
1. Corgard
2. Solgol
3. Sq 11725
4. Sq-11725
5. Sq11725
1. Corgard
2. 42200-33-9
3. Solgol
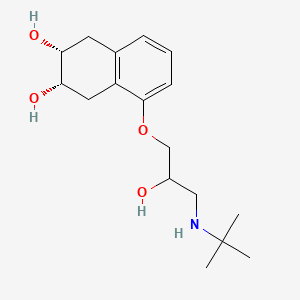
4. (2r,3s)-5-[3-(tert-butylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene-2,3-diol
5. Sq-11725
6. Anabet
7. (2r,3s)-5-(3-(tert-butylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene-2,3-diol
8. Nadolol [mi]
9. Nadolol [hsdb]
10. Nadolol [inn]
11. Nadolol [jan]
12. Nadolol [usan]
13. Nadolol [vandf]
14. Nadolol [mart.]
15. Nadolol [who-dd]
16. Corzide Component Nadolol
17. Chembl649
18. Nadolol [orange Book]
19. Nsc-758430
20. Nadolol Component Of Corzide
21. Nadolol [usp Monograph]
22. Mls000028580
23. Fen504330v
24. Smr000058975
25. Dsstox_cid_3342
26. Dsstox_rid_76983
27. Dsstox_gsid_23342
28. 1403-22-1
29. 1-(tert-butylamino)-3-((5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-cis-6,7-dihydroxy-1-naphthyl)oxy)-2-propanol
30. Cis-5-(3-((1,1-dimethylethyl)amino)-2-hydroxy-propoxy)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2,3-naphthalenediol
31. Sr-01000000251
32. 2,3-naphthalenediol, 5-(3-((1,1-dimethylethyl)amino)-2-hydroxypropoxy)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-, Cis-
33. Sq11725
34. Unii-fen504330v
35. Candidin B
36. Ncgc00016851-01
37. 220045-89-6
38. Prestwick_108
39. Nadolol [ep]
40. Nadolol [usp]
41. Cas-42200-33-9
42. Nadolol [usp-rs]
43. Spectrum_001643
44. Opera_id_1099
45. Prestwick0_000818
46. Prestwick1_000818
47. Prestwick2_000818
48. Spectrum2_001546
49. Spectrum3_001586
50. Spectrum4_000193
51. Spectrum5_001255
52. Schembl4177
53. Nadolol, Analytical Standard
54. Bspbio_003152
55. Gtpl554
56. Kbiogr_000765
57. Kbioss_002123
58. Cid_39147
59. Mls001148087
60. Mls002548875
61. Divk1c_000427
62. Nadolol (jp17/usp/inn)
63. Nadolol [ep Impurity]
64. Spectrum1503260
65. Spbio_001392
66. Spbio_002636
67. Nadolol [ep Monograph]
68. Inv102
69. Nadolol 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
70. Bdbm25766
71. Hms501f09
72. Kbio1_000427
73. Kbio2_002123
74. Kbio2_004691
75. Kbio2_007259
76. Kbio3_002652
77. Inv-102
78. Ninds_000427
79. Hms1570d17
80. Hms1922o05
81. Hms2093a15
82. Hms2233e12
83. Hms3259c07
84. Hms3714d17
85. Pharmakon1600-01503260
86. Tox21_110646
87. Ccg-39324
88. Nsc758430
89. S5023
90. Akos015895037
91. Tox21_110646_1
92. Db01203
93. Nc00464
94. Idi1_000427
95. Smp1_000203
96. Ncgc00021623-03
97. Ncgc00021623-05
98. Ncgc00089811-02
99. (2r,3s)-5-({3-[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-2-hydroxypropyl}oxy)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene-2,3-diol
100. Sbi-0051806.p002
101. En300-50860
102. Vu0239635-6
103. A12516
104. D00432
105. Ab00052338_13
106. 200n339
107. Q424952
108. Sr-01000000251-2
109. Sr-01000000251-3
110. Brd-a87606379-001-03-4
111. Brd-a87606379-001-13-3
112. Nadolol, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
113. Nadolol, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 309.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H27NO4 |
| XLogP3 | 0.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 309.19400834 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 309.19400834 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 82 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 344 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Corgard |
| PubMed Health | Nadolol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | CORGARD (nadolol) is a synthetic nonselective beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agent designated chemically as 1-(tert-butylamino)-3-[(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-cis-6,7-dihydroxy-1-naphthyl)oxy]-2-propanol. Structural formula:C17H27NO4MW 309... |
| Active Ingredient | Nadolol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 80mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | King Pharms |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Nadolol |
| PubMed Health | Nadolol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Nadolol is a synthetic nonselective beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agent designated chemically as 1-(tert-butylamino)-3-[(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-cis-6,7-dihydroxy-1-naphthyl)oxy]-2-propanol. Its structural formula is:Nadolol is a white crystalline pow... |
| Active Ingredient | Nadolol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 80mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sandoz; Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Mylan |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Corgard |
| PubMed Health | Nadolol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | CORGARD (nadolol) is a synthetic nonselective beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agent designated chemically as 1-(tert-butylamino)-3-[(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-cis-6,7-dihydroxy-1-naphthyl)oxy]-2-propanol. Structural formula:C17H27NO4MW 309... |
