

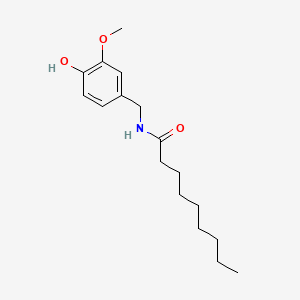

1. N-vanillylnonanamide
2. Vanillyl-n-nonylamide
3. Vanillylnonanamide
1. 2444-46-4
2. N-vanillylnonanamide
3. Pseudocapsaicin
4. Pelargonic Acid Vanillylamide
5. N-vanillylnonamide
6. N-vanillylpelargonamide
7. N-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)nonanamide
8. Nonanoic Acid Vanillylamide
9. N-nonanoyl Vanillylamide
10. Vanillyl-n-nonylamide
11. Vanillyl Pelargonic Amide
12. Pelargonyl Vanillylamide
13. Hydroxymethoxybenzyl Pelargonamide
14. Nonylic Acid Vanillylamide
15. Vanillyl N-nonoylamide
16. Nonanamide, N-vanillyl-
17. Nonivamide [inn]
18. Nonanamide, N-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-
19. Nonanoyl Vanillylamide
20. Desmethyldihydrocapsaicin
21. N-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]nonanamide
22. Fema No. 2787
23. N-vanillylnonanoamide
24. Hansaplast
25. Nsc 172795
26. Nonanoyl 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylamide
27. N-vanillyl Nonanamide
28. Nonylic Acid Vanillyamide
29. N-((4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl)nonanamide
30. N-((hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl)4-nonanamide
31. Nsc-172795
32. Chembl75124
33. Chebi:46936
34. S846b891or
35. Nonivamide (inn)
36. Ah-23491x
37. Mfcd00017286
38. Nonanamide, N-((4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl)-
39. Ncgc00016089-05
40. Nonylvanylamide
41. Dsstox_cid_14769
42. Dsstox_rid_79200
43. Dsstox_gsid_34769
44. Nonivamida
45. Nonivamidum
46. Nonivamidum [inn-latin]
47. Nonivamida [inn-spanish]
48. Cas-2444-46-4
49. Pava
50. 8-nordihydrocapsaicin
51. N-vanillyl-nonanamide
52. Nonanoylvanillyl Amide
53. Vanillyl N-nonylamide
54. Capsaicin (synthetic)
55. N-((4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl)-nonanamide
56. N-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-nonanamide
57. Einecs 219-484-1
58. Brn 2144300
59. Capscaisin
60. Unii-s846b891or
61. N-nonylvanylamide
62. Pava Spray
63. Hansaplast (tn)
64. Nonanoylvanilylamide
65. Nonylic Vanillamide
66. Synthetic Capsaicin
67. Nonoyl Vanillylamide
68. Psva
69. Nonylicacidvanillylamide
70. Spectrum_000311
71. Pelargonoyl Vanillylamide
72. Specplus_000799
73. N-pelargonylvanillylamide
74. Spectrum2_001091
75. Spectrum4_000916
76. Spectrum5_001853
77. Lopac-v-9130
78. N-vanillylnonanamide, 8ci
79. Nonivamide [mart.]
80. Nonivamide [who-dd]
81. Lopac0_001218
82. Schembl81939
83. Kbiogr_001412
84. Kbioss_000791
85. Mls002153373
86. Divk1c_006895
87. Spectrum2300192
88. Spbio_001162
89. N-pelargonic Acid Vanillylamide
90. Dtxsid1034769
91. Fema 2787
92. Kbio1_001839
93. Kbio2_000791
94. Kbio2_003359
95. Kbio2_005927
96. Hh 50
97. Hms2234e23
98. Hms3374k02
99. Hms3885c14
100. Pharmakon1600-01506172
101. Albb-025790
102. Zinc1697652
103. Tox21_110302
104. Tox21_301218
105. Bdbm50044767
106. Ccg-39764
107. Nsc172795
108. Nsc760391
109. S3935
110. Akos001719931
111. N-vanillylnonanamide, >=97%, Powder
112. Tox21_110302_1
113. Ac-4807
114. Db11324
115. Nsc-760391
116. 8-methyl-n-vanillyl-trans-b-nonenamide
117. N-vanillylnonanamide, Analytical Standard
118. Ncgc00016089-01
119. Ncgc00016089-02
120. Ncgc00016089-03
121. Ncgc00016089-04
122. Ncgc00016089-06
123. Ncgc00094463-01
124. Ncgc00094463-02
125. Ncgc00094463-03
126. Ncgc00094463-04
127. Ncgc00255553-01
128. As-13519
129. Hy-17568
130. Smr001230764
131. N-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)nonanamide #
132. Eu-0101218
133. Ft-0603609
134. Ft-0623446
135. M0900
136. Nonanamide, N-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)-
137. 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-n-(1-oxononyl)-benzamide
138. D08282
