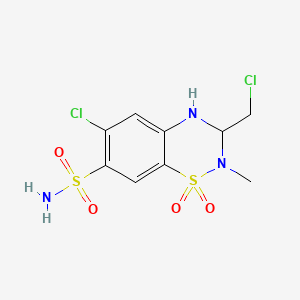

1. 135-07-9
2. Enduron
3. Aquatensen
4. Duretic
5. Methyclothiazid
6. Methycyclothiazide
7. Enduronum
8. Methychlothiazide
9. Methylclothiazide
10. Methylcyclothiazide
11. Methylchlorothiazide
12. Aquaresen
13. Ciba 7272-su
14. Nsc-110431
15. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-, 1,1-dioxide
16. Aquatensen;enduron
17. Nsc 110431
18. Methyclothiazide, (+)-
19. Methyclothiazide, (-)-
20. 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
21. R00uul4srn
22. R6kdh2s0sx
23. 6-chloro-3-chloromethyl-2-methyl-7-sulfamyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
24. Mls002704228
25. Chebi:6847
26. L3h46uac61
27. 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-2-methyl-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
28. Nsc110431
29. 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-1$l^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
30. Naturon (van)
31. Ncgc00167446-01
32. Meticlotiazida
33. Meticlotiazide
34. Methyclothiazidum
35. Meticlotiazide [dcit]
36. Dsstox_cid_3313
37. Dsstox_rid_76970
38. Dsstox_gsid_23313
39. 96783-15-2
40. Meticlotiazida [inn-spanish]
41. Methyclothiazidum [inn-latin]
42. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-, 1,1-dioxide, (+)-
43. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-, 1,1-dioxide, (-)-
44. 96783-14-1
45. Cas-135-07-9
46. Enduron (tn)
47. Hsdb 3363
48. Einecs 205-172-2
49. Ci-625
50. Brn 0765361
51. Unii-l3h46uac61
52. Methyclothiazide (jan/usp/inn)
53. Methyclothiazide [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
54. Unii-r00uul4srn
55. Unii-r6kdh2s0sx
56. Chembl1577
57. Schembl49396
58. Methyclothiazide [mi]
59. (+-)-6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
60. Methyclothiazide [inn]
61. Methyclothiazide [jan]
62. Methyclothiazide [hsdb]
63. Methyclothiazide [usan]
64. Gtpl7235
65. Methyclothiazide [vandf]
66. Dtxsid6023313
67. Methyclothiazide [mart.]
68. Methyclothiazide [usp-rs]
69. Methyclothiazide [who-dd]
70. Hms3264d19
71. Hms3652e06
72. Pharmakon1600-01503841
73. Hy-b0562
74. Tox21_112450
75. Nsc760078
76. S4057
77. Methyclothiazide [orange Book]
78. Akos015896465
79. Tox21_112450_1
80. Ccg-213705
81. Db00232
82. Ks-5138
83. Nsc-760078
84. Eutron Component Methyclothiazide
85. Methyclothiazide [usp Monograph]
86. Ncgc00167446-02
87. Ncgc00167446-03
88. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-, 1,1-dioxide, (+-)-
89. 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-2h-1,2, 4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
90. As-12982
91. Smr001550236
92. Enduronyl Component Methyclothiazide
93. Methyclothiazide Component Of Eutron
94. Diutensen-r Component Methyclothiazide
95. Ft-0654252
96. Sw219271-1
97. Methyclothiazide Component Of Enduronyl
98. C07765
99. D00656
100. Wln: T66 Bswn Em Dhj C1 D1g Hg Iszw
101. Ab01014600_03
102. Ab01014600_04
103. Methyclothiazide Component Of Diutensen-r
104. 135m079
105. A806880
106. Q6823919
107. Brd-a95340155-001-05-5
108. 3-amino-3-(2,5-dihydroxy-phenyl)-propionicacid
109. Z1550675459
110. 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-3,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
111. (+/-)-6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
112. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-, 1,1-dioxide, (+/-)-
113. 2h-1,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-, 1,1-dioxide
114. 6-chloranyl-3-(chloromethyl)-2-methyl-1,1-bis(oxidanylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1$l^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
115. 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-1?^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
116. 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-16,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
117. 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-1lambda6,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
118. 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2h-1$l^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
119. 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2h-1lambda6,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
120. 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-2-methyl-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide #
121. 6-chloro-3-(chloromethyl)-2-methyl-3,4-dihydro-2h-benzo[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
| Molecular Weight | 360.2 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H11Cl2N3O4S2 |
