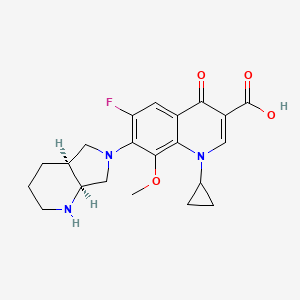

1. 1-cyclopropyl--7-(2,8-diazabicyclo(4.3.0)non-8-yl)-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
2. Actira
3. Avalox
4. Avelox
5. Bay 12 8039
6. Bay 12-8039
7. Bay 128039
8. Bay-12-8039
9. Bay-128039
10. Bay128039
11. Izilox
12. Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride
13. Octegra
14. Proflox
1. 151096-09-2
2. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-((4as,7as)-hexahydro-1h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6(2h)-yl)-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
3. Moxeza
4. Zimoxin
5. Avelox Iv
6. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-((4as,7as)-octahydro-6h-pyrrolo(3,4-b)pyridin-6-yl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
7. 7-[(4as,7as)-1,2,3,4,4a,5,7,7a-octahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
8. Bay 12-8039
9. U188xyd42p
10. Chebi:63611
11. Izilox
12. Moxifloxacin (inn)
13. (1's,6's)-1-cyclopropyl-7-(2,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-8-yl)-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
14. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-[(4as,7as)-octahydro-6h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
15. Moxifloxacine
16. Avolex
17. Moxifloxacin [inn]
18. Moxifloxacin [inn:ban]
19. 7-[(4as,7as)-octahydro-1h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
20. Mfx
21. 3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid, 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-[(4as,7as)-octahydro-6h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-4-oxo-
22. 7-[(4as,7as)-1,2,3,4,4a,5,7,7a-octahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
23. Mxfx
24. Bay-128039
25. Actira (*hydrochloride*)
26. Avelox (*hydrochloride*)
27. Moxyfloxacin
28. Unii-u188xyd42p
29. Ccris 8690
30. Mfcd04117996
31. Hsdb 8026
32. 3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid, 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-((4as,7as)-octahydro-6h-pyrrolo(3,4-b)pyridin-6-yl)-4-oxo-
33. Avelox Iv (tn)
34. (4r,7r)-moxifloxacin
35. Moxifloxacin [mi]
36. Moxifloxacin [vandf]
37. Schembl24007
38. Naproxendiisopropylamide
39. Moxifloxacin [who-dd]
40. Moxivig (opthalmic Solution)
41. Dtxsid3048491
42. Gtpl10915
43. Ex-a016
44. Hms3715p05
45. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-[(4ar,7ar)-octahydro-6h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
46. Bcp22895
47. Rkl10080
48. Zinc3826253
49. Bay128039
50. Bdbm50366824
51. Hy-66011a
52. Nsc782304
53. S5535
54. Bay 12-8039 (*hydrochloride*)
55. Akos015895251
56. Am84644
57. Bcp9000962
58. Ccg-221192
59. Cs-1895
60. Db00218
61. Nsc-782304
62. Ncgc00271749-08
63. Ac-25913
64. As-41986
65. Mxf
66. Bcp0726000137
67. Sbi-0206792.p001
68. 96m092
69. D08237
70. Ab00171653-11
71. Ab00171653-13
72. Ab00171653-14
73. Ab00171653_15
74. Ar-270/43507941
75. Q424940
76. Sr-01000763482
77. Sr-01000763482-3
78. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-((4as,7as)-hexahydro-1h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6(2h)-yl)-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylicacid
79. 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-octahydro-6h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
80. 3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid,1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-[(4as,7as)-octahydro-6h-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-4-oxo-
| Molecular Weight | 401.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H24FN3O4 |
| XLogP3 | 0.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 401.17508442 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 401.17508442 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 82.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 29 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 727 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Avelox |
| PubMed Health | Moxifloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | DESCRIPTIONAVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) is a synthetic broad spectrum antibacterial agent and is available as AVELOX Tablets for oral administration and as AVELOX I.V. for intravenous administration. Moxifloxacin, a fluoroquinolone, is availab... |
| Active Ingredient | Moxifloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | eq 400mg base; 400mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bayer Pharms; Bayer Hlthcare |
| 2 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Moxeza |
| PubMed Health | Moxifloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | MOXEZA is a sterile solution for topical ophthalmic use.Moxifloxacin hydrochloride is an 8-methoxy fluoroquinolone anti-infective, with a diazabicyclononyl ring at the C7 position. C21H24FN3O4HClMol Wt 437.9... |
| Active Ingredient | Moxifloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | eq 0.5% base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alcon Pharms |
| 3 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Moxifloxacin |
| PubMed Health | Moxifloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | DESCRIPTIONAVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) is a synthetic broad spectrum antibacterial agent and is available as AVELOX Tablets for oral administration and as AVELOX I.V. for intravenous administration. Moxifloxacin, a fluoroquinolone, is availab... |
| Active Ingredient | Moxifloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | ophthalmic |
| Strength | 0.5% |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval |
| Company | Akorn |
| 4 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Vigamox |
| PubMed Health | Moxifloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | VIGAMOX (moxifloxacin HCl ophthalmic solution) 0.5% is a sterile ophthalmic solution. It is an 8-methoxy fluoroquinolone anti-infective for topical ophthalmic use.Chemical Name:1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-[(4aS,7aS)-octahydro-6H-... |
| Active Ingredient | Moxifloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | eq 0.5% base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alcon Pharms |
| 5 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Avelox |