139. V 9130
140. V-3000
141. Ab00053157_06
142. Hydroxymethoxybenzyl Pelargonamide [inci]
143. N-((4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl)-nonanamid
144. Nonanamide, N-((4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)meth
145. 444n464
146. A817309
147. Nonivamide (constituent Of Capsicum) [dsc]
148. Q420228
149. Sr-01000076196
150. Sr-01000076196-1
151. N-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]nonanamide, 9ci
152. Z373586944
153. N-nonanoyl-4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl-amide [fhfi]
154. Nonivamide, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
155. N-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)nonanamide, N-vanillylpelargonamide, Nonanoic Acid Vanillylamide, Nonylvanylamide, Pelargonic Acid Vanillylamide
| Molecular Weight | 293.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H27NO3 |
| XLogP3 | 4.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 293.19909372 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 293.19909372 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 58.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 283 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Nonivamide is used as a topical analgesic and is also used as a flavoring ingredient,,.
Relieves minor aches and pains of muscles and joints,.
Limited information is available on pharmacokinetics and metabolism of nonivamide. For the closely related [DB06774] and other capsaicinoids, gastrointestinal absorption is rapid and almost entirely complete in studies of rats (oral dose of about 10 to 15 mg/kg of combined capsaicin and dihydrocapsaicin) with about 85% of the dose being absorbed within 3 hours. Both substances undergo first-pass metabolism in the liver and partly metabolized at the site of absorption.
About 7 minutes.
Nonivamide is a naturally occurring analog of [DB06774], isolated from peppers, described to produce effects similar to [DB06774]. It is an agonist of the VR1 (vanilloid/TRPV1 receptor). It serves as a transient agonist of these receptors, which are potentiated by pro-inflammatory drugs, a phenomenon that leads to thermal hyperalgesia, or increased heat sensation. Nonivamide has been shown to stimulate afferent neurons with about half the potency of [DB06774]. Agonism of the VR1 (TRPV1) (vanilloid) receptor by Nonivamide was demonstrated to induce the release of Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of human lung cells, producing ER stress and cell death [MSDS]. Nonivamide, like other capsaicinoids, acts on the vanilloid receptors located in the peripheral afferent nerve fibers, providing short-acting irritant and algesic properties. Applied dermally, these substances act by stimulating sensitive chemoreceptors of the skin and by reflex, hyperemia and a local elevation in temperature. After repetitive administration, capsaicinoids have been reported to lead to desensitization to nociceptive stimuli possibly by long-acting depletion of peptide neurotransmitters (substance P) from peripheral sensory neurons. Capsaicinoids can modulate muscle tone (in bladder, bronchus etc.). Intravenous injection of nonivamide to rats (10 g/kg) has been found to lead to bradycardia. The cardiovascular effects are partly explained by substance P release. Nonivamide given to rats subcutaneously (1 mg/kg) was found to cause body temperature decrease, vasodilatation, and increased salivation. Capsaicinoids have shown to illicit bronchospastic effects in guinea pigs. Capsaicin and its analogs were reported to increase barbiturate sleeping time in rats by interacting with hepatic metabolizing enzymes.

