
1. Bay M 1099
2. Bay-m 1099
3. Bay-m-1099
4. Diastabol
5. Glyset
6. Miglitol, 4-methylbenzenesulfonate Salt, ((d)-isomer)
7. N-hydroxyethyl-1-desoxy-nojirimycin
8. N-hydroxyethyl-1-desoxynojirimycin
9. Plumarol
1. 72432-03-2
2. Glyset
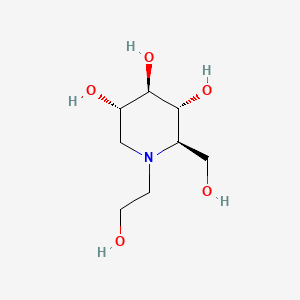
3. (2r,3r,4r,5s)-1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)piperidine-3,4,5-triol
4. Bay-m-1099
5. Bay M 1099
6. Miglitol (glyset)
7. Seibule
8. Chembl1561
9. (2r,3r,4r,5s)-1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-3,4,5-piperidinetriol
10. 0v5436jaqw
11. Chebi:6935
12. Diastabol
13. Plumarol
14. Nsc-758702
15. Dsstox_cid_3323
16. Dsstox_rid_76977
17. Dsstox_gsid_23323
18. Miglitolum
19. N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-deoxynojirimycin
20. Smr000466381
21. Miglitolum [latin]
22. Cas-72432-03-2
23. Glyset (tn)
24. Unii-0v5436jaqw
25. Miglitol [usan:inn:ban]
26. Bay 1099
27. Hsdb 8022
28. Ncgc00095127-01
29. Einecs 276-661-6
30. Mfcd00867240
31. Sk-983
32. Baym1099
33. Miglitol [usan]
34. Miglitol [inn]
35. Miglitol [jan]
36. Miglitol [mi]
37. Miglitol [vandf]
38. Miglitol [mart.]
39. Bay M1009
40. Miglitol [who-dd]
41. Schembl22593
42. Mls000759514
43. Mls001424128
44. Mls006011963
45. Bidd:gt0732
46. Bay-m1099
47. Miglitol [orange Book]
48. Cid_441314
49. Gtpl4842
50. Miglitol (jp17/usan/inn)
51. Dtxsid0023323
52. Bay1099
53. Hms2051d05
54. Hms3713j07
55. N-hydroxylethyl-1-deoxynojirimycin
56. Hy-b0481
57. Zinc4097426
58. Tox21_111436
59. Bdbm50242271
60. Akos015969689
61. Tox21_111436_1
62. Ccg-100920
63. Db00491
64. Ks-1242
65. Nc00170
66. Nsc 758702
67. Ncgc00270540-02
68. M2302
69. S2589
70. C07708
71. C76308
72. D00625
73. Ab00639982-06
74. Ab00639982_08
75. 432m032
76. A837526
77. Q772735
78. Sr-01000759413
79. Sr-01000759413-4
80. W-104490
81. 1,5-dideoxy-1,5-((2-hydroxyethyl)imino)-d-glucitol
82. Brd-k44779798-001-06-5
83. Z1541638520
84. (2r,3r,4r,5s)-1-ethoxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)piperidine-3,4,5-triol
85. (4r,5r)-1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)piperidine-3,4,5-triol
86. (2r,3r,4r,5s)-1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-(2-hydroxymethyl)-3,4,5-piperidinetriol
87. 1204250-58-7
88. 3,4,5-piperidinetriol, 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-, (2r-(2.alpha.,3.beta.,4.alpha.,5.beta.))-
89. 3,4,5-piperidinetriol, 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-, (2r-(2alpha,3beta,4alpha,5beta))-
| Molecular Weight | 207.22 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H17NO5 |
| XLogP3 | -2.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 207.11067264 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 207.11067264 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 104 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 179 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glyset |
| PubMed Health | Miglitol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antidiabetic |
| Drug Label | GLYSET Tablets contain miglitol, an oral alpha-glucosidase inhibitor for use in the management of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). Miglitol is a desoxynojirimycin derivative, and is chemically known as 3,4,5-piperidinetriol, 1-(2-hydr... |
| Active Ingredient | Miglitol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; 100mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pharmacia And Upjohn |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glyset |
| PubMed Health | Miglitol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antidiabetic |
| Drug Label | GLYSET Tablets contain miglitol, an oral alpha-glucosidase inhibitor for use in the management of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). Miglitol is a desoxynojirimycin derivative, and is chemically known as 3,4,5-piperidinetriol, 1-(2-hydr... |
| Active Ingredient | Miglitol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; 100mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pharmacia And Upjohn |
1-Deoxynojirimycin/*analogs & derivatives; alpha-Glucosidases/antagonists & inhibitors; Enzyme Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2009)
