyl-methylamino]phenyl]-oxomethyl]amino]pentanedioic Acid;hydrate
270. (2s)-2-[[4-[(2,4-diaminopteridin-6-yl)methyl-methyl-amino]benzoyl]amino]glutaric Acid;hydrate
271. (2s)-2-[[4-[[2,4-bis(azanyl)pteridin-6-yl]methyl-methyl-amino]phenyl]carbonylamino]pentanedioic Acid;hydrate
272. 102613-64-9
273. L-glutamic Acid,n-[4-[[(2,4-diamino-6-pteridinyl)methyl]methylamino]benzoyl]-, Hydrate (9ci)
274. Methotrexate, Pharmagrade, Manufactured Under Appropriate Controls For Use As A Raw Material In Pharma Or Biopharmaceutical Production, Meets Ep, Usp Testing Specifications
| Molecular Weight | 454.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H22N8O5 |
| XLogP3 | -1.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 454.17131583 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 454.17131583 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 211 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 704 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Methotrexate sodium |
| Drug Label | Methotrexate (formerly Amethopterin) is an antimetabolite used in the treatment of certain neoplastic diseases, severe psoriasis, and adult rheumatoid arthritis. Chemically methotrexate is N-[4-[[(2,4-diamino-6-pteridinyl)methyl]methylamino]benzoyl]-... |
| Active Ingredient | Methotrexate sodium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | eq 200mg base/8ml (eq 25mg base/ml); eq 250mg base/10ml (eq 25mg base/ml); eq 50mg base/2ml (eq 25mg base/ml); eq 2.5mg base; eq 100mg base/4ml (eq 25mg base/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira; Roxane; Dava Pharms; Fresenius Kabi Usa; Eurohlth Intl; Mylan; Barr |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Trexall |
| PubMed Health | Methotrexate |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Antipsoriatic, Antirheumatic, Antirheumatic, Cytotoxic |
| Drug Label | Trexall (methotrexate tablets USP) (formerly Amethopterin) is an antimetabolite used in the treatment of certain neoplastic diseases, severe psoriasis, and adult rheumatoid arthritis. Chemically methotrexate, USP is N-[4[[(2,4-diamino-6-pteridiny... |
| Active Ingredient | Methotrexate sodium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 5mg base; eq 7.5mg base; eq 15mg base; eq 10mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Barr |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Methotrexate sodium |
| Drug Label | Methotrexate (formerly Amethopterin) is an antimetabolite used in the treatment of certain neoplastic diseases, severe psoriasis, and adult rheumatoid arthritis. Chemically methotrexate is N-[4-[[(2,4-diamino-6-pteridinyl)methyl]methylamino]benzoyl]-... |
| Active Ingredient | Methotrexate sodium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | eq 200mg base/8ml (eq 25mg base/ml); eq 250mg base/10ml (eq 25mg base/ml); eq 50mg base/2ml (eq 25mg base/ml); eq 2.5mg base; eq 100mg base/4ml (eq 25mg base/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira; Roxane; Dava Pharms; Fresenius Kabi Usa; Eurohlth Intl; Mylan; Barr |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Trexall |
| PubMed Health | Methotrexate |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Antipsoriatic, Antirheumatic, Antirheumatic, Cytotoxic |
| Drug Label | Trexall (methotrexate tablets USP) (formerly Amethopterin) is an antimetabolite used in the treatment of certain neoplastic diseases, severe psoriasis, and adult rheumatoid arthritis. Chemically methotrexate, USP is N-[4[[(2,4-diamino-6-pteridiny... |
| Active Ingredient | Methotrexate sodium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 5mg base; eq 7.5mg base; eq 15mg base; eq 10mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Barr |
Abortifacient Agents, Nonsteroidal; Antimetabolites, Antineoplastic; Antirheumatic Agents; Dermatologic Agents; Enzyme Inhibitors; Folic Acid Antagonists; Immunosuppressive Agents; Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Methotrexate is indicated for treatment of breast carcinoma, head and neck cancers (epidermoid), non-small cell lung carcinoma (especially squamous cell types), small cell lung carcinoma, and gestational trophoblastic tumors (gestational choriocarcinoma, chorioadenoma destruens, hydatidiform mole). /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1911
Methotrexate is indicated for treatment of cervical carcinoma, ovarian carcinoma, bladder carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, esophageal carcinoma, gastric carcinoma, pancreatic carcinoma, and penile carcinoma. /NOT included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1911
Methotrexate is indicated for treatment of acute lymphocytic leukemia and prophylaxis and treatment of meningeal leukemia. /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1911
