


1. Corotrop
2. Corotrope
3. Lactate, Milrinone
4. Milrinone
5. Primacor
6. Win 47203
7. Win-47203
8. Win47203
1. 100286-97-3
2. 9k8xr81mo8
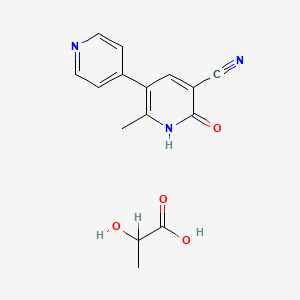
3. 6-methyl-2-oxo-5-pyridin-4-yl-1h-pyridine-3-carbonitrile Lactate
4. 2-hydroxypropanoic Acid;6-methyl-2-oxo-5-pyridin-4-yl-1h-pyridine-3-carbonitrile
5. Chebi:34850
6. Unii-9k8xr81mo8
7. Milrinonelactate
8. Milrinone Lactose In 5% Dextrose
9. Primacor (tn)
10. Primacor In Dextrose 5% In Plastic Container
11. Milrinone Lactate [mi]
12. Milrinone Lactate In 5% Dextrose In Plastic Container
13. Chembl1200977
14. Milrinone Lactate [vandf]
15. Milrinone Lactate [mart.]
16. Milrinone Lactate In Dextrose 5% In Plastic Container
17. Milrinone Lactate [who-dd]
18. Akos015917733
19. Milrinone Lactate [orange Book]
20. 1,6-dihydro-2-methyl-6-oxo(3,4'-bipyridine)-5-carbonitrile, Compd. With 2-hydroxypropionic Acid
21. Ls-14389
22. Ft-0739660
23. D02085
24. 286m973
25. A897507
26. Q27116295
27. 2-[(4-chlorobenzyl)sulfanyl]benzenecarboxylicacid
28. 1,6-dihydro-2-methyl-6-oxo[3,4'-bipyridine]-5-carbonitrile Lactate
29. 2-hydroxypropanoic Acid,6-methyl-2-oxo-5-pyridin-4-yl-1h-pyridine-3-carbonitrile
30. 6-methyl-2-oxo-5-pyridin-4-yl-1h-pyridine-3-carbonitrile 2-hydroxypropanoic Acid
31. Hydron;2-hydroxypropanoate;6-methyl-2-oxo-5-pyridin-4-yl-1h-pyridine-3-carbonitrile
32. Propanoic Acid, 2-hydroxy-, Compd. With 1,6-dihydro-2-methyl-6-oxo(3,4'-bipyridine)-5-carbonitrile
| Molecular Weight | 301.30 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H15N3O4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 301.10625597 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 301.10625597 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 123 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 478 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Milrinone lactate |
| Drug Label | Milrinone Lactate Injection is a member of a new class of bipyridine inotropic/vasodilator agents with phosphodiesterase inhibitor activity, distinct from digitalis glycosides or catecholamines. Milrinone lactate is designated chemically as 1,6-Dihyd... |
| Active Ingredient | Milrinone lactate |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | injection; Injection |
| Strength | 20mg/20ml; eq 1mg base/ml; eq 20mg /20ml (1mg/ml); eq 50mg /50ml (1mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bedford; Hospira; Gland Pharma; Apotex; Hikma Farmaceutica; Fresenius Kabi Usa; Hikma Maple; Intl Medicated |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Milrinone lactate |
| Drug Label | Milrinone Lactate Injection is a member of a new class of bipyridine inotropic/vasodilator agents with phosphodiesterase inhibitor activity, distinct from digitalis glycosides or catecholamines. Milrinone lactate is designated chemically as 1,6-Dihyd... |
| Active Ingredient | Milrinone lactate |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | injection; Injection |
| Strength | 20mg/20ml; eq 1mg base/ml; eq 20mg /20ml (1mg/ml); eq 50mg /50ml (1mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bedford; Hospira; Gland Pharma; Apotex; Hikma Farmaceutica; Fresenius Kabi Usa; Hikma Maple; Intl Medicated |
Cardiotonic Agents
Agents that have a strengthening effect on the heart or that can increase cardiac output. They may be CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES; SYMPATHOMIMETICS; or other drugs. They are used after MYOCARDIAL INFARCT; CARDIAC SURGICAL PROCEDURES; in SHOCK; or in congestive heart failure (HEART FAILURE). (See all compounds classified as Cardiotonic Agents.)
Phosphodiesterase 3 Inhibitors
Compounds that specifically inhibit PHOSPHODIESTERASE 3. (See all compounds classified as Phosphodiesterase 3 Inhibitors.)
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)
Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors
Drugs or agents which antagonize or impair any mechanism leading to blood platelet aggregation, whether during the phases of activation and shape change or following the dense-granule release reaction and stimulation of the prostaglandin-thromboxane system. (See all compounds classified as Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors.)
