

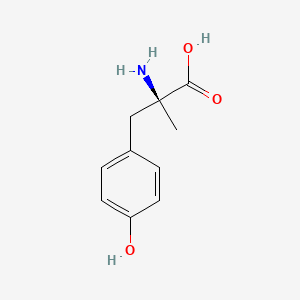

1. Alpha Methyl P Tyrosine
2. Alpha Methyl Para Tyrosine
3. Alpha Methyltyrosine
4. Alpha Methyltyrosine Hydrochloride
5. Alpha Mpt
6. Alpha-methyl- Dl-tyrosine
7. Alpha-methyl-p-tyrosine
8. Alpha-methyl-para-tyrosine
9. Alpha-methyltyrosine
10. Alpha-methyltyrosine Hydrochloride
11. Alpha-methyltyrosine, (+,-)-isomer
12. Alpha-methyltyrosine, (d,l)-isomer
13. Alpha-methyltyrosine, (l)-isomer
14. Alpha-mpt
15. Demser
16. Dl-tyrosine, Alpha-methyl-
17. Hydrochloride, Alpha-methyltyrosine
18. Metirosine
19. Racemetirosine
1. 672-87-7
2. Alpha-methyl-l-tyrosine
3. Metirosine
4. Demser
5. Methyltyrosine
6. (s)-alpha-methyltyrosine
7. (s)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methylpropanoic Acid
8. L-alpha-methyltyrosine
9. L-alpha-methyl-p-tyrosine
10. Metirosinum
11. Metirosina
12. Alpha-methyltyrosine
13. Alpha-methyl-l-p-tyrosine
14. (2s)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methylpropanoic Acid