| XLogP3 | 1.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 358.9568036 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 358.9568036 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 126 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 571 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Methyclothiazide |
| PubMed Health | Methyclothiazide (Oral route) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent, Diuretic, Thiazide |
| Drug Label | Methyclothiazide, a diuretic-antihypertensive agent, is a member of the benzothiadiazine (thiazide) class of drugs. It is an analogue of hydrochlorothiazide and occurs as a white to practically white crystalline powder which is basically odorless. Me... |
| Active Ingredient | Methyclothiazide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Methyclothiazide |
| PubMed Health | Methyclothiazide (Oral route) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent, Diuretic, Thiazide |
| Drug Label | Methyclothiazide, a diuretic-antihypertensive agent, is a member of the benzothiadiazine (thiazide) class of drugs. It is an analogue of hydrochlorothiazide and occurs as a white to practically white crystalline powder which is basically odorless. Me... |
| Active Ingredient | Methyclothiazide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms |
Diuretics, Thiazide
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Thiazides...may be used to control edema associated with premenstrual tension and to reduce fluid retention following administration of corticosteroids or estrogens. /thiazide diuretics/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 81
Indications include edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis with ascites, corticosteroid and estrogen therapy, and some forms of renal function impairment including nephrotic syndrome, acute glomerulonephritis, and chronic renal failure. /Included in US product labeling; Thiazide diuretics/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1242
Thiazide diuretics are indicated either alone or as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of hypertension. /Included in US product labeling; Thiazide diuretics/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1242
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for METHYCLOTHIAZIDE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Because hypokalemia accelerates glucose intolerance, fall in serum potassium level can aggravate diabetes. Diuretic therapy may cause pronounced hypokalemia in presence of incr mineralocorticoid activity due to primary adrenal disease...or corticosteroid therapy. /thiazide diuretics/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 84
Reversible elevation of blood urea nitrogen level may occur... This prerenal azotemia is caused by decrease in renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate secondary to reduction in blood volume induced by diuretic. ...thiazides may directly depress renal blood flow. /thiazide diuretics/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 84
Necrotizing vasculitis of skin and kidney has occurred in elderly patients, but its relationship to thiazides is still unproved. /thiazide diuretics/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 86
When cardiac decompensation or hypertension is accompanied by significant impairment of renal function, thiazides should be admin with caution because of their capacity to aggravate renal insufficiency. /thiazide diuretics/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 832
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for METHYCLOTHIAZIDE (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
3. 3= Moderately toxic: probable oral lethal dose (human) 0.5-5 g/kg, between 1 oz and 1 pint for 70 Kg person (150 lb). /thiazide diuretics/
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-239
For use in the management of hypertension either as the sole therapeutic agent or to enhance the effect of other antihypertensive drugs in the more severe forms of hypertension. Also used as adjunctive therapy in edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, and corticosteroid and estrogen therapy.
Methyclothiazide, a diuretic-antihypertensive agent, is a member of the benzothiadiazine (thiazide) class of drugs. Methyclothiazide has a per mg natriuretic activity approximately 100 times that of the prototype thiazide, chlorothiazide. At maximal therapeutic dosages, all thiazides are approximately equal in their diuretic/natriuretic effects. Like other benzothiadiazines, methyclothiazide also has antihypertensive properties, and may be used for this purpose either alone or to enhance the antihypertensive action of other drugs.
