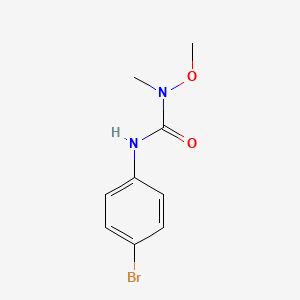

1. 3-(p-bromophenyl)-1-methoxy-1-methylurea
2. Patoran
1. 3060-89-7
2. Metbromuron
3. Patoran
4. 3-(4-bromophenyl)-1-methoxy-1-methylurea
5. Metobromurone
6. Monobromuron
7. Pattonex
8. Urea, N'-(4-bromophenyl)-n-methoxy-n-methyl-
9. N'-(4-bromophenyl)-n-methoxy-n-methylurea
10. Ciba-3126
11. 3-(p-bromophenyl)-1-methoxy-1-methylurea
12. Urea, 3-(p-bromophenyl)-1-methoxy-1-methyl-
13. 3-(p-bromophenyl)-1-methyl-1-methoxyurea
14. 3-(4-bromphenyl)-1-methoxyharnstoff
15. Chebi:81964
16. Metobromuron 10 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
17. Metobromuron 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
18. 4251089p3l
19. Caswell No. 579a
20. Metobromuron [iso]
21. Ccris 6765
22. Metobromuron [ansi:bsi:iso]
23. Hsdb 1741
24. Einecs 221-301-5
25. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 035901
26. Brn 2103964
27. Patoran Fl
28. 3-(4-bromphenyl)-1-methoxyharnstoff [german]
29. C-3126
30. Unii-4251089p3l
31. N-(4-bromophenyl)-n'-methyl-n'-methoxy-harnstoff [german]
32. 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-methoxy-3-methylurea
33. Metobromuron [mi]
34. Metobromuron [hsdb]
35. Dsstox_cid_22157
36. Dsstox_rid_79940
37. Dsstox_gsid_42157
38. Schembl53871
39. N-(4-bromophenyl)-n'-methyl-n'-methoxy-harnstoff
40. Chembl1356637
41. Dtxsid6042157
42. Metobromuron, Analytical Standard
43. Zinc260866
44. Dndi1246791
45. Tox21_301964
46. Akos001609255
47. Ncgc00166156-01
48. Ncgc00255893-01
49. Cas-3060-89-7
50. Db-047812
51. Ft-0603626
52. N-(p-bromophenyl)-n'-methyl-n'-methoxyurea
53. C18793
54. Metobromuron, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
55. 060m897
56. J-018035
57. Q18213352
58. Pesticide3_metobromuron_c9h11brn2o2_urea, N'-(4-bromophenyl)-n-methoxy-n-methyl-
| Molecular Weight | 259.10 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H11BrN2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 258.00039 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 258.00039 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 41.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 193 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
METOBROMURON IS ABSORBED BY ROOTS AND LEAVES ...
Worthing, C. R. (ed.). Pesticide Manual. 6th ed. Worcestershire, England: British Crop Protection Council, l979., p. 359
... Different urea herbicides exhibit different mobilities in plant systems. ... Uptake and translocation of chloroxuron, fluometuron, and metobromuron by bean plants when supplied to nutrient cultures in equal concn (essentially equimolar) and specific radioactivities were studied. Whereas the movement of chloroxuron to aerial parts was found to be restricted under the short-term conditions applied, both fluometuron and metobromuron were rapidly translocated into leaves. However, the two latter cmpd differed strikingly with regard to their distribution pattern within the leaves. In contrast to metobromuron, which was mainly confined to tracheal veins, fluometuron had almost completely moved out into the mesophyll tissues. Although no extensive comparisons of the movement of different urea structures are available at this time, it would appear that their apoplastic distribution in plants is regulated in part by the same physical-chemical phenomena which control the mobility and availability of the cmpd in soil.
Spencer, E. Y. Guide to the Chemicals Used in Crop Protection. 7th ed. Publication 1093. Research Institute, Agriculture Canada, Ottawa, Canada: Information Canada, 1982., p. 235
METOBROMURON IS METABOLIZED IN PLANTS & ANIMALS BY N-DEMETHYLATION & N-DEMETHOXYLATION, RESPECTIVELY.
Martin, H. and C.R. Worthing (eds.). Pesticide Manual. 4th ed. Worcestershire, England: British Crop Protection Council, 1974., p. 355
... RING-LABELED (14)C-METOBROMURON WAS SUPPLIED TO POTATOES AND CORN SEEDLINGS. ... FOLLOWING METABOLITES ... /WERE IDENTIFIED/: 3-(4-BROMOPHENYL)-1-METHOXYUREA, 3-(4-BROMOPHENYL)-1-METHYLUREA, AND 4-BROMOPHENYLUREA.
Kearney, P.C., and D.D. Kaufman. Degradation of Herbicides. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc., 1969., p. 99
METOBROMURON YIELDS 3-(P-BROMOPHENYL)-1-METHYLUREA AND 3-(P-BROMOPHENYL)-1-METHOXYUREA IN TALAROMYCES. /FROM TABLE/
Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. M45
(14)C-Metobromuron was incubated with human embryonic lung (HEL) cells. More than 95% of the label was recovered as unchanged metobromuron. Of four metabolites, three were identified: 3-(4-bromophenyl)-1-methylurea; 4-bromophenylurea; and 3-(4-bromophenyl)-1-methylurea.
Menzie, C.M. Metabolism of Pesticides-Update III. Special Scientific Report- Wildlife No. 232. Washington, DC: U.S.Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service, 1980., p. 563