15. (-)-alpha-methyl-l-tyrosine
16. Mk-781
17. Metirosine [inn]
18. Racemetirosine, (s)-
19. Alpha-methyl-para-tyrosine
20. Doq0j0tpf7
21. Alpha-methyl-l-tyr
22. Chebi:6912
23. L-588357-0
24. Ncgc00094144-03
25. Dsstox_cid_3315
26. L-2-methyl-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)alanine
27. Dsstox_rid_76972
28. Dsstox_gsid_23315
29. Mfcd00064201
30. Alpha-mpt
31. Cas-672-87-7
32. Metyrosine [usan]
33. (r)-alpha-methyltyrosine
34. Alpha-methyl-paratyrosine
35. Metyrosine [usan:usp]
36. Metirosinum [inn-latin]
37. Unii-doq0j0tpf7
38. Mk 781
39. Metirosina [inn-spanish]
40. L-2-me-tyr-oh
41. Metyrosine (usp)
42. Einecs 211-599-5
43. Demser (tn)
44. A-methyl-l-p-tyrosine
45. Metyrosine [mi]
46. Metirosine (jan/inn)
47. Metirosine [jan]
48. Spectrum3_001846
49. Metyrosine [vandf]
50. H-(me)tyr-oh
51. A-methyl-l-tyrosine
52. Metirosine [mart.]
53. (s)-2-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-2-aminopropanoic Acid
54. Metirosine [who-dd]
55. Metyrosine [usp-rs]
56. Lopac0_000811
57. Schembl50398
58. Bspbio_003232
59. Zinc693
60. Spectrum2300312
61. A-methyltyrosinea-methyltyrosine
62. Gtpl6956
63. L 588357-0
64. Chembl1200862
65. Dtxsid6023315
66. Metyrosine [orange Book]
67. Kbio3_002732
68. (-)-(s)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methylpropionsaeure
69. Hms3262d03
70. Metyrosine [usp Monograph]
71. L-tyrosine, Alpha-methyl-, (-)-
72. Tox21_111253
73. Tox21_500811
74. S5797
75. Akos016844271
76. Tox21_111253_1
77. Ab02561
78. Am83582
79. Ccg-204895
80. Cs-w015723
81. Db00765
82. Hy-w015007
83. Lp00811
84. Sdccgsbi-0050788.p002
85. (-)-.alpha.-methyl-l-tyrosine
86. Ncgc00015701-06
87. Ncgc00094144-01
88. Ncgc00094144-04
89. Ncgc00094144-05
90. Ncgc00094144-06
91. Ncgc00094144-07
92. Ncgc00094144-11
93. Ncgc00261496-01
94. Ac-32982
95. Alpha-methyl-l-tyrosine, >=98% (tlc)
96. As-47139
97. Eu-0100811
98. L-tyrosine, .alpha.-methyl-, (-)-
99. C07921
100. D00762
101. F12275
102. M 8131
103. 672m877
104. A835693
105. Q6824116
106. (s)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methylpropanoicacid
107. Z1617901128
108. (2s)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methyl-propanoic Acid
109. (s)-a-methyl-4-hydroxy Phenylalanine, (s)-a-methyltyrosine
110. Metyrosine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 195.21 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H13NO3 |
| XLogP3 | -1.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 195.08954328 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 195.08954328 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 83.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 211 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Demser |
| PubMed Health | Metyrosine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihypertensive |
| Drug Label | DEMSERRegistered trademark of ATON PHARMA, INC.COPYRIGHT 2007 ATON PHARMA, INC.All rights reserved (Metyrosine) is ()--methyl-L-tyrosine or (-MPT). It has the following structural formula:Metyrosine is a white, crystalline compound of molec... |
| Active Ingredient | Metyrosine |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Aton Pharma Vpna |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Demser |
| PubMed Health | Metyrosine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihypertensive |
| Drug Label | DEMSERRegistered trademark of ATON PHARMA, INC.COPYRIGHT 2007 ATON PHARMA, INC.All rights reserved (Metyrosine) is ()--methyl-L-tyrosine or (-MPT). It has the following structural formula:Metyrosine is a white, crystalline compound of molec... |
| Active Ingredient | Metyrosine |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Aton Pharma Vpna |
For use in the treatment of patients with pheochromocytoma, for preoperative preparation of patients for surgery, management of patients when surgery is contraindicated, and chronic treatment of patients with malignant pheochromocytoma.
In patients with pheochromocytoma, who produce excessive amounts of norepinephrine and epinephrine, administration of one to four grams of metyrosine per day has reduced catecholamine biosynthesis from about 35 to 80 percent as measured by the total excretion of catecholamines and their metabolites (metanephrine and vanillylmandelic acid). The maximum biochemical effect usually occurs within two to three days, and the urinary concentration of catecholamines and their metabolites usually returns to pretreatment levels within three to four days after metyrosine is discontinued. Most patients with pheochromocytoma treated with metyrosine experience decreased frequency and severity of hypertensive attacks with their associated headache, nausea, sweating, and tachycardia. In patients who respond, blood pressure decreases progressively during the first two days of therapy with metyrosine; after withdrawal, blood pressure usually increases gradually to pretreatment values within two to three days.
Enzyme Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme combination and the catalytic reaction. (See all compounds classified as Enzyme Inhibitors.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C02 - Antihypertensives
C02K - Other antihypertensives
C02KB - Tyrosine hydroxylase inhibitors
C02KB01 - Metirosine
Absorption
Well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Route of Elimination
Because the first step is also the rate-limiting step, blockade of tyrosine hydroxylase activity results in decreased endogenous levels of catecholamines, usually measured as decreased urinary excretion of catecholamines and their metabolites.
Little biotransformation, with catechol metabolites accounting for less than 1% of the administered dose.
3.4 to 3.7 hours
Metyrosine inhibits tyrosine hydroxylase, which catalyzes the first transformation in catecholamine biosynthesis, i.e., the conversion of tyrosine to dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA). Because the first step is also the rate-limiting step, blockade of tyrosine hydroxylase activity results in decreased endogenous levels of catecholamines and their synthesis. This consequently, depletes the levels of the catecholamines dopamine, adrenaline and noradrenaline in the body,usually measured as decreased urinary excretion of catecholamines and their metabolites. One main end result of the catecholamine depletion is a decrease in blood presure.