


1. Wck 4873
1. Nafithromycin [inn]
2. 75f74y2r70
3. 1691240-78-4
4. Wck 4873
5. Chembl4297519
6. Unii-75f74y2r70
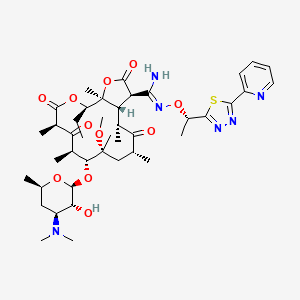
7. (3r,31z,3as,4r,6r,8r,9r,10r,12r,15r,15as)-15-ethyl-8-methoxy-4,6,8,10,12,15a-hexamethyl-2,5,11,13-tetraoxo-n'-((1s)-1-(5-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)ethoxy)-9-((3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-.beta.-d-xylohexopyranosyl)oxy)tetradecahydro-2h-furo(2,3-c)oxacyclotetradecine-3-carboximidamide
8. (3r,31z,3as,4r,6r,8r,9r,10r,12r,15r,15as)-15-ethyl-8-methoxy-4,6,8,10,12,15a-hexamethyl-2,5,11,13-tetraoxo-n'-((1s)-1-(5-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)ethoxy)-9-((3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-beta-d-xylohexopyranosyl)oxy)tetradecahydro-2
9. 2h-furo(2,3-c)oxacyclotetradecin-3-carboximidamide, 15-ethyltetradecahydro-8-methoxy-4,6,8,10,12,15a-hexamethyl-2,5,11,13-tetraoxo-n'-((1s)-1-(5-(2-pyridinyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)ethoxy)-9-((3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-.beta.-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)-, (c(z),3r,3as,4r,6r,8r,9r,10r,12r,15r,15as)-
10. 2h-furo(2,3-c)oxacyclotetradecin-3-carboximidamide, 15-ethyltetradecahydro-8-methoxy-4,6,8,10,12,15a-hexamethyl-2,5,11,13-tetraoxo-n'-((1s)-1-(5-(2-pyridinyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)ethoxy)-9-((3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-beta-d-xylo-hexopyrano
| Molecular Weight | 859.0 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C42H62N6O11S |
| XLogP3 | 4.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 17 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 858.41972799 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 858.41972799 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 252 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 60 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1580 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 15 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
Compounds which inhibit the synthesis of proteins. They are usually ANTI-BACTERIAL AGENTS or toxins. Mechanism of the action of inhibition includes the interruption of peptide-chain elongation, the blocking the A site of ribosomes, the misreading of the genetic code or the prevention of the attachment of oligosaccharide side chains to glycoproteins. (See all compounds classified as Protein Synthesis Inhibitors.)
