

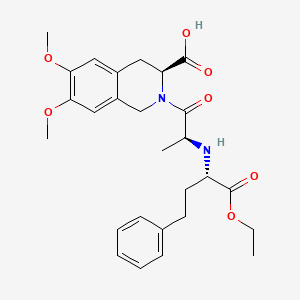

1. 2-((1-ethoxycarbony)-3-phenylpropylamino-1-oxopropyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
2. Fempress
3. Moex
4. Moexipril Hydrochloride
5. Perdix
6. Rs 10085
7. Rs-10085
8. Univasc
1. 103775-10-6
2. Uniretic
3. Univasc
4. Moexiprilum [inn-latin]
5. (3s)-2-[(2s)-2-[[(2s)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino]propanoyl]-6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydro-1h-isoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
6. Moexipril (inn)
7. Ci-925
8. 109715-88-0
9. Rs-10085
10. Chembl1165
11. Wt87c52tjz
12. Chebi:6960
13. Moexiprilum
14. Moexipril [inn]
15. Moexipril [inn:ban]
16. (3s)-2-((2s)-n-((1s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)alanyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-3-isoquinolinecarboxylic Acid, 2-ethyl Ester
17. (s)-2-(((s)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl)-l-alanyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
18. (s)-2-((s)-2-(((s)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl)amino)propanoyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
19. (s)-2-((s)-2-((s)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylamino)propanoyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
20. 3-isoquinolinecarboxylic Acid,2-[(2s)-2-[[(1s)-1-(ethoxycarbonyl)-3-phenylpropyl]amino]-1-oxopropyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-, (3s)-
21. Unii-wt87c52tjz
22. Moexipril [mi]
23. Moexipril [vandf]
24. Moexipril [who-dd]
25. Schembl34030
26. Bidd:gt0007
27. Gtpl6571
28. Dtxsid9023330
29. Zinc3812306
30. Bdbm50084673
31. Akos015843317
32. Db00691
33. Ncgc00263546-03
34. (3s)-2-(n-{(1s)-1-[(ethyloxy)carbonyl]-3-phenylpropyl}-l-alanyl)-6,7-bis(methyloxy)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
35. Hy-117281
36. Cs-0064930
37. 75m106
38. C07704
39. D08225
40. Ab01565830_02
41. A800803
42. Q2291605
43. Brd-k34441861-003-01-3
44. 4-(4-oxopiperidine-1-carbonyl)phenylboronicacid
45. (3s)-2-((2s)-2-(((1s)-1-(ethoxycarbonyl)-3-phenylpropyl)amino)-1-oxopropyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-3-isoquinolinecarboxylic Acid
46. (3s)-2-[(2s)-2-{[(2s)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino}propanoyl]-6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
47. 1-[2-(1-ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenyl-propylamino)-propionyl]-octahydro-indole-2-carboxylic Acid(moexipril)
48. 3-isoquinolinecarboxylic Acid, 2-(2-((1-(ethoxycarbonyl)-3-phenylpropyl)amino)-1-oxopropyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-, (3s-(2(r*(r*)),3r*))-
| Molecular Weight | 498.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H34N2O7 |
| XLogP3 | 1.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 |
| Exact Mass | 498.23660143 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 498.23660143 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 114 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 36 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 742 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of hypertension.
Moexipril is a non-sulfhydryl containing precursor of the active angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor moexiprilat. It is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). It works by relaxing blood vessels, causing them to widen. Lowering high blood pressure helps prevent strokes, heart attacks and kidney problems.
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
A class of drugs whose main indications are the treatment of hypertension and heart failure. They exert their hemodynamic effect mainly by inhibiting the renin-angiotensin system. They also modulate sympathetic nervous system activity and increase prostaglandin synthesis. They cause mainly vasodilation and mild natriuresis without affecting heart rate and contractility. (See all compounds classified as Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C09 - Agents acting on the renin-angiotensin system
C09A - Ace inhibitors, plain
C09AA - Ace inhibitors, plain
C09AA13 - Moexipril
Absorption
Moexipril is incompletely absorbed, with bioavailability as moexiprilat of about 13% compared to intravenous (I.V.) moexipril (both measuring the metabolite moexiprilat), and is markedly affected by food, which reduces Cmax and AUC by about 70% and 40%, respectively, after the ingestion of a low-fat breakfast or by 80% and 50%, respectively, after the ingestion of a high-fat breakfast.
Route of Elimination
Moexiprilat undergoes renal elimination.
Volume of Distribution
183 L
Clearance
441 mL/min
Rapidly converted to moexiprilat, the active metabolite. Conversion to the active metabolite is thought to require carboxyesterases and is likely to occur in organs or tissues, other than the gastrointestinal tract, in which carboxyesterases occur. The liver is thought to be one site of conversion, but not the primary site.
Moexipril elimination half-life is approximately 1 hour. Moexiprilat elimination half-life is 2 to 9 hours.
Moexipril is a prodrug for moexiprilat, which inhibits ACE in humans and animals. The mechanism through which moexiprilat lowers blood pressure is believed to be primarily inhibition of ACE activity. ACE is a peptidyl dipeptidase that catalyzes the conversion of the inactive decapeptide angiotensin I to the vasoconstrictor substance angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a potent peripheral vasoconstrictor that also stimulates aldosterone secretion by the adrenal cortex and provides negative feedback on renin secretion. ACE is identical to kininase II, an enzyme that degrades bradykinin, an endothelium-dependent vasodilator. Moexiprilat is about 1000 times as potent as moexipril in inhibiting ACE and kininase II. Inhibition of ACE results in decreased angiotensin II formation, leading to decreased vasoconstriction, increased plasma renin activity, and decreased aldosterone secretion. The latter results in diuresis and natriuresis and a small increase in serum potassium concentration (mean increases of about 0.25 mEq/L were seen when moexipril was used alone). Whether increased levels of bradykinin, a potent vasodepressor peptide, play a role in the therapeutic effects of moexipril remains to be elucidated. Although the principal mechanism of moexipril in blood pressure reduction is believed to be through the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, ACE inhibitors have some effect on blood pressure even in apparent low-renin hypertension.
