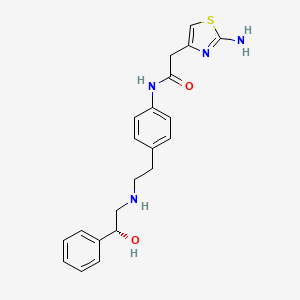

1. 2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-4'-(2-((2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl)amino)ethyl)acetanilide
2. Betanis
3. Betmiga
4. Ym 178
5. Ym-178
1. 223673-61-8
2. Myrbetriq
3. Betanis
4. Betmiga
5. Ym178
6. Mirabegron (ym178)
7. Ym-178
8. Ym 178
9. 2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-n-[4-(2-{[(2r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl]amino}ethyl)phenyl]acetamide
10. Mvr3jl3b2v
11. Chebi:65349
12. 2-amino-n-[4-[2-[[(2r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl]amino]ethyl]phenyl]-4-thiazoleacetamide
13. (r)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-n-(4-(2-((2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl)amino)ethyl)phenyl)acetamide
14. 4-thiazoleacetamide, 2-amino-n-(4-(2-(((2r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl)amino)ethyl)phenyl)-
15. Myrbetriq (tn)
16. 2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-n-[4-[2-[[(2r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl]amino]ethyl]phenyl]acetamide
17. 2-(2-azanyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-n-[4-[2-[[(2r)-2-oxidanyl-2-phenyl-ethyl]amino]ethyl]phenyl]ethanamide
18. Mirabegron [usan:inn]
19. Unii-mvr3jl3b2v
20. 2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-n-(4-(2-(((2r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl)amino)ethyl)phenyl)acetamide
21. Mirabegron [mi]
22. Mirabegron [inn]
23. Mirabegron [jan]
24. Mirabegron (usan/jan)
25. Mirabegron [usan]
26. Mirabegron [vandf]
27. Mirabegron [mart.]
28. Mirabegron [who-dd]
29. N-(4-(2-(2-hydroxy-2-phenylethylamino)ethyl)phenyl)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)acetamide
30. Schembl904788
31. Gtpl7445
32. Chembl2095212
33. Mirabegron [orange Book]
34. Amy1800
35. Dtxsid101021648
36. Hms3714i09
37. Hms3885m16
38. 2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-n-(4-{2-[(2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl)amino]ethyl}phenyl)acetamide
39. Ex-a1050
40. Zinc1996784
41. Mfcd11100356
42. S4009
43. Akos016340341
44. Ccg-268611
45. Cs-0915
46. Db08893
47. Ks-1398
48. 2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-4'-(2-((2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl)amino)ethyl)acetanilide
49. Ncgc00386239-01
50. Hy-14773
51. Sw220301-1
52. D09535
53. Ab01565808_02
54. A816162
55. Ar-270/43507997
56. Q3702534
57. (r)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-4'-[2-[(2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl)amino]ethyl]acetanilide
58. (r)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-4-{2-[(2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl)amino]ethyl}acetanilide
59. (r)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-n-(4-(2-(2-hydroxy-2-phenylethylamino)ethyl)phenyl)acetamide
60. 2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-n-(4-(2-(((2r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl)amino)ethyl)phenyl)acetamide
61. H6u
62. Ym 178;2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-n-[4-[2-[[(2r)-2-hydroxy-2-phenyl-ethyl]amino]ethyl]phenyl]acetamide
| Molecular Weight | 396.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H24N4O2S |
| XLogP3 | 2.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 396.16199719 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 396.16199719 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 129 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 467 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Myrbetriq |
| PubMed Health | Mirabegron (Oral route) |
| Drug Label | Mirabegron is a beta-3 adrenergic agonist. The chemical name is 2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-N-[4-(2-{[(2R)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl]amino}ethyl)phenyl]acetamide having an empirical formula of C21H24N4O2S and a molecular weight of 396.51. The structural fo... |
| Active Ingredient | Mirabegron |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Apgdi |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Myrbetriq |
| PubMed Health | Mirabegron (Oral route) |
| Drug Label | Mirabegron is a beta-3 adrenergic agonist. The chemical name is 2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-N-[4-(2-{[(2R)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl]amino}ethyl)phenyl]acetamide having an empirical formula of C21H24N4O2S and a molecular weight of 396.51. The structural fo... |
| Active Ingredient | Mirabegron |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Apgdi |
Mirabegron is indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder (OAB) - with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and urinary frequency - either alone or in combination with [solifenacin]. It is also indicated for the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO) in pediatric patients 3 years of age and older and weighing 35kg or more.
