

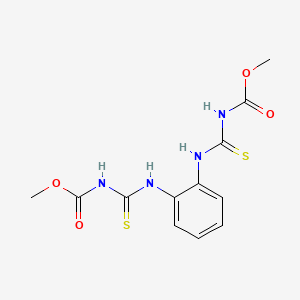

1. Bis-thioallophanate, Dimethylphenylene
2. Cercobin M 70
3. Cercobin M-70
4. Cercobin M70
5. Dimethylphenylene Bis Thioallophanate
6. Dimethylphenylene Bis-thioallophanate
7. Mildothane
8. Thiophanate
9. Thiophanate Methyl
1. 23564-05-8
2. Thiophanate Methyl
3. Thiophanate M
4. Methylthiofanate
5. Methylthiophanate
6. Mildothane
7. Methyl Topsin
8. Methyl Thiophanate
9. Caligran
10. Neotopsin
11. Metoben
12. Fungo
13. Cercobin Methyl
14. Topsin Methyl
15. Topsin M
16. Cycosin
17. Thiopan
18. Easout
19. Enovit Methyl
20. Enovit Super
21. Cercobin M
22. Enovit M
23. Sipcaplant
24. Sipcasan
25. Sipcavit
26. Trevin
27. Ditek
28. Rilon
29. Topsin Nf-44
30. Topsin Wp Methyl
31. Pelt 14
32. Fungo 50
33. Nf 44
34. O-bis(3-methoxycarbonyl-2-thioureido)benzene
35. Tiofanate Metile
36. 1,2-bis(methoxycarbonylthioureido)benzene
37. Methyl N-[[2-(methoxycarbonylcarbamothioylamino)phenyl]carbamothioyl]carbamate
38. Topsin Turf And Ornamentals
39. Bas 32500f
40. Dimethyl 4,4'-o-phenylenebis(3-thioallophanate)
41. Td 1771
42. Pei 190
43. F 6385
44. 1,2-di-(3-methoxycarbonyl-2-thioureido)benzene
45. 1,2-bis(3-(methoxycarbonyl)-2-thioureido)benzene
46. Dimethyl 4,4-o-phenylene-bis (3-thiophanate)
47. Pelt 44
48. Chebi:35014
49. K4n81r84l8
50. 1,2-bis[3-(methoxycarbonyl)-2-thioureido]benzene
51. Carbamic Acid, (1,2-phenylenebis(iminocarbonothioyl))bis-, Dimethyl Ester
52. Dimethyl (1,2-phenylenedicarbamothioyl)biscarbamate
53. Nsc-170811
54. Allophanic Acid, 4,4'-o-phenylenebis(3-thio-, Dimethyl Ester
55. Dsstox_cid_4338
56. Topsin-m
57. Carbamic Acid, [1,2-phenylenebis(iminocarbonothioyl)]bis-, Dimethyl Ester
58. Dsstox_rid_77373
59. Dsstox_gsid_24338
60. Topsin Nf 44
61. Dimethyl (1,2-phenylenebis(iminocarbonothioyl))biscarbamate
62. Dimethyl [1,2-phenylenebis(iminocarbonothioyl)]biscarbamate
63. Caswell No. 375a
64. Allophanic Acid, 4,4'-o-phenylenebis[3-thio-, Dimethyl Ester
65. Enovit-methyl
66. Tiofanate Metile [italian]
67. Pelt-44
68. Nsc 170811
69. Cas-23564-05-8
70. Ccris 6101
71. Hsdb 6937
72. Einecs 245-740-7
73. Thiophanate-methyl [ansi:bsi:iso]
74. Thiophanate-methyl [iso]
75. Rcra Waste No. U409
76. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 102001
77. Brn 0937942
78. Frumidor
79. Unii-k4n81r84l8
80. Ai3-27905
81. Methyl Thiophamate
82. Labilite (salt/mix)
83. Cercobin-m
84. Spot Kleen
85. Spectrum_001761
86. Specplus_000748
87. Dimethyl ((1,2-phenylene)bis-(iminocarbonothioyl))bis(carbamate)
88. Spectrum2_000646
89. Spectrum3_001211
90. Spectrum4_000096
91. Spectrum5_001330
92. Thiophanate, Methyl Ester
93. Schembl41622
94. Bspbio_002622
95. Kbiogr_000392
96. Kbioss_002242
97. Mls002207244
98. Bidd:er0424
99. Divk1c_006844
100. Spectrum1503974
101. Spbio_000651
102. Chembl487187
103. Dtxsid1024338
104. Schembl22261863
105. Kbio1_001788
106. Kbio2_002241
107. Kbio2_004809
108. Kbio2_007377
109. Kbio3_002122