| Active Ingredient | Nadolol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 80mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | King Pharms |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Nadolol |
| PubMed Health | Nadolol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Nadolol is a synthetic nonselective beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agent designated chemically as 1-(tert-butylamino)-3-[(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-cis-6,7-dihydroxy-1-naphthyl)oxy]-2-propanol. Its structural formula is:Nadolol is a white crystalline pow... |
| Active Ingredient | Nadolol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 80mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sandoz; Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Mylan |
Adrenergic beta-Antagonists; Anti-Arrhythmia Agents; Antihypertensive Agents; Sympatholytics
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
... Nadolol /is/ indicated in the treatment of hypertension when used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive medication. ... /Included in US product labeling/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 23rd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2003. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 550
Nadolol has been used in a limited number of patients with atrial flutter or fibrillation for the management of frequent ventricular premature contractions, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, and sinus tachycardia and to decrease heart rate. Nadolol has been used with some success in a limited number of patients for the prophylaxis of common migraine headache.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1771
/Exptl/ This investigation reports pilot data on two points originally raised in the earliest reports of the efficacy of beta-blockers in akathisia: their potential utility in the akathisia of idiopathic Parkinson's disease and the possibility of determining a central vs a peripheral site of action by comparing the time course of the effects of lipophilic and hydrophilic agents. Akathisia improved in 4 patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease after low dose propranolol treatment. Six patients with neuroleptic induced akathisia were treated with the hydrophilic beta-blocker nadolol. Effects on akathisia occurred, but evolved much more slowly than after treatment with lipophilic agents, such as propranolol and metoprolol, thus suggesting a central site of action.
Adler LA et al; Psychopharmacol Bul 27 (2): 107-11 (1991)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for NADOLOL (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Nadolol is contraindicated in patients with bronchial asthma, sinus bradycardia and heart block greater than first degree, cardiogenic shock, or overt cardiac failure.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1773
Nadolol should be used with caution in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, and it may be necessary to reduce the dosage of the drug in those with renal impairment.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1773
Signs of hyperthyroidism (eg, tachycardia) may be masked by nadolol, and patients having or suspected of developing thyrotoxicosis should be monitored closely because abrupt withdrawal of beta-adrenergic blockade might precipitate thyroid storm. It is recommended that nadolol be used with caution in patients with diabetes mellitus (especially those with labile diabetes or those prone to hypoglycemia) since the drug may also mask the signs and symptoms associated with acute hypoglycemia (eg, tachycardia and blood pressure changes but not sweating), the drug should be used with caution in patients with diabetes mellitus receiving hypoglycemic agents, especially in those with labile disease or those prone to hypoglycemia. Beta-adrenergic blocking agents may also impair glucose tolerance; delay the rate of recovery of blood glucose concentration following drug-induced hypoglycemia; alter the hemodynamic response to hypoglycemia, possibly resulting in an exaggerated hypertensive response; and possibly impair peripheral circulation. If nadolol is used in diabetic patients receiving hypoglycemic agents, it may be necessary to adjust the dosage of the hypoglycemic agent. In one study in nondiabetic patients, nadolol therapy did not produce changes in glucose tolerance.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1773
Nadolol is distributed into milk. Because of the potential for adverse reactions to nadolol in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the woman.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1773
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for NADOLOL (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Nadolol is indicated to treat angina pectoris and hypertension. Another product formulated with [bendroflumethiazide] is indicated to treat hypertension.