| PubMed Health | Moxifloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | DESCRIPTIONAVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) is a synthetic broad spectrum antibacterial agent and is available as AVELOX Tablets for oral administration and as AVELOX I.V. for intravenous administration. Moxifloxacin, a fluoroquinolone, is availab... |
| Active Ingredient | Moxifloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | eq 400mg base; 400mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bayer Pharms; Bayer Hlthcare |
| 6 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Moxeza |
| PubMed Health | Moxifloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | MOXEZA is a sterile solution for topical ophthalmic use.Moxifloxacin hydrochloride is an 8-methoxy fluoroquinolone anti-infective, with a diazabicyclononyl ring at the C7 position. C21H24FN3O4HClMol Wt 437.9... |
| Active Ingredient | Moxifloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | eq 0.5% base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alcon Pharms |
| 7 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Moxifloxacin |
| PubMed Health | Moxifloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | DESCRIPTIONAVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) is a synthetic broad spectrum antibacterial agent and is available as AVELOX Tablets for oral administration and as AVELOX I.V. for intravenous administration. Moxifloxacin, a fluoroquinolone, is availab... |
| Active Ingredient | Moxifloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | ophthalmic |
| Strength | 0.5% |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval |
| Company | Akorn |
| 8 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Vigamox |
| PubMed Health | Moxifloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | VIGAMOX (moxifloxacin HCl ophthalmic solution) 0.5% is a sterile ophthalmic solution. It is an 8-methoxy fluoroquinolone anti-infective for topical ophthalmic use.Chemical Name:1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-[(4aS,7aS)-octahydro-6H-... |
| Active Ingredient | Moxifloxacin hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | eq 0.5% base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alcon Pharms |
Anti-Infective Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2012)
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride ophthalmic solution is used for the treatment of conjunctivitis caused by susceptible strains of Corynebacterium spp., Micrococcus luteus, Staphylococcus aureus, S. epidermidis, S. haemolyticus, S. hominis, S. warneri, Streptococcus pneumoniae, viridans streptococci, Acinetobacter lwoffii, Haemophilus influenzae, H. parainfluenzae, or Chlamydia trachomatis. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011
Moxifloxacin is used for the treatment of acute bacterial sinusitis caused by susceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, or Moraxella catarrhalis; acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis caused by susceptible S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, H. parainfluenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus (oxacillin-susceptible [methicillin-susceptible] strains), or M. catarrhalis; and community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) caused by susceptible S. pneumoniae (including multidrug-resistant strains), S. aureus (oxacillin-susceptible strains), K. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydophila pneumoniae (formerly Chlamydia pneumoniae), or M. catarrhalis. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 392
Moxifloxacin is used for the treatment of uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections caused by susceptible S. aureus (oxacillin-susceptible strains) or Streptococcus pyogenes (group A beta-hemolytic streptococci) and for the treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections caused by susceptible S. aureus (oxacillin-susceptible strains), Escherichia coli, K. pneumoniae, or Enterobacter cloacae. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 393
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Moxifloxacin (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: Fluoroquinolones, including Avelox, are associated with an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all ages. This risk is further increased in older patients usually over 60 years of age, in patients taking corticosteroid drugs, and in patients with kidney, heart or lung transplants.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) injection, solution AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (October 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=56b4f979-bf20-4908-9d7c-5536221d77f8
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: Fluoroquinolones, including Avelox, may exacerbate muscle weakness in persons with myasthenia gravis. Avoid Avelox in patients with known history of myasthenia gravis.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) injection, solution AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (October 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=56b4f979-bf20-4908-9d7c-5536221d77f8
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity and/or anaphylactic reactions reported in patients receiving fluoroquinolones, including moxifloxacin. Although generally reported after multiple doses, these reactions may occur with first dose. Some reactions have been accompanied by cardiovascular collapse, loss of consciousness, tingling, edema (pharyngeal or facial), dyspnea, urticaria, or pruritus. In addition, other possible severe and potentially fatal reactions (may be hypersensitivity reactions or of unknown etiology) have been reported, most frequently after multiple doses. These include fever, rash or severe dermatologic reactions (e.g., toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome), vasculitis, arthralgia, myalgia, serum sickness, allergic pneumonitis, interstitial nephritis, acute renal insufficiency or failure, hepatitis, jaundice, acute hepatic necrosis or failure, anemia (including hemolytic and aplastic), thrombocytopenia (including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura), leukopenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, and/or other hematologic effects. Discontinue moxifloxacin at first appearance of rash, jaundice, or any other sign of hypersensitivity. Institute appropriate therapy as indicated (e.g., epinephrine, corticosteroids, and maintenance of an adequate airway and oxygen).