Symptomatic treatment of urgency.
Increased micturition frequency and / or urgency incontinence as may occur in adult patients with overactive-bladder syndrome.
Treatment of idiopathic overactive bladder
Treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity
Mirabegron exerts its pharmacologic effects by forcing bladder smooth muscle to relax, thereby expanding its capacity and relieving urgency. Mirabegron does not appear to adversely affect the mean maximum flow rate or mean detrusor pressure at maximum flow rate in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms and bladder outlet obstruction (BOO), but should be used with in patients with BOO due to reports of significant urinary retention. Furthermore, mirabegron increases both blood pressure and heart rate in a dose-dependent manner and should therefore be used with caution in patients with severely uncontrolled hypertension or others for whom these increases may prove dangerous.
Adrenergic beta-3 Receptor Agonists
Compounds that bind to and activate ADRENERGIC BETA-3 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic beta-3 Receptor Agonists.)
Urological Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of urological conditions and diseases such as URINARY INCONTINENCE and URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS. (See all compounds classified as Urological Agents.)
G04BD12
G - Genito urinary system and sex hormones
G04 - Urologicals
G04B - Urologicals
G04BD - Drugs for urinary frequency and incontinence
G04BD12 - Mirabegron
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of orally administered mirabegron ranges from 29% at a dose of 25 mg to 35% at a dose of 50 mg. The Tmax for the extended-release tablet and suspension formulations are approximately 3.5 hours, while the Tmax for the granule formulation is 4-5 hours. Both Cmax and AUC increase more than dose proportionally - an increase in dose from 50mg to 100mg results in a 2.9- and 2.6-fold increase in Cmax and AUC, respectively, whereas an increase from 50mg to 200mg results in a 8.4- and 6.5-fold increase in Cmax and AUC, respectively. Steady-state concentrations of mirabegron are achieved after approximately 7 days of once-daily administration.
Route of Elimination
Of a 160mg radiolabeled dose administered to healthy volunteers, approximately 55% of the radioactivity was recovered in the urine and 34% in the feces. Approximately 25% of unchanged mirabegron was recovered in the urine while 0% was recovered in the feces. Renal elimination is achieved primarily via active tubular secretion with some contribution by glomerular filtration.
Volume of Distribution
Following intravenous administration, mirabegron has an apparent steady-state volume of distribution (Vd) of 1670 L indicating extensive distribution.
Clearance
Total plasma clearance following intravenous administration is approximately 57 L/h, with renal clearance accounting for roughly 25% at approximately 13 L/h.
Mirabegron is extensively metabolized via a number of mechanisms, although unchanged parent drug is still the major circulating component following oral administration. Presumed metabolic pathways and their resultant metabolites include amide hydrolysis (M5, M16, M17), glucuronidation (mirabegron O-glucuronide, N-glucuronide, N-carbamoylglucuronide, M12), and secondary amine oxidation or dealkylation (M8, M9, M15), amongst others. The enzymes responsible for the oxidative metabolism of mirabegron are thought to be CYP3A4 and CYP2D6, while the UDP-glucuronosyltransferases responsible for conjugation reactions have been identified as UGT2B7, UGT1A3, and UGT1A8. Other enzymes that may be involved in the metabolism of mirabegron include butylcholinesterase and possibly alcohol dehydrogenase.
The mean terminal elimination half-life of mirabegron in adults being treated for overactive bladder is approximately 50 hours. In pediatric patients receiving the granule formulation for the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity, the mean terminal elimination half-life is approximately 26-31 hours.
Mirabegron is a potent and selective agonist of beta-3 adrenergic receptors. The activation of beta-3 receptors relaxes detrusor smooth muscle during the storage phase of the urinary bladder fill-void cycle, which increases the bladder's storage capacity thereby alleviating feelings of urgency and frequency.