Diuretics
Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. (See all compounds classified as Diuretics.)
Sodium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit SODIUM CHLORIDE SYMPORTERS. They act as DIURETICS. Excess use is associated with HYPOKALEMIA. (See all compounds classified as Sodium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C03 - Diuretics
C03A - Low-ceiling diuretics, thiazides
C03AA - Thiazides, plain
C03AA08 - Methyclothiazide
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed following oral administration.
Thiazides are absorbed from GI tract and owe their usefulness largely to their effectiveness by oral route. Absorption is relatively rapid. Most agents show demonstrable diuretic effect within hr after oral administration. /thiazide diuretics/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 831
In general, thiazides with relatively long durations of action show proportionately high degrees of both binding to plasma proteins and reabsorption by renal tubules. ... Drug passes readily through placental barrier to fetus. All thiazides probably undergo active secretion in proximal tubule. /thiazide diuretics/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 831
Methyclothiazide is absorbed from the GI tract. Little information is available on the extent of absorption and the distribution of methyclothiazide in the body. Methyclothiazide is excreted unchanged in urine.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2554
Methyclothiazide is excreted unchanged in urine.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2554
Methyclothiazide appears to block the active reabsorption of chloride and possibly sodium in the ascending loop of Henle, altering electrolyte transfer in the proximal tubule. This results in excretion of sodium, chloride, and water and, hence, diuresis. As a diuretic, methyclothiazide inhibits active chloride reabsorption at the early distal tubule via the Na-Cl cotransporter, resulting in an increase in the excretion of sodium, chloride, and water. Thiazides like methyclothiazide also inhibit sodium ion transport across the renal tubular epithelium through binding to the thiazide sensitive sodium-chloride transporter. This results in an increase in potassium excretion via the sodium-potassium exchange mechanism. The antihypertensive mechanism of methyclothiazide is less well understood although it may be mediated through its action on carbonic anhydrases in the smooth muscle or through its action on the large-conductance calcium-activated potassium (KCa) channel, also found in the smooth muscle.
Acute admin of thiazides increases the excretion of uric acid. However, uric acid excretion is reduced following chronic admin... . The acute effects of inhibitors of Na+-Cl- symport on Ca2+ excretion are variable; when admin chronically, thiazide diuretics decr Ca2+ excretion. The mechanism is unknown but may involve increased proximal reabsorption due to volume depletion as well as direct effects of thiazides to incr Ca2+ reabsorption in the /distal convoluted tubule/. Thiazide diuretics may cause a mild magnesuria by a poorly understood mechanism, and there is increasing awareness that long-term use of thiazide diuretics may cause magnesium deficiency, particularly in the elderly. /Thiazide diuretics/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 775
Thiazides inhibit reabsorption of sodium and ...chloride in distal segment. ... As /a/ class...have important action on excretion of potassium that results from increased secretion of cation by distal tubule. ... Glomerular filtration rate may be reduced by thiazides, particularly with iv admin for exptl purposes. /thiazide diuretics/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 901
Nature of chemical interaction between thiazides and specific renal receptors responsible for chloruretic effect is not known; no critical enzymatic reactions have been identified. /thiazides/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 901
Thiazide diuretics increase urinary excretion of sodium and water by inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the early distal tubules. They increase the rate of delivery of tubular fluid and electrolytes to the distal sites of hydrogen and potassium ion secretion, while plasma volume contraction increases aldosterone production. The increased delivery and increase in aldosterone levels promote sodium reabsorption at the distal tubules, thus increasing the loss of potassium and hydrogen ions. /Thiazide diuretics/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1243
The antidiuretic effect of thiazide diuretics is a result of mild sodium and water depletion leading to increased reabsorption of glomerular filtrate in the proximal renal tubule and reduced delivery of tubular fluid available for excretion. /Thiazide diuretics/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1243