Reduction in postprandial blood glucose concentrations persists for 3-4 hours following a single dose in healthy individuals.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011
Miglitol is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus./Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for GLYSET (miglitol) tablet, film coated (October 2010). Available from, as of February 21, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=75711d16-2d27-476e-a312-d5af448a0e25
Miglitol is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug or diabetic ketoacidosis. The drug is also contraindicated in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, colonic ulceration, partial intestinal obstruction or predisposition to this condition, chronic intestinal diseases associated with marked disorders of digestion or absorption, and coexisting conditions that may deteriorate as a result of increased intestinal gas formation.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011
Miglitol should not cause hypoglycemia when administered alone in the fasting or postprandial state. There is an increased risk of hypoglycemia when miglitol is used concomitantly with insulinor a sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent. If hypoglycemia occurs, dosage of these agents should be adjusted appropriately.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011
Oral glucose (dextrose) should be used for the treatment of mild to moderate hypoglycemia instead of sucrose (table sugar, a disaccharide); absorption of oral glucose (a monosaccharide) is not delayed by miglitol. Severe hypoglycemia may require the use of either iv glucose infusion or parenteral glucagon.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011
There is a risk of possible loss of glycemic control in patients receiving miglitol during periods of stress (e.g., fever, trauma, infection, surgery); temporary administration of insulin may be required.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Miglitol (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For use as an adjunct to diet to improve glycemic control in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) whose hyperglycemia cannot be managed with diet alone.
Miglitol, an oral alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, is a desoxynojirimycin derivative that delays the digestion of ingested carbohydrates, thereby resulting in a smaller rise in blood glucose concentration following meals. As a consequence of plasma glucose reduction, miglitol reduce levels of glycosylated hemoglobin in patients with Type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Systemic nonenzymatic protein glycosylation, as reflected by levels of glycosylated hemoglobin, is a function of average blood glucose concentration over time. Because its mechanism of action is different, the effect of miglitol to enhance glycemic control is additive to that of sulfonylureas when used in combination. In addition, miglitol diminishes the insulinotropic and weight-increasing effects of sulfonylureas. Miglitol has minor inhibitory activity against lactase and consequently, at the recommended doses, would not be expected to induce lactose intolerance.
Enzyme Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme combination and the catalytic reaction. (See all compounds classified as Enzyme Inhibitors.)
Glycoside Hydrolase Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit or block the activity of GLYCOSIDE HYDROLASES such as ALPHA-AMYLASES and ALPHA-GLUCOSIDASES. (See all compounds classified as Glycoside Hydrolase Inhibitors.)
Hypoglycemic Agents
Substances which lower blood glucose levels. (See all compounds classified as Hypoglycemic Agents.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10 - Drugs used in diabetes
A10B - Blood glucose lowering drugs, excl. insulins
A10BF - Alpha glucosidase inhibitors
A10BF02 - Miglitol
Absorption
Absorption of miglitol is saturable at high doses with 25 mg being completely absorbed while a 100-mg dose is only 50-70% absorbed. No evidence exists to show that systemic absorption of miglitol adds to its therapeutic effect.