Nadolol is a nonselective beta adrenal receptor blocker that is used to lower blood pressure. It has a long duration of action as it is usually taken once daily and a wide therapeutic index as patients start at doses of 40mg daily but may be increased to doses as high as 240mg daily. Patients taking nadolol should not aburptly stop taking it as this may lead to exacerbation of ischemic heart disease.
Adrenergic beta-Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate beta-adrenergic receptors thereby blocking the actions of beta-adrenergic agonists. Adrenergic beta-antagonists are used for treatment of hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, angina pectoris, glaucoma, migraine headaches, and anxiety. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic beta-Antagonists.)
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)
Sympatholytics
Drugs that inhibit the actions of the sympathetic nervous system by any mechanism. The most common of these are the ADRENERGIC ANTAGONISTS and drugs that deplete norepinephrine or reduce the release of transmitters from adrenergic postganglionic terminals (see ADRENERGIC AGENTS). Drugs that act in the central nervous system to reduce sympathetic activity (e.g., centrally acting alpha-2 adrenergic agonists, see ADRENERGIC ALPHA-AGONISTS) are included here. (See all compounds classified as Sympatholytics.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C07 - Beta blocking agents
C07A - Beta blocking agents
C07AA - Beta blocking agents, non-selective
C07AA12 - Nadolol
Absorption
Oral doses of nadolol are approximately 30% absorbed. In healthy subjects, nadolol has a Tmax of 2.7h with a Cmax or 6915ng/mL following a 60mg oral dose and 13227ng/mL after a 120mg oral dose. The AUC following a 60mg oral dose was 1021ng\*h/mL and following a 120mg oral dose was 1913382ng\*h/mL.
Route of Elimination
Nadolol is not metabolized in the liver and excreted mainly in the urine. In healthy subjects, following intravenous dosing, 60% of a dose is eliminated in the urine and 15% in the feces after 72 hours. The remainder of the dose is expected to be eliminated in the feces afterwards.
Volume of Distribution
In healthy subjects, the volume of distribution of nadolol is 147-157L.
Clearance
In healthy subjects, the total body clearance of nadolol is 219-250mL/min and the renal clearance is 131-150mL/min.
Following oral administration of nadolol, absorption is variable and averages about 30-40% of a dose. The presence of food in the GI tract does not affect the rate or extent of absorption. After oral administration of 2 mg of nadolol (in a capsule), peak plasma concentrations usually occur in 2-4 hours. In one study in hypertensive adults who received 80 mg, 160 mg, or 320 mg of nadolol daily, mean steady state plasma concentrations were 25.5-35.5 ng/ml, 51.7-74.1 ng/ml, and 154-191.4 ng/ml, respectively. With doses of 40-320 mg daily, the duration of nadolol's antihypertensive and antianginal effects is at least 24 hours.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1774
Following oral administration of 2 mg of radiolabeled nadolol (in a capsule) in one study in patients with normal renal function, about 24.6% and 76.9% of the radioactivity was recovered in urine and feces, respectively, in 4 days.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1774
Nadolol is widely distributed into body tissues. In dogs, minimal amounts of nadolol were detected in the brain and, in rats, the drug crosses the placenta. The drug is distributed into bile. Nadolol is distributed into milk. About 30% of nadolol in serum is bound to plasma proteins.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1774
The beta-adrenoceptor antagonists ... are adequately absorbed, and some like atenolol, sotalol and nadolol which are poorly lipid-soluble are excreted unchanged in the urine, accumulating in renal failure but cleared normally in liver disease. The more lipid-soluble drugs are subject to variable metabolism in the liver, which may be influenced by age, phenotype, environment, disease and other drugs, leading to more variable plasma concentrations. Their clearance is reduced in liver disease but is generally unchanged in renal dysfunction. All the beta-adrenoceptor antagonists reduce cardiac output and this may reduce hepatic clearance of highly extracted drugs. In addition, the metabolised drugs compete with other drugs for enzymatic biotransformation and the potential for interaction is great, but because of the high therapeutic index of beta-adrenoceptor antagonists, any unexpected clinical effects are more likely to be due to changes in the kinetics of the other drug.
