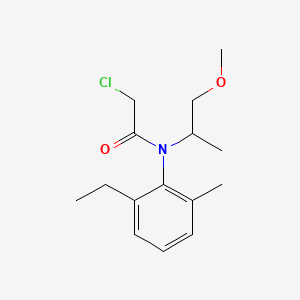

1. 2-chloro-n-(2-ethyl-6-methylphenyl)-n-(2-methoxyethyl)acetamide
1. 51218-45-2
2. Yibingjiacaoan
3. Pennant
4. Codal
5. Dual
6. Dual Magnum
7. Dual Triple
8. Dual Ii
9. 2-chloro-n-(2-ethyl-6-methylphenyl)-n-(1-methoxypropan-2-yl)acetamide
10. Metelilachlor
11. Ontrack 8e
12. Dual 720ec
13. Dual 960 Ec
14. Dual 8e
15. 2-chloro-n-(2-ethyl-6-methylphenyl)-n-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)acetamide
16. N-(1-methyl-2-methoxyethyl)-n-chloroacetyl-2-ethyl-6-methylaniline
17. Cga-24705
18. Acetamide, 2-chloro-n-(2-ethyl-6-methylphenyl)-n-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)-
19. Cga 24705
20. Chebi:83645
21. Metolachlor-d6
22. X0i01k05x2
23. Humextra
24. Dsstox_cid_2448
25. Acetamide, 2-chloro-n-(2-ethyl-6-methylphenyl)-n-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)-, Stereoisomer
26. Dsstox_rid_76595
27. Dsstox_gsid_22448
28. 82535-90-8
29. Metolachlor Technical
30. Metolachlor, Analytical Standard
31. Metetilachlor
32. Metolachlore
33. Jindual
34. Metoken
35. Caswell No. 188dd
36. Metolachlore [iso-french]
37. Metolachlor [iso]
38. Cas-51218-45-2
39. Metolachlor [ansi:bsi:iso]
40. Hsdb 6706
41. Einecs 257-060-8
42. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 108801
43. Brn 2743537
44. Unii-x0i01k05x2
45. Bicep (salt/mix)
46. Turbo (salt/mix)
47. Cga-77102
48. Metolachor
49. Primagram (salt/mix)
50. Primextra (salt/mix)
51. (as,5s)-metolachlor
52. Spectrum_001833
53. Metolaclor (salt/mix)
54. Specplus_000434
55. 2-chloro-6'-ethyl-n-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)acet-o-toluidide
56. Pace 6l (salt/mix)
57. Bicep 6l (salt/mix)
58. Metolachlor [mi]
59. 2-chloro-6'-ethyl-n-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)-o-acetotoluidine
60. 2-ethyl-6-methyl-1-n-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)chloroacetanilide
61. Spectrum2_001885
62. Spectrum3_000827
63. Spectrum4_000667
64. Spectrum5_001966
65. 2-aethyl-6-methyl-n-(1-methyl-2-methoxyaethyl)-chloracetanilid [german]
66. Acetamide, 2-chloro-n-(6-ethyl-o-tolyl)-n-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)-
67. Dual 25g (salt/mix)
68. N-(2'-methoxy-1'-methylethyl)-2'-ethyl-6'-methyl-2-chloroacetanilide
69. Metolachlor [hsdb]
70. Metolachlor, Herbicide (c15-h22-n-o2-cl)
71. 2-etylo-6-metylo-n-(1'-metylo-2'-metoksyetylo)chloroacetanilid [polish]
72. Alpha-chlor-6'-aethyl-n-(2-methoxy-1-methylaethyl)-acet-o-toluidin [german]
73. Alpha-chloro-2'-ethyl-6'-methyl-n-(1-methyl-2-methoxyethyl)-acetanilide
74. Schembl21385
75. Bspbio_002353
76. Kbiogr_001073
77. Kbioss_002338
78. Spectrum330035
79. Divk1c_006530
80. Spbio_001790
81. Chembl1884974
82. Dtxsid4022448
83. Kbio1_001474
84. Kbio2_002335
85. Kbio2_004903
86. Kbio2_007471
87. Kbio3_001853
88. 2-aethyl-6-methyl-n-(1-methyl-2-methoxyaethyl)-chloracetanilid
89. 2-etylo-6-metylo-n-(1'-metylo-2'-metoksyetylo)chloroacetanilid
90. Bca21845
91. Hy-b1871
92. Tox21_201376
93. Tox21_300982
94. Alpha-chlor-6'-aethyl-n-(2-methoxy-1-methylaethyl)-acet-o-toluidin
95. Ccg-39423
96. Mfcd00055293
97. O-acetotoluidide, 2-chloro-6'-ethyl-n-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)-
98. 2-chloro-n-(2-ethyl-6-methyl-phenyl)-n-(2-methoxy-1-methyl-ethyl)acetamide
99. Akos015888371
100. Metolachlor 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
101. Acetamide, 2-chloro-n-(2-ethyl-6-methylphenyl)-n-((1s)-2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)-, (n(s))-
102. Metolachlor 1000 Microg/ml In Acetone
103. Metolachlor 10 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
104. Ncgc00095767-01
105. Ncgc00095767-02
106. Ncgc00095767-03
107. Ncgc00095767-04
108. Ncgc00095767-05
109. Ncgc00095767-06
110. Ncgc00254884-01
111. Ncgc00258927-01
112. Bs-42451
113. Metolachlor 10 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
114. Metolachlor 100 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
115. Metolachlor 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
116. Db-051924
117. Cs-0013937
118. Ft-0630641
119. M3381
120. E84049
121. Metolachlor, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
122. 218m452
123. Q409598
124. Brd-a43135847-001-02-3
125. 2-chloro-2'-ethyl-6'-methyl-n-(1-methyl-2-methoxyethyl)acetanilide
126. 2-chloro-2'-ethyl-6'-methyl-n-(1-methyl-2-methoxyethyl)-acetanilide
127. 2-chloro-6-ethyl-n-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)acet-o-toluidide
128. 2-chloro-n-(2-ethyl-6-methyl-phenyl)-n-(1-methoxypropan-2-yl) Acetamide
129. .alpha.-chloro-2-ethyl-6-methyl-n-(1-methyl-2-methoxyethyl)acetanilide
130. Acetamide,2-chloro-n-(2-ethyl-6-methylphenyl)-n-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)-
131. Metolachlor Solution, 100 Mug/ml In Acetonitrile, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
| Molecular Weight | 283.79 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H22ClNO2 |
| XLogP3 | 3.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 283.1339066 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 283.1339066 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 29.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 285 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Herbicides
Pesticides used to destroy unwanted vegetation, especially various types of weeds, grasses (POACEAE), and woody plants. Some plants develop HERBICIDE RESISTANCE. (See all compounds classified as Herbicides.)
S-metolachlor is extensively absorbed and metabolized following oral administration. Elimination is via the urine and feces. Tissue residues were highest in whole blood. /s-metolachlor/
USEPA; s-Metolachlor: s-Metolachlor Aggregate Human Health Risk Assessment. Document ID: EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0292 p. 16 (July 13, 2006). Available from, as of February 3, 2012: https://www.regulations.gov/#!home
Selective herbicide, absorbed predominantly by the hypocotyls and shoots.
Hartley, D. and H. Kidd (eds.). The Agrochemicals Handbook. 2nd ed. Lechworth, Herts, England: The Royal Society of Chemistry, 1987., p. A278/Aug 87
Rats were administered a single oral dose (28.6 or 52.4 mg/kg) of metolachlor (purity not specified, but (14)C labeled and unlabeled metolachlor were synthesized for these experiments). The chemical was readily absorbed, since 70 to 90% of the metolachlor was excreted as metabolites within 48 hr.
USEPA; Health Advisories for 50 Pesticides p.617 (1988) NTIS PB88-245931
Data from rats given radioactive metolachlor (approximately 3.2 to 3.5 mg/kg) orally demonstrated that the chemical is rapidly metabolized. Residues in meat tissue and blood were very low and only blood contained residue levels in excess of 0.1 ppm.
USEPA; Health Advisories for 50 Pesticides p.618 (1988) NTIS PB88-245931
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for METOLACHLOR (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
METABOLISM IN PLANTS AFTER PREEMERGENCE APPLICATION OF METOLACHLOR APPEARS TO PROCEED BY NATURAL PRODUCT CONJUGATION OF THE ACETYL-CHLORO GROUP WITH THIS BOND LINKAGE PREDOMINANT OVER OXO. FURTHER REACTION OCCURS AT THE ETHER GROUP WITH HYDROLYSIS FOLLOWED BY SUGAR CONJUGATION. FINAL METABOLITES ARE RESULTS OF DISCONJUGATION, AND ARE POLAR, AQUEOUS SOLUBLE, NONVOLATILE AS WELL AS SENSITIVE TO DEGRADATION. HYDROLYSIS PROCEDURES CONVERT THE OXO-METABOLITES TO THE DEACETYLATED DERIVATIVE AND THE THIO-METABOLITES TO A MORPHOLINE DERIVATIVE.
Weed Science Society of America. Herbicide Handbook. 5th ed. Champaign, Illinois: Weed Science Society of America, 1983., p. 314
STUDIES WITH THE ANTOR ANALOG METOLACHLOR (DUAL) WERE ALSO CONDUCTED WITH THE FUNGUS CHAETOMIUM GLOBOSUM. COMPOUNDS PRODUCED BY THIS ORGANISM WHEN INCUBATED WITH METOLACHLOR ARE: 2-CHLORO-N-(2-ETHYL-6- METHYLPHENYL)-N-(2-HYDROXY-1-METHYLETHYL)ACETAMIDE; 2-CHLORO-N-(2-ETHYL- 6-METHYLPHENYL)ACETAMIDE; N-(2-METHOXY-1-METHYLETHYL)-2-METHYL-6-VINYLANILINE; N-(2-METHOXY-1-METHYLETHYL)-2,3-DIHYDRO-7-METHYLINDOLE; 8-ETHYL-3-HYDROXY- N-(2-METHOXY-1-METHYLETHYL)-2-OXO-1,2,3,4-TETRAHYDROQUINOLINE; 8-ETHYL-3- HYDROXY-N-ISOPROPYL-2-OXO-1,2,3,4-TETRAHYDROQUINOLINE; 2-HYDROXY-N-(2- METHOXY-1-METHYLETHYL)-N-(2-METHYL-6-VINYLPHENYL)ACETAMIDE; N-(2-METHOXY- 1-METHYLETHYL)-8-METHYL-2-OXO-1,2,3,4-TETRAHYDROQUINOLINE.
Menzie, C.M. Metabolism of Pesticides-Update III. Special Scientific Report- Wildlife No. 232. Washington, DC: U.S.Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service, 1980., p. 30
IN FUNGI, ALPHA-CHLORINE ATOMS OF THESE PESTICIDES /INCLUDING METOLACHLOR/ ARE NOT DISPLACED BY SULFHYDRYL GROUPS BUT BY HYDROXYL GROUPS ALTHOUGH THE CHLORINE ATOM OF PROPACHLOR IS DISPLACED BY A SULFHYDRYL GROUP IN THE FIRST DEGRADATION STEP IN PLANTS. DEALKYLATION, DEACYLATION, AND RING FORMATION TO FORM INDOLINES AND QUINOLINES OCCUR IN FUNGI.
Aizawa, H. Metabolic Maps of Pesticides. New York, NY: Academic Press, 1982., p. 9
Studies conducted to identify urinary and fecal metabolites in the rat indicated that metolachlor is metabolized via dechlorination, o-methylation, N-dealkylation and side-chain oxidation. Urinary metabolites included 2-ethyl-6-methylhydroxyacetanilide and N-(2-ethyl-6-methyl- phenyl)-N-(hydroxyacetyl)-DL-alanine). Fecal metabolites included 2-chloro-N-(2-ethyl-6-methylphenyl)-N-(2-hydroxy-l-methylethyl) and N-(2-ethyl-6-methylphenyl)-N-(hydroxyacetyl)-DL-alamine).
USEPA; Health Advisories for 50 Pesticides p.618 (1988) NTIS PB88-245931
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for METOLACHLOR (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.