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for METHOTREXATE (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Methotrexate is a highly toxic drug with a very low therapeutic index and a therapeutic response is not likely to occur without some evidence of toxicity. ... When methotrexate is used in combination with other antineoplastic agents and/or radiation therapy, toxic reactions may be more severe than would occur with methotrexate therapy alone. Although doses of methotrexate used in the management of psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis are usually lower than those used in antineoplastic chemotherapy, severe toxicity may occur in any patient receiving the drug and deaths have been reported with the use of methotrexate in the management of psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1111
Methotrexate should be used with extreme caution in patients with infection, peptic ulcer, ulcerative colitis, or debility, and in very young or geriatric patients. Methotrexate should be used with extreme caution, if at all, in patients with malignant disease who have preexisting liver damage or impaired hepatic function, preexisting bone marrow depression, aplasia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, or anemia; the drug is usually contraindicated in patients with impaired renal function. In the management of psoriasis, methotrexate is contraindicated in patients with poor nutritional status or severe renal or hepatic disorders, those with overt or laboratory evidence of an immunodeficiency syndrome, and in those with preexisting blood dyscrasias such as bone marrow hypoplasia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, or clinically important anemia; relative contraindications also include cirrhosis, active or recent hepatitis, or excessive alcohol consumption. In the management of rheumatoid arthritis, methotrexate is contraindicated in patients with preexisting blood dyscrasias such as bone marrow hypoplasia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, or clinically important anemia; those with overt or laboratory evidence of immunodeficiency syndromes; and those with excessive alcohol consumption, alcoholic liver disease, or chronic liver disease.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1112
Elevations in serum uric acid concentrations may occur in patients receiving methotrexate as a result of cell destruction and hepatic and renal damage. In some patients, uric acid nephropathy and acute renal failure may result. Tumor lysis syndrome associated with other cytotoxic drugs (e.g., fludarabine, cladribine), also has been reported in patients with rapidly growing tumors who were receiving methotrexate. Pharmacologic and appropriate supportive treatment may prevent or alleviate this complication. Methotrexate also was reported to precipitate acute gouty arthritis in two patients being treated for psoriasis. Administration of large volumes of fluids, alkalinization of the urine, and/or administration of allopurinol may be useful in preventing acute attacks of hyperuricemia and uric acid nephropathy.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1111
Severe nephropathy manifested by azotemia, hematuria, and renal failure may occur in patients receiving methotrexate; fatalities have been reported. In one study, postmortem examination revealed extensive necrosis of the epithelium of the convoluted tubules. In patients with renal impairment, methotrexate accumulation and increased toxicity or additional renal damage may occur.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1111
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for METHOTREXATE (22 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Methotrexate oral solution is indicated for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia and pediatric polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Methotrexate injections for subcutaneous use are indicated for severe active rheumatoid arthritis, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis and severe, recalcitrant, disabling psoriasis. Other formulations are indicated to treat gestational choriocarcinoma, chorioadenoma destruens, hydatiform mole, breast cancer, epidermoid cancer of the head and neck, advanced mycosis fungoides, lung cancer, and advanced non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. It is also used in the maintenance of acute lymphocytic leukemia. Methotrexate is also given before treatment with leucovorin to prolong relapse-free survival following surgical removal of a tumour in non-metastatic osteosarcoma.
FDA Label
Nordimet is indicated for the treatment of:
- active rheumatoid arthritis in adult patients,
- polyarthritic forms of severe, active juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), when the response to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) has been inadequate,
- severe recalcitrant disabling psoriasis, which is not adequately responsive to other forms of therapy such as phototherapy, psoralens and ultraviolet A (PUVA), and retinoids, and severe psoriatic arthritis in adult patients,
- induction of remission in moderate steroid-dependent Crohn's disease in adult patients, in combination with corticosteroids and for maintenance of remission, as monotherapy, in patients who have responded to methotrexate.