PMID:2886244 Riddell JG et al; Clin Pharmacokinet 12 (5): 305-20 (1987)
Nadolol 20 mg was administered orally as a single-blind, single dose to nine patients about to undergo cataract extraction. Intraocular pressures fell by a mean of 24% 3 hr after administration. During the operation, aqueous humor and serum samples were taken for measurement of nadolol concentrations. Aqueous nadolol concentrations ranged from 3.8 to 13.4 ng/mL, and correlated with the serum drug concentrations (r=0.84). The fall in intraocular pressure did not correlate with either the aqueous humor or plasma concentrations of nadolol.
PMID:3203065 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1386505 Tiong T et al; Br J Clin Pharmacol 26 (1): 92-5 (1988)
Nadolol is not metabolized by the liver in humans.
Nadolol is not metabolized.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1774
The half life of nadolol is 20 to 24 hours.
The elimination half-life of nadolol is 18 hr. /From table/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 525
In patients with normal renal function, the plasma half-life of nadolol is 10-24 hr and, with once daily doses, steady state is attained in 6-9 days. In patients with renal impairment, plasma half-life is increased.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1774
Although nadolol is described as a non selective beta blocker, it does not interact with beta 3 adrenal receptors. Antagonism of beta-1 and beta-2 adrenoceptors in the heart inhibits cyclic AMP and its signalling pathway, decreasing the strength and speed of contractions as well as the speed of relaxation and conduction. Antagonism of beta-2 adrenoceptors in the smooth muscle cells of the vasculature inhibits their relaxation, leading to an increase in peripheral vascular resistance and reducing the risk of severe hypotension. The increase in peripheral vascular resistance may contribute to the decrease in insulin sensitivity associated with nadolol use. Antagonism of beta-1 adrenoceptors in the juxtaglomerular apparatus of the kidney inhibits the release of renin, and therefore angiotensin II mediated vasoconstriction, aldosterone mediated water retention, and the release of epinephrine. Antagonism of beta-2 adrenoceptors in the liver and skeletal muscle inhibits glycogenolysis, in the lungs prevents bronchodilation, and in the pancrease inhibits insulin release.
Nadolol inhibits response to adrenergic stimuli by competitively blocking beta1-adrenergic receptors within the myocardium and beta2-adrenergic receptors within bronchial and vascular smooth muscle.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1774
In the management of angina pectoris, the mechanism of action of nadolol is thought to be blockade of catecholamine induced increases in heart rate, velocity and extent of myocardial contraction, and blood pressure which result in a net decrease in myocardial oxygen consumption. However, nadolol may increase oxygen requirements by increasing left ventricular fiber length and end diastolic pressure, particularly in patients with heart failure.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1774
Through its beta-adrenergic blocking action, nadolol increases airway resistance (especially in asthmatic patients) and inhibits the release of free fatty acids and insulin by adrenergic stimulation.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1774
It has been postulated that beta-adrenergic blocking agents reduce blood pressure by blocking peripheral (especially cardiac) adrenergic receptors (decreasing cardiac output), by decreasing sympathetic outflow from the CNS, and/or by suppressing renin release. Nadolol decreases blood pressure in both supine and standing positions.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1774