Route of Elimination
Miglitol is not metabolized in man or in any animal species studied. It is eliminated by renal excretion as an unchanged drug.
Volume of Distribution
0.18 L/kg
Absorption of miglitol is saturable at high doses: a dose of 25 mg is completely absorbed, whereas a dose of 100 mg is only 50% - 70% absorbed. For all doses, peak concentrations are reached in 2-3 hours.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for GLYSET (miglitol) tablet, film coated (October 2010). Available from, as of February 21, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=75711d16-2d27-476e-a312-d5af448a0e25
Therapeutic effects principally result from local actions on the small intestine; there is no evidence that systemic absorption contributes to therapeutic response.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011
The protein binding of miglitol is negligible (<4.0%). Miglitol has a volume of distribution of 0.18 L/kg, consistent with distribution primarily into the extracellular fluid.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for GLYSET (miglitol) tablet, film coated (October 2010). Available from, as of February 21, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=75711d16-2d27-476e-a312-d5af448a0e25
Miglitol is distributed principally into extracellular fluid and concentrated in enterocytes of the small intestine.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Miglitol (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Miglitol is not metabolized in man or in any animal species studied.
Miglitol is not metabolized in man or in any animal species studied. No metabolites have been detected in plasma, urine, or feces, indicating a lack of either systemic or pre-systemic metabolism.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for GLYSET (miglitol) tablet, film coated (October 2010). Available from, as of February 21, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=75711d16-2d27-476e-a312-d5af448a0e25
The elimination half-life of miglitol from plasma is approximately 2 hours.
... Miglitol is rapidly eliminated from plasma with apparent elimination half-lives of 0.4-1.8 hr. ... At very low concentration levels a terminal elimination phase of radioactivity characterized by half-lives of 50-110 hr...
PMID:9239452 Ahr HJ et al; Arzneimittelforschung 47 (6): 734-45 (1997)
The elimination half-life of miglitol from plasma is approximately 2 hours.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for GLYSET (miglitol) tablet, film coated (October 2010). Available from, as of February 21, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=75711d16-2d27-476e-a312-d5af448a0e25
In contrast to sulfonylureas, miglitol does not enhance insulin secretion. The antihyperglycemic action of miglitol results from a reversible inhibition of membrane-bound intestinal a-glucoside hydrolase enzymes. Membrane-bound intestinal a-glucosidases hydrolyze oligosaccharides and disaccharides to glucose and other monosaccharides in the brush border of the small intestine. In diabetic patients, this enzyme inhibition results in delayed glucose absorption and lowering of postprandial hyperglycemia.
Miglitol is a desoxynojirimycin derivative that delays the digestion of ingested carbohydrates, thereby resulting in a smaller rise in blood glucose concentration following meals. As a consequence of plasma glucose reduction, miglitol tablets reduce levels of glycosylated hemoglobin in patients with Type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Systemic nonenzymatic protein glycosylation, as reflected by levels of glycosylated hemoglobin, is a function of average blood glucose concentration over time.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for GLYSET (miglitol) tablet, film coated (October 2010). Available from, as of February 21, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=75711d16-2d27-476e-a312-d5af448a0e25
Miglitol inhibits alpha-glucosidase enzymes (e.g., sucrase, glucoamylase, maltase, isomaltase) that hydrolyze oligosaccharides, trisaccharides, and disaccharides to glucose and other monosaccharides in the small intestinal brush border. The drug has little or no inhibitory effect on trehalase, lactase, or pancreatic alpha-amylase; it is not expected to produce lactose intolerance. Miglitol delays carbohydrate breakdown and glucose absorption and reduces postprandial hyperglycemia in diabetic patients; fasting blood glucose concentrations are mildly decreased.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011