Methotrexate inhibits enzymes responsible for nucleotide synthesis which prevents cell division and leads to anti-inflammatory actions. It has a long duration of action and is generally given to patients once weekly. Methotrexate has a narrow therapeutic index. Do not take methotrexate daily.
Abortifacient Agents, Nonsteroidal
Non-steroidal chemical compounds with abortifacient activity. (See all compounds classified as Abortifacient Agents, Nonsteroidal.)
Enzyme Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme combination and the catalytic reaction. (See all compounds classified as Enzyme Inhibitors.)
Antimetabolites, Antineoplastic
Antimetabolites that are useful in cancer chemotherapy. (See all compounds classified as Antimetabolites, Antineoplastic.)
Immunosuppressive Agents
Agents that suppress immune function by one of several mechanisms of action. Classical cytotoxic immunosuppressants act by inhibiting DNA synthesis. Others may act through activation of T-CELLS or by inhibiting the activation of HELPER CELLS. While immunosuppression has been brought about in the past primarily to prevent rejection of transplanted organs, new applications involving mediation of the effects of INTERLEUKINS and other CYTOKINES are emerging. (See all compounds classified as Immunosuppressive Agents.)
Antirheumatic Agents
Drugs that are used to treat RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. (See all compounds classified as Antirheumatic Agents.)
Dermatologic Agents
Drugs used to treat or prevent skin disorders or for the routine care of skin. (See all compounds classified as Dermatologic Agents.)
Folic Acid Antagonists
Inhibitors of the enzyme, dihydrofolate reductase (TETRAHYDROFOLATE DEHYDROGENASE), which converts dihydrofolate (FH2) to tetrahydrofolate (FH4). They are frequently used in cancer chemotherapy. (From AMA, Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p2033) (See all compounds classified as Folic Acid Antagonists.)
Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit cell production of DNA or RNA. (See all compounds classified as Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors.)
L04AX03
L04AX03
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01B - Antimetabolites
L01BA - Folic acid analogues
L01BA01 - Methotrexate
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L04 - Immunosuppressants
L04A - Immunosuppressants
L04AX - Other immunosuppressants
L04AX03 - Methotrexate
Absorption
Methotrexate has a bioavailability of 64-90%, though this decreases at oral doses above 25mg due to saturation of the carrier mediated transport of methotrexate.. Methotrexate has a Tmax of 1 to 2 hours. oral doses of 10-15g reach serum levels of 0.01-0.1M.
Route of Elimination
Methotrexate is >80% excreted as the unchanged drug and approximately 3% as the 7-hydroxylated metabolite. Methotrexate is primarily excreted in the urine with 8.7-26% of an intravenous dose appearing in the bile.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of methotrexate at steady state is approximately 1L/kg.
Clearance
Methotrexate clearance varies widely between patients and decreases with increasing doses. Currently, predicting clearance of methotrexate is difficult and exceedingly high serum levels of methotrexate can still occur when all precautions are taken.
In adults, oral absorption of methotrexate appears to be dose dependent. Peak serum levels are reached within one to two hours. At doses of 30 mg/sq m or less, methotrexate is generally well absorbed with a mean bioavailability of about 60%. The absorption of doses greater than 80 mg/sq m is significantly less, possibly due to a saturation effect.
Physicians Desk Reference. 58th ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 2004., p. 806
After intravenous administration, the initial volume of distribution is approximately 0.18 L/kg (18% of body weight) and steady-state volume of distribution is approximately 0.4 to 0.8 L/kg (40% to 80% of body weight).
