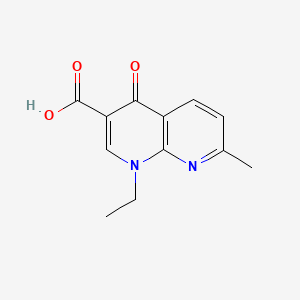

1. Acid, Nalidixic
2. Anhydrous, Nalidixate Sodium
3. Nalidixate Sodium
4. Nalidixate Sodium Anhydrous
5. Nalidixin
6. Nevigramon
7. Sodium Anhydrous, Nalidixate
8. Sodium Nalidixic Acid, Anhydrous
9. Sodium Nalidixic Acid, Monohydrate
10. Sodium, Nalidixate
1. 389-08-2
2. Nalidixate
3. Nalidixin
4. Nevigramon
5. Uronidix
6. Neggram
7. Innoxalon
8. Nalidixan
9. Nalitucsan
10. Sicmylon
11. Unaserus
12. Nalidic Acid
13. Nalidixinic Acid
14. 1-ethyl-7-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
15. Wintomylon
16. Dixiben
17. Dixinal
18. Jicsron
19. Nalurin
20. Naxuril
21. Nogram
22. Urisal
23. Cybis
24. Nalix
25. Uroman
26. Nalidicron
27. Betaxina
28. Kusnarin
29. Narigix
30. Nicelate
31. Specifen
32. Specifin
33. Uralgin
34. Uriclar
35. Urodixin
36. Negram
37. Poleon
38. Uriben
39. Uroneg
40. Uropan
41. Acide Nalidixique
42. Eucistin
43. Acide Nalidixico
44. Acido Nalidixico
45. Nsc-82174
46. Acidum Nalidixicum
47. 1-ethyl-1,4-dihydro-7-methyl-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
48. Win 18,320
49. Nalidixane
50. 1-ethyl-7-methyl-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
51. 3-carboxy-1-ethyl-7-methyl-1,8-naphthyridin-4-one
52. Nci-c56199
53. 1,4-dihydro-1-ethyl-7-methyl-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
54. 1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid, 1-ethyl-1,4-dihydro-7-methyl-4-oxo-
55. 3-carboxy-1-ethyl-7-methyl-1,8-naphthidin-4-one
56. Mfcd00006884
57. 1-ethyl-7-methyl-1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridin-4-one-3-carboxylic Acid
58. 1-aethyl-7-methyl-1,8-naphthyridin-4-on-3-karbonsaeure
59. Nalidixic Acid (neggram)
60. Win-18320
61. Mls000028504
62. 3b91hwa56m
63. Acide 1-etil-7-metil-1,8-naftiridin-4-one-3-carbossilico
64. Win 18320
65. Chebi:100147
66. 1-ethyl-7-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-[1,8]naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
67. Nsc82174
68. Ncgc00018181-08
69. Smr000058264
70. Wintron
71. Dsstox_cid_912
72. Acido Nalidissico
73. Nalidixic Acid 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
74. Dsstox_rid_75859
75. Dsstox_gsid_20912
76. Acido Nalidissico [dcit]
77. Acide Nalidixico [italian]
78. Acide Nalidixique [french]
79. Nalidixic
80. Acide Nalidixique [inn-french]
81. Acido Nalidixico [inn-spanish]
82. Acidum Nalidixicum [inn-latin]
83. Cas-389-08-2
84. Neggram (tn)
85. Ccris 2365
86. Hsdb 3241
87. Einecs 206-864-7
88. Brn 0750515
89. Unii-3b91hwa56m
90. Innoxalomn
91. Eucisten
92. Nalidixic-acid
93. Sr-01000003086
94. 1-aethyl-7-methyl-1,8-naphthyridin-4-on-3-karbonsaeure [german]
95. Acide 1-etil-7-metil-1,8-naftiridin-4-one-3-carbossilico [italian]
96. Nalidixicacid
97. Win 183203
98. Chembl5
99. Spectrum_000918
100. Nalidixic Acid [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
101. Maybridge1_007101
102. Opera_id_1064
103. Prestwick0_000187
104. Prestwick1_000187
105. Prestwick2_000187
106. Prestwick3_000187
107. Spectrum2_001360
108. Spectrum3_000075
109. Spectrum4_000817
110. Spectrum5_001540
111. 1,4-dihydro-1-ethyl-7-methyl-1,8-naphthyridin-4-one-3-carboxylic Acid
112. Nalidixic Acid, >=98%
113. Upcmld-dp129
114. N-1200
115. Nalidixic Acid [mi]
116. Nciopen2_004342
117. Lopac0_000837
118. Oprea1_010545
119. Schembl21736
120. Bspbio_000113
121. Bspbio_001889
122. Kbiogr_001333
123. Kbioss_001398
124. Nalidixic Acid [inn]
125. Nalidixic Acid [jan]
126. 5-25-07-00384 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
127. Mls001148578
128. Mls002303041
129. Mls004820190
130. Mls006011875
131. 1-ethyl-7-methyl-4-oxo-1
132. Bidd:gt0529
133. Divk1c_000058
134. Nalidixic Acid [hsdb]
135. Nalidixic Acid [usan]
136. Spectrum1500756
137. Spbio_001579
138. Spbio_002034
139. Nalidixic Acid [vandf]
140. Bpbio1_000125
141. Nalidixic Acid [mart.]
142. Dtxsid3020912
143. Nalidixic Acid [who-dd]
144. Upcmld-dp129:001
145. Bdbm21691
146. Hms500c20
147. Hms561k17
148. Kbio1_000058
149. Kbio2_001398
150. Kbio2_003966
151. Kbio2_006534
152. Kbio3_001109
153. Zinc57421
154. Ninds_000058
155. Hms1921g10
156. Hms2092k04
157. Hms2232h24
158. Hms3259o13
159. Hms3374g11
160. Hms3656k05
161. Pharmakon1600-01500756
162. Nalidixic Acid (jp17/usp/inn)
163. Nalidixic Acid, Analytical Standard
164. Albb-021275
165. Hy-b0398
166. Tox21_110835
167. Tox21_201477
168. Tox21_302754
169. Bbl012279
170. Ccg-39298
171. Nalidixic Acid [ep