In contrast to sulfonylurea antidiabetic agents, miglitol does not enhance insulin secretion. The drug does not produce hypoglycemia when given as monotherapy in the fasted or postprandial state. When used in combination with sulfonylurea antidiabetic agents, miglitol reduces the insulinotropic and weight-increasing effects of sulfonylureas. Miglitol does not produce clinically important weight loss.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011
Oral administration of miglitol has been reported to produce glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). /The authors/ hypothesized that p.o. administration of miglitol, an absorbable antidiabetic drug, reduces myocardial infarct size by stimulating GLP-1 receptors and inhibiting glycogenolysis in the myocardium. The effects of p.o. and i.v. administration of miglitol on myocardial infarct size were compared in a rabbit model of ischemia induced by 30 min of coronary occlusion and 48 hr of reperfusion. The levels of phospho(p)-PI3kinase and p-Akt were measured in cardiac tissue by use of Western blot analysis. Both p.o. and i.v. administration of miglitol reduced the infarct size, and this effect was greater after p.o. than after i.v. administration under similar plasma miglitol concentrations. The reduction in infarct size induced by p.o. miglitol but not that induced by i.v. miglitol was partially inhibited by treatment with exendin(9-39), a GLP-1 receptor blocker. Both p.o. and i.v. miglitol improved ejection fraction and +/-dP/dt after myocardial infarction. Miglitol administered p.o. but not i.v. up-regulated the myocardial expression of phospho(p)-PI3kinase and p-Akt following myocardial infarction; an effect that was inhibited by exendin(9-39). Administration of miglitol p.o. reduces myocardial infarct size through stimulation of GLP-1 receptors and activation of PI3kinase-Akt pathway in addition to the inhibition of glycogenolysis. These findings may have clinical implications for the p.o. administration of miglitol for the treatment of patients with diabetes mellitus combined with coronary artery disease.
PMID:21426318 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3171865 Iwasa M et al; Br J Pharmacol 164 (1): 119-31 (2011)
Imino sugars are used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (miglitol (Glyset)) and lysosomal storage disorders (miglustat (Zavesca)) based on the inhibition of alpha-glucosidases and glucosyltransferases. In this substrate specificity study, /investigators/ examined the interactions of imino sugars with a novel human glucose sensor, sodium/glucose cotransporter type 3 (hSGLT3), using expression in Xenopus laevis oocytes and electrophysiology. The results for hSGLT3 are compared with those for alpha-glucosidases and human SGLT type 1 (hSGLT1), a well characterized sodium/glucose cotransporter of the SGLT family. In general, substrates have lower apparent affinities (K0.5) for hSGLT3 than hSGLT1 (D-glucose, alpha-methyl-D-glucose, 1-deoxy-D-glucose, and 4-deoxy-4-fluoro-D-glucose exhibit K0.5 values of 19, 21, 43, and 17 mM, respectively, for hSGLT3, and 0.5, 0.7, 10, and 0.07 mM, respectively, for hSGLT1). However, specificity of hSGLT3 binding is greater (D-galactose and 4-deoxy-4-fluoro-D-galactose are not hSGLT3 substrates, but have hSGLT1 K0.5 values of 0.6 and 1.3 mM). An important deviation from this trend is potent hSGLT3 activation by the imino sugars 1-deoxynojirimycin (DNJ), N-hydroxylethyl-1-deoxynojirimycin (miglitol), N-butyl-1-deoxynojirimycin (miglustat), N-ethyl-1-deoxynojirimycin, and 1-deoxynojirimycin-1-sulfonic acid, with K0.5 values of 0.5 to 9 microM. The diastereomer 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin activates hSGT3 with a K0.5 value of 11 mM, a 3000-fold less potent interaction than is observed for DNJ (4 microM). These imino sugar binding characteristics are similar to those for alpha-glucosidases, but there are no interactions with hSGLT1. This work provides insights into hSGLT3 and -1 substrate binding interactions, establishes a pharmacological profile to study endogenous hSGLT3, and may have important ramifications for the clinical application of imino sugars.
PMID:17110502 Voss AA et al; Mol Pharmacol 71 (2): 628-34 (2007)