Physicians Desk Reference. 58th ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 2004., p. 806
Protein binding: Moderate (approximately 50%), primarily to albumin.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1912
At serum methotrexate concentrations exceeding 0.1 umol/mL passive diffusion becomes a major means of intracellular transport of the drug. The drug is widely distributed into body tissues with highest concn in the kidneys, gallbladder, spleen, liver, and skin.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1113
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for METHOTREXATE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Methotrexate is metabolized by folylpolyglutamate synthase to methotrexate polyglutamate in the liver as well as in tissues. Gamma-glutamyl hydrolase hydrolyzes the glutamyl chains of methotrexate polyglutamates converting them back to methotrexate. A small amount of methotrexate is also converted to 7-hydroxymethotrexate.
After absorption, methotrexate undergoes hepatic and intracellular metabolism to form methotrexate polyglutamate, metabolites which by hydrolysis may be converted back to methotrexate. Methotrexate polyglutamates inhibit dihydrofolate reductase and thymidylate synthetase. Small amounts of these polyglutamate metabolites may remain in tissues for extended periods; the retention and prolonged action of these active metabolites vary among different cells, tissues, and tumors. In addition, small amounts of methotrexate polyglutamate may be converted to 7-hydroxymethotrexate; accumulation of this metabolite may become substantial following administration of high doses of methotrexate, since the aqueous solubility of 7-hydroxymethotrexate is threefold to fivefold lower than that of the parent compound. Following oral administration of methotrexate, the drug also is partially metabolized by the intestinal flora.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1113
The half life of low dose methotrexate is 3 to 10 hours in adults. The half life for high dose methotrexate is 8 to 15 hours. Pediatric patients taking methotrexate for acute lymphoblastic anemia experience a terminal half life of 0.7 to 5.8 hours. Pediatric patients taking methotrexate for juvenile idiopathic arthritis experience a half life of 0.9 to 2.3 hours.
Terminal: Low doses: 3 to 10 hours. High doses: 8 to 15 hours. Note: There is wide interindividual variation in clearance rates. Small amounts of methotrexate and its metabolites are protein-bound and may remain in tissues (kidneys, liver) for weeks to months; the presence of fluid loads, such as ascites or pleural effusion, and renal function impairment will also delay clearance.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1912
Methotrexate enters tissues and is converted to a methotrexate polyglutamate by folylpolyglutamate. Methotrexate's mechanism of action is due to its inhibition of enzymes responsible for nucleotide synthesis including dihydrofolate reductase, thymidylate synthase, aminoimidazole caboxamide ribonucleotide transformylase (AICART), and amido phosphoribosyltransferase. Inhibtion of nucleotide synthesis prevents cell division. In rheumatoid arthritis, methotrexate polyglutamates inhibit AICART more than methotrexate. This inhibition leads to accumulation of AICART ribonucleotide, which inhibits adenosine deaminase, leading to an accumulation of adenosine triphosphate and adenosine in the extracellular space, stimulating adenosine receptors, leading to anti-inflammatory action.
Methotrexate and its polyglutanate metabolites reversibly inhibits dihydrofolate reductase, the enzyme that reduces folic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid. Inhibition of tetrahydrofolate formation limits the availability of one-carbon fragments necessary for synthesis of purines and the conversion of deoxyuridylate to thymidylate in the synthesis of DNA and cell reproduction. The affinity of dihydrofolate reductase for methotrexate is far greater than its affinity for folic acid or dihydrofolic acid. and, therefore, even very large doses of folic acid given simultaneously will not reverse the effects of methotrexate. Leucovorin calcium, a derivative of tetrahydrofolic acid, may block the effects of methotrexate if given shortly after the antineoplastic agent. Results of one study indicate that methotrexate also causes an increase in intracellular deoxyadenosine triphosphate, which is thought to inhibit ribonucleotide reduction, and polynucleotide ligase, an enzyme concerned in DNA synthesis and repair. Tissues with high rates of cellular proliferation such as neoplasms, psoriatic epidermis, bone marrow, the lining of the GI tract, hair matrix, and fetal cells are most sensitive to the effects of methotrexate.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1113
Methotrexate ... has immunosuppressive activity, in part possibly as a result of inhibition of lymphocyte multiplication. The mechanism(s) of action in the management of rheumatoid arthritis of the drug is not known, although suggested mechanisms have included immunosuppressive and/or antiinflammatory effects.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1113