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 395
Sensory or sensorimotor axonal polyneuropathy affecting small and/or large axons resulting in paresthesias, hypoesthesias, dysesthesias, and weakness have been reported with fluoroquinolones.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 395
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Moxifloxacin (22 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of sinus and lung infections such as sinusitis, pneumonia, and secondary infections in chronic bronchitis. Also for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis (pinkeye).
FDA Label
Moxifloxacin is a quinolone/fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Moxifloxacin can be used to treat infections caused by the following bacteria: Aerobic Gram-positive microorganisms: Corynebacterium species, Micrococcus luteus, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus hominis, Staphylococcus warneri, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Streptococcus viridans group. Aerobic Gram-negative microorganisms: Acinetobacter lwoffii, Haemophilus influenzae, and Haemophilus parainfluenzae. Other microorganisms: Chlamydia trachomatis.
Moxifloxacin is bactericidal and its mode of action depends on blocking of bacterial DNA replication by binding itself to an enzyme called DNA gyrase, which allows the untwisting required to replicate one DNA double helix into two. Notably the drug has 100 times higher affinity for bacterial DNA gyrase than for mammalian. Moxifloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Topoisomerase II Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit the activity of DNA TOPOISOMERASE II. Included in this category are a variety of ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS which target the eukaryotic form of topoisomerase II and ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS which target the prokaryotic form of topoisomerase II. (See all compounds classified as Topoisomerase II Inhibitors.)
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
J01MA14
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01M - Quinolone antibacterials
J01MA - Fluoroquinolones
J01MA14 - Moxifloxacin
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01A - Antiinfectives
S01AE - Fluoroquinolones
S01AE07 - Moxifloxacin
Absorption
Well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Absolute oral bioavailability is approximately 90%. Food has little effect on absorption.
Route of Elimination
Approximately 45% of an oral or intravenous dose of moxifloxacin is excreted as unchanged drug (~20% in urine and ~25% in feces).
Volume of Distribution
1.7 to 2.7 L/kg
Clearance
12 +/- 2 L/hr
Moxifloxacin is approximately 30-50% bound to serum proteins, independent of drug concentration. The volume of distribution of moxifloxacin ranges from 1.7 to 2.7 L/kg. Moxifloxacin is widely distributed throughout the body, with tissue concentrations often exceeding plasma concentrations. Moxifloxacin has been detected in the saliva, nasal and bronchial secretions, mucosa of the sinuses, skin blister fluid, subcutaneous tissue, skeletal muscle, and abdominal tissues and fluids following oral or intravenous administration of 400 mg.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) injection, solution AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (October 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=moxifloxacin
Approximately 45% of an oral or intravenous dose of moxifloxacin is excreted as unchanged drug (~20% in urine and ~25% in feces). A total of 96% + or - 4% of an oral dose is excreted as either unchanged drug or known metabolites. The mean (+ or - SD) apparent total body clearance and renal clearance are 12 + or - 2 L/hr and 2.6 + or - 0.5 L/hr, respectively.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) injection, solution AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (October 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=moxifloxacin
Moxifloxacin, given as an oral tablet, is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The absolute bioavailability of moxifloxacin is approximately 90 percent. Co-administration with a high fat meal (that is, 500 calories from fat) does not affect the absorption of moxifloxacin.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) injection, solution AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (October 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=moxifloxacin
The ocular penetration and pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin in comparison to other fluoroquinolones (ofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, gatifloxacin, norfloxacin, levofloxacin, and lomefloxacin) have been determined by in vitro and ex vivo techniques, as well as in animal and human studies. ... The results consistently demonstrate higher maximum concentrations for moxifloxacin relative to the other fluoroquinolones in ocular tissues with levels well above its minimum inhibitory concentrations for relevant ocular pathogens. This superior performance is due to the unique structure of moxifloxacin that combines high lipophilicity for enhanced corneal penetration with high aqueous solubility at physiological pH. The latter property creates a high concentration gradient at the tear film/corneal epithelial interface providing a driving force for better ocular penetration for moxifloxacin. In addition, the higher concentration of moxifloxacin in VIGAMOX (i.e., 0.5% vs. 0.3%) allows more antibiotic to be available to ocular tissues. It is clear from the array of studies summarized in this report that moxifloxacin penetrates ocular tissues better (two- to three-fold) than gatifloxacin, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, or levofloxacin. This consistent, enhanced penetration of topical moxifloxacin offers powerful advantages for ophthalmic therapy.