110. Thiophanate-methyl [hsdb]
111. Nf-44
112. Amy22462
113. Dimethyl ((1,2-phenylene)bis(iminocarbonothioyl))bis(carbamate)
114. Hy-b0842
115. Zinc3872305
116. Tox21_201679
117. Tox21_300830
118. Ccg-39648
119. Mfcd00055294
120. Nsc170811
121. Stk366090
122. Akos005443059
123. Carbamic Acid, (1,2-phenylenebis(iminocarbonothioyl)bis-, Dimethyl Ester
124. Ncgc00091407-01
125. Ncgc00091407-02
126. Ncgc00091407-03
127. Ncgc00091407-04
128. Ncgc00091407-05
129. Ncgc00091407-06
130. Ncgc00091407-07
131. Ncgc00091407-08
132. Ncgc00254734-01
133. Ncgc00259228-01
134. Ac-12584
135. As-14875
136. Smr000778087
137. Db-046179
138. Cs-0012854
139. Ft-0630502
140. T3986
141. Thiophanate O,o-dimethyl Analog [mi]
142. Bis[(3-methoxycarbonyl)-2-thioureido]benzene
143. E78643
144. Pesticide2_thiophanate-methyl_c12h14n4o4s2_
145. Ab00052398_04
146. 564t058
147. A816770
148. Dimethyl 4,4'-o-phenylene-bis[3-thioallophanate]
149. Q126625
150. Thiophanate-methyl 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
151. Dimethyl 4,4'-(o-phenylene)bis(3-thioallophanate)
152. W-110573
153. Brd-k90168339-001-02-9
154. Brd-k90168339-001-04-5
155. Dimethyl (benzene-1,2-diyldicarbamothioyl)biscarbamate
156. Thiophanate-methyl, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
157. Allophanic Acid,4'-o-phenylenebis[3-thio-, Dimethyl Ester
158. Allophanic Acid, 4,4'-o-phenylenebis*3-thio-, Dimethyl Ester
159. Dimethyl N,n'-[1,2-phenylenebis(azanediylcarbonothioyl)]dicarbamate
160. Dimethyl N,n'-[1,2-phenylenebis(iminocarbonothioyl)]bis[carbamate]
161. Carbamic Acid,2-phenylenebis(iminocarbonothioyl)]bis-, Dimethyl Ester
162. Carbamic Acid, N,n'-(1,2-phenylenebis(iminocarbonothioyl))bis-, C,c'-dimethyl Ester
163. Methyl [2-(([(methoxycarbonyl)amino]carbothioyl)amino)anilino]carbothioylcarbamate #
164. N-[[2-[[(methoxycarbonylamino)-sulfanylidenemethyl]amino]anilino]-sulfanylidenemethyl]carbamic Acid Methyl Ester
| Molecular Weight | 342.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H14N4O4S2 |
| XLogP3 | 2.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 342.04564729 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 342.04564729 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 165 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 407 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Fungicides, Industrial
Chemicals that kill or inhibit the growth of fungi in agricultural applications, on wood, plastics, or other materials, in swimming pools, etc. (See all compounds classified as Fungicides, Industrial.)
Anthelmintics
Agents that kill parasitic worms. They are used therapeutically in the treatment of HELMINTHIASIS in man and animal. (See all compounds classified as Anthelmintics.)
Antinematodal Agents
Substances used in the treatment or control of nematode infestations. They are used also in veterinary practice. (See all compounds classified as Antinematodal Agents.)
Nearly all thiophanate-methyl is eliminated from the body in 24 hr; that left in tissues after 24 hr is largely eliminated within 96 hr.
Hayes, W.J., Jr., E.R. Laws, Jr., (eds.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 3. Classes of Pesticides. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc., 1991., p. 1457
Thiophanate-methyl was efficiently absorbed, and rapidly excreted. There was evidently some saturability of uptake processes and lengthening of elimination half-life at high dose levels or following sustained low dose exposures. Blood levels diminished quickly, and tissue levels were very low by day 4 (post-exposure) in all cases.
California Environmental Protection Agency/Department of Pesticide Regulation; Toxicology Data Review Summary for Thiophanatemethyl (23564-05-8). Available from, as of May 11, 2009: https://www.cdpr.ca.gov/docs/risk/toxsums/toxsumlist.htm
Studies in mice with four radioactive forms of the molecule (14C in the ring or as the thiourea carbon of the methyl carbon and 35S) showed that the C=S bond was cleaved to a great extent prior to absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. Some of the methyl carbon apparently is metabolized to carbon dioxide. The major urinary metabolites are carbendazim and its 6-hydroxy derivative; these are excreted as O- or N-glucuronides. A compound in which the two =S's of thiophanate-methyl are replaced by =O's is a minor metabolite. Some other metabolites detectable by thin-layer chromatography of radioactive material remain unidentified.
Hayes, W.J., Jr., E.R. Laws, Jr., (eds.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 3. Classes of Pesticides. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc., 1991., p. 1457
... Primary metabolic changes included hydrolysis of side chain extremities, closure of remaining side chain portions, and oxidation of the phenyl moiety, producing a methyl hydroxybenzimidazolyl carbamate. The primary urinary metabolite was conjugated with sulfate. Fecal residues were largely thiophanate-methyl and a phenyl ring hydroxylated product.
California Environmental Protection Agency/Department of Pesticide Regulation; Toxicology Data Review Summary for Thiophanatemethyl (23564-05-8). Available from, as of May 11, 2009: https://www.cdpr.ca.gov/docs/risk/toxsums/toxsumlist.htm
As a class of compounds, thiocarbamates do not produce consistent cholinesterase inhibition patterns. In the rat subchronic toxicity study, serum cholinesterase activity was increased in males by 22-38% relative to controls but decreased in females by 25-28% at >/= 293.2 mg/kg/day. In the rat chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity study, males showed increases in serum ChE at 280.6 mg/kg/day (HDT) at 6 and 12 months (41-42%) whereas at 24 months, it was decreased (-38%). ChE activity in females was slightly decreased (18035%) at 6 and 12 months at >/= 63.5 mg/kg/day ... /thiocarbamates/
USEPA, Office of Prevention, Pesticides, and Toxic Substances; Revised HED Human Health Risk Assessment for Thiophanate-methyl (23564-05-8) (April 2002). EPA Docket No.: EPA-HQ-OPP-2004-0265-0010.
In order to characterize the mechanism of thyroid tumorigenesis, a series of short term studies were undertaken to determine whether TM had antithyroid activity. These studies demonstrated that TM caused liver and thyroid enlargement, increased circulating TSH and decreased T3/T4 after 2 to 8 days' treatment with TM at 6000 ppm (equivalent to the HDT in the rat chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity study). Some liver microsomal enzymes, including UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, were increased. The effects on liver and thyroid weight were reversible, but reversibility of the alterations in circulating hormone levels and on microscopic effects were not evaluated. Supplementation of treated animals with T4 prevented thyroid enlargement and increased TSH but did not prevent liver enlargement. TM also appeared to have a mild inhibitory effect on microsomal thyroid peroxidase. These data were considered necessary to adequately support this mechanism.
USEPA, Office of Prevention, Pesticides, and Toxic Substances; Revised HED Human Health Risk Assessment for Thiophanate-methyl (23564-05-8) (April 2002). EPA Docket No.: EPA-HQ-OPP-2004-0265-0010.

LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?