
1. Diulo
2. Microx
3. Mykrox
4. Sr 720 22
5. Sr-720-22
6. Sr72022
7. Zaroxolyn
1. 17560-51-9
2. Zaroxolyn
3. Diulo
4. Mykrox
5. Oldren
6. Metenix
7. Microx
8. Metalozone
9. Metolazona
10. Metolazonum
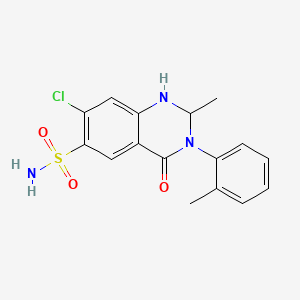
11. 7-chloro-2-methyl-4-oxo-3-(o-tolyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinazoline-6-sulfonamide
12. Metolazonum [inn-latin]
13. Metolazona [inn-spanish]
14. Sr-720-22
15. Metozalone
16. 7-chloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-methyl-3-(2-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-6-quinazolinesulfonamide
17. Sr 720-22
18. 6-quinazolinesulfonamide, 7-chloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-methyl-3-(2-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-
19. Metazoline
20. Metolazone (zaroxolyn)
21. Normelan
22. 7-chloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-methyl-4-oxo-3-o-tolyl-6-quinazolinesulfonamide
23. 2-methyl-3-o-tolyl-6-sulfamyl-7-chloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-4-quinazolinone
24. 7-chloro-2-methyl-3-(2-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinazoline-6-sulfonamide
25. Metolazone, (+)-
26. Metolazone, (-)-
27. Nsc-759581
28. Nm7v2y3g0u
29. Tz7v40x7vx
30. 7-chloro-2-methyl-3-(2-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinazoline-6-sulfonamide
31. Chebi:64354
32. 6-quinazolinesulfonamide, 7-chloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-methyl-4-oxo-3-o-tolyl-
33. Nn9u607695
34. Ncgc00093985-07
35. Metalazone
36. Xuret
37. 6-quinazolinesulfonamide, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-7-chloro-2-methyl-4-oxo-3-o-tolyl-
38. Dsstox_cid_25167
39. Dsstox_rid_80717
40. Dsstox_gsid_45167
41. Zaroxolyn (tn)
42. 56436-31-8
43. 56436-32-9
44. 6-quinazolinesulfonamide, 7-chloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-methyl-3-(2-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-, (+)-
45. 6-quinazolinesulfonamide, 7-chloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-methyl-3-(2-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-, (-)-
46. Smr001230730
47. Hsdb 3367
48. Sr-05000001765
49. Einecs 241-539-3
50. Unii-tz7v40x7vx
51. Brn 0965506
52. Metolazone (jan/usp/inn)
53. Prestwick_333
54. Cas-17560-51-9
55. Mfcd00069304
56. Metolazone [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
57. Spectrum_000456
58. Metolazone [mi]
59. Metolazone [inn]
60. Metolazone [jan]
61. Prestwick0_000112
62. Prestwick1_000112
63. Prestwick2_000112
64. Prestwick3_000112
65. Spectrum2_001741
66. Spectrum4_000229
67. Spectrum5_001237
68. Metolazone [hsdb]
69. Metolazone [usan]
70. Metolazone [vandf]
71. Chembl878
72. Unii-nm7v2y3g0u
73. Metolazone [mart.]
74. (non-labelled)metolazone-d7
75. Metolazone [usp-rs]
76. Metolazone [who-dd]
77. Schembl40558
78. Bspbio_000124
79. Bspbio_002422
80. Kbiogr_000897
81. Kbioss_000936
82. 5-25-09-00212 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
83. Mls002153316
84. Mls002154200
85. Divk1c_000275
86. Spectrum2300325
87. Spbio_001842
88. Spbio_002063
89. Bpbio1_000138
90. Gtpl4838
91. Dtxsid6045167
92. Metolazone [ep Impurity]
93. Metolazone [orange Book]
94. Unii-nn9u607695
95. Bdbm25899
96. Hms500n17
97. Kbio1_000275
98. Kbio2_000936
99. Kbio2_003504
100. Kbio2_006072
101. Metolazone [ep Monograph]
102. Ninds_000275
103. Bcpp000166
104. Hms1568g06
105. Hms1922l16
106. Hms2093p14
107. Hms2095g06
108. Hms2230j15
109. Hms3261j22
110. Hms3373c11
111. Hms3655m09
112. Hms3712g06
113. Hms3744i19
114. Metolazone [usp Monograph]
115. Pharmakon1600-02300325
116. Bcp21574
117. Hy-b0209
118. Tox21_110186
119. Tox21_113526
120. Tox21_500610
121. Ccg-39450
122. Nsc759581
123. S1610
124. Akos015897109
125. Metolazone, >=98% (hplc), Solid
126. Tox21_110186_1
127. Bcp9000920
128. Db00524
129. Ks-5139
130. Lp00610
131. Nsc 759581
132. Sdccgsbi-0051460.p003
133. Idi1_000275
134. Ncgc00093985-01
135. Ncgc00093985-02
136. Ncgc00093985-03
137. Ncgc00093985-04
138. Ncgc00093985-05
139. Ncgc00093985-06
140. Ncgc00093985-08
141. Ncgc00093985-10
142. Ncgc00093985-11
143. Ncgc00093985-20
144. Ncgc00261295-01
145. As-13016
146. Sbi-0051460.p002
147. Db-044227
148. Ab00052055
149. Sw196612-3
150. D00431
151. 7-chloro-2-methyl-4-oxo-3-o-tolyl-1,2,3,4
152. Ab00052055-08
153. Ab00052055_09
154. Ab00052055_10
155. 560m519
156. Q-201399
157. Q1169561
158. Sr-05000001765-1
159. Sr-05000001765-4
160. Sr-05000001765-7
161. Brd-a61793559-001-05-7
162. Brd-a61793559-001-08-1
163. Metolazone, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
164. Metolazone, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
165. 7-chloro-2-methyl-3-(2-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-quinazolinesulfonamide #
166. Metolazone For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 365.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H16ClN3O3S |
| XLogP3 | 4.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 365.0600902 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 365.0600902 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 101 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 594 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Metolazone |
| PubMed Health | Metolazone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | ZAROXOLYN Tablets (metolazone tablets, USP) for oral administration contain 2 or 5 mg of metolazone, USP, a diuretic/saluretic/antihypertensive drug of the quinazoline class.Metolazone has the molecular formula C16H16ClN3S, the chemical name 7-chlo... |
| Active Ingredient | Metolazone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg; 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sandoz; Roxane; Mylan |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zaroxolyn |
| PubMed Health | Metolazone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | ZAROXOLYN Tablets (metolazone tablets, USP) for oral administration contain 2 or 5 mg of metolazone, USP, a diuretic/saluretic/antihypertensive drug of the quinazoline class.Metolazone has the molecular formula C16H16ClN3S, the chemical name 7-chlo... |
| Active Ingredient | Metolazone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg; 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ucb |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Metolazone |
| PubMed Health | Metolazone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | ZAROXOLYN Tablets (metolazone tablets, USP) for oral administration contain 2 or 5 mg of metolazone, USP, a diuretic/saluretic/antihypertensive drug of the quinazoline class.Metolazone has the molecular formula C16H16ClN3S, the chemical name 7-chlo... |
| Active Ingredient | Metolazone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg; 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sandoz; Roxane; Mylan |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zaroxolyn |
| PubMed Health | Metolazone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | ZAROXOLYN Tablets (metolazone tablets, USP) for oral administration contain 2 or 5 mg of metolazone, USP, a diuretic/saluretic/antihypertensive drug of the quinazoline class.Metolazone has the molecular formula C16H16ClN3S, the chemical name 7-chlo... |
| Active Ingredient | Metolazone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg; 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ucb |
Antihypertensive Agents; Diuretics, Sulfamyl
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
DIURETIC & ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUG. ... METOLAZONE IS INDICATED FOR EDEMA ACCOMPANYING CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE, RENAL DISEASE INCL NEPHROTIC SYNDROME, & OTHER CONDITIONS OF DIMINISHED RENAL FUNCTION.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 873
METOLAZONE MAY BE USEFUL IN PT WITH GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE LESS THAN 20 ML/MIN & IN UNRESPONSIVE PT, IF TREATED CONCURRENTLY WITH FUROSEMIDE.
Evaluations of Drug Interactions. 2nd ed. and supplements. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Assn., 1976, 1978., p. 415
RANGE OF OPTIMALLY EFFECTIVE ORAL DIURETIC DOSE IN MAN: 25-100 MG/DAY; RELATIVE ORAL NATRIURETIC MAXIMAL RESPONSE IN MAN: 1.8. /FROM TABLE/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 829
IT IS CONTRAINDICATED IN ANURIA, HEPATIC COMA, KNOWN ALLERGY OR HYPERSENSITIVITY, PREGNANCY, & NURSING MOTHERS. ... MORE EXTENSIVE CLINICAL EXPERIENCE IS REQUIRED BEFORE DEFINITIVE EVALUATION CAN BE MADE.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 873
For the treatment of hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs of a different class.
FDA Label
Metolazone is a quinazoline diuretic, with properties generally similar to the thiazide diuretics. A proximal action of metolazone has been shown in humans by increased excretion of phosphate and magnesium ions and by a markedly increased fractional excretion of sodium in patients with severely compromised glomerular filtration. This action has been demonstrated in animals by micropuncture studies.
Diuretics
Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. (See all compounds classified as Diuretics.)
Sodium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit SODIUM CHLORIDE SYMPORTERS. They act as DIURETICS. Excess use is associated with HYPOKALEMIA. (See all compounds classified as Sodium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C03 - Diuretics
C03B - Low-ceiling diuretics, excl. thiazides
C03BA - Sulfonamides, plain
C03BA08 - Metolazone
Absorption
Peak blood levels are obtained within 2 to 4 hours of oral administration. The rate and extent of absorption are formulation dependent.
Route of Elimination
Most of the drug is excreted in the unconverted form in the urine.
75% OF DOSE /ADMIN TO DOGS/ ...EXCRETED IN URINE & 25% IN BILE. 60%...AS HYDROXYLATED DERIV...& FURTHER PRODUCTS OF OXIDN...& UNIDENTIFIED POLAR METABOLITES ARE ALSO PRESENT IN URINE.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 287
RENAL CLEARANCES OF.../THIAZIDE DIURETICS/ ARE...HIGH. MOST COMPOUNDS ARE RAPIDLY EXCRETED WITHIN 3-6 HR. BENDROFLUMETHIAZIDE & POLYTHIAZIDE HAVE LONGER DURATION OF ACTION THAT IS CORRELATED WITH SLOWER EXCRETION... SAME IS TRUE OF...METOLAZONE.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 831
Not substantially metabolized. 70-95% is excreted unchanged in urine via glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion. Undergoes enterohepatic recycling.
SEVENTY-FIVE PER CENT OF DOSE /ADMIN TO DOGS/ IS EXCRETED IN URINE & 25% IN BILE. 60%...AS HYDROXYLATED DERIV...& FURTHER PRODUCTS OF OXIDN...& UNIDENTIFIED POLAR METABOLITES ARE ALSO PRESENT IN URINE.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 287
Approximately 14 hours.
LONG T/2 VALUE...IN DOGS IS RELATED TO TRANSPORT MECHANISM IN BLOOD & PARTITION BETWEEN FORMED ELEMENTS & SERUM PROTEINS.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 287
...METOLAZONE IS EXCRETED BY GLOMERULAR FILTRATION & TUBULAR SECRETION IN DOGS, ALTHOUGH DRUG:CREATININE CLEARANCE RATIO IS LOWER THAN FOR MOST OTHER DIURETICS. T/2 IN DOGS OF 5-6 HR IS INFLUENCED BY EXTENSIVE BINDING TO ERYTHROCYTES & PLASMA PROTEINS, & POSSIBLY TO TISSUE PROTEINS.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 161
The actions of metolazone result from interference with the renal tubular mechanism of electrolyte reabsorption. Metolazone acts primarily to inhibit sodium reabsorption at the cortical diluting site and to a lesser extent in the proximal convoluted tubule. Sodium and chloride ions are excreted in approximately equivalent amounts. The increased delivery of sodium to the distal tubular exchange site results in increased potassium excretion. Metolazone does not inhibit carbonic anhydrase. The antihypertensive mechanism of action of metolazone is not fully understood but is presumed to be related to its saluretic and diuretic properties.
IT ACTS PRIMARILY TO INHIBIT SODIUM REABSORPTION AT CORTICAL DILUTING SITE & IN PROXIMAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE. SODIUM & CHLORIDE IONS ARE EXCRETED IN APPROX EQUAL AMT; INCR POTASSIUM EXCRETION MAY ALSO OCCUR. DIURETIC POTENCY APPROXIMATES THAT OF THIAZIDES.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 873