PMID:16257309 Robertson SM et al; Surv Ophthalmol 50 (Suppl 1): S32-45 (2005)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Moxifloxacin (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Approximately 52% or oral or intravenous dose is metabolized via glucuronide and sulphate conjugation. The cytochrome P450 system is not involved in metabolism. The sulphate conjugate accounts for 38% of the dose, and the glucuronide conjugate accounts for 14% of the dose.
Approximately 52% of an oral or intravenous dose of moxifloxacin is metabolized via glucuronide and sulfate conjugation. The cytochrome P450 system is not involved in moxifloxacin metabolism, and is not affected by moxifloxacin. The sulfate conjugate (M1) accounts for approximately 38% of the dose, and is eliminated primarily in the feces. Approximately 14% of an oral or intravenous dose is converted to a glucuronide conjugate (M2), which is excreted exclusively in the urine. Peak plasma concentrations of M2 are approximately 40% those of the parent drug, while plasma concentrations of M1 are generally less than 10% those of moxifloxacin.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) injection, solution AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (October 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=moxifloxacin
11.5-15.6 hours (single dose, oral)
The mean (+ or - SD) elimination half-life from plasma is 12 + or - 1.3 hours
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) injection, solution AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (October 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=moxifloxacin
The bactericidal action of moxifloxacin results from inhibition of the enzymes topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV. DNA gyrase is an essential enzyme that is involved in the replication, transcription and repair of bacterial DNA. Topoisomerase IV is an enzyme known to play a key role in the partitioning of the chromosomal DNA during bacterial cell division.
The fluoroquinolone antibiotic moxifloxacin has been associated with the acquired long QT syndrome and is used as a positive control in the evaluation of the QT-interval prolonging potential of new drugs. In common with other QT-prolonging agents, moxifloxacin is known to inhibit the hERG potassium K+ channel, but at present there is little mechanistic information available on this action. This study was conducted in order to characterise the inhibition of hERG current (I(hERG)) by moxifloxacin, and to determine the role in drug binding of the S6 aromatic amino-acid residues Tyr652 and Phe656. hERG currents were studied using whole-cell patch clamp (at room temperature and at 35-37 degrees C) in an HEK293 cell line stably expressing hERG channels. Moxifloxacin reversibly inhibited currents in a dose-dependent manner. We investigated the effects of different voltage commands to elicit hERG currents on moxifloxacin potency. Using a 'step-ramp' protocol, the IC50 was 65 uM at room temperature and 29 microM at 35 degrees C. When a ventricular action potential waveform was used to elicit currents, the IC50 was 114 microM. Block of hERG by moxifloxacin was found to be voltage-dependent, occurred rapidly and was independent of stimulation frequency. Mutagenesis of the S6 helix residue Phe656 to Ala failed to eliminate or reduce the moxifloxacin-mediated block whereas mutation of Tyr652 to Ala reduced moxifloxacin block by approximately 66%. Our data demonstrate that moxifloxacin blocks the hERG channel with a preference for the activated channel state. The Tyr652 but not Phe656 S6 residue is involved in moxifloxacin block of hERG, concordant with an interaction in the channel inner cavity.
PMID:16474415 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1760709 Alexandrou AJ et al; Br J Pharmacol 147 (8): 905-16 (2006)
The bactericidal action of moxifloxacin results from inhibition of the topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV required for bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair, and recombination. It appears that the C8-methoxy moiety contributes to enhanced activity and lower selection of resistant mutants of Gram-positive bacteria compared to the C8-H moiety. The presence of the bulky bicycloamine substituent at the C-7 position prevents active efflux, associated with the NorA or pmrA genes seen in certain Gram-positive bacteria.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) injection, solution AVELOX (moxifloxacin hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (October 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=moxifloxacin
Torsade de pointes (TdP) is increasingly recognized as a complication of drug therapy. The most common cause of drug-induced QT prolongation is inhibition of the rapidly activating component of the delayed potassium current (I(Kr)). Moxifloxacin, a widely used fluoroquinolone, is a weak I(Kr) inhibitor and has been associated with QT prolongation.
PMID:18651388 Sherazi S et al; Cardiol J 15 (1): 71-3 (2008)
Fluoroquinolones prolong the QT interval by blocking voltage-gated potassium channels, especially the rapid component of the delayed rectifier potassium current I(Kr), expressed by HERG (the human ether-a-go-go-related gene). According to the available case reports and clinical studies, moxifloxacin carries the greatest risk of QT prolongation from all available quinolones in clinical practice and it should be used with caution in patients with predisposing factors for Torsades de pointes (TdP).
PMID:22156660 Briasoulis A et al; Cardiology 120 (2): 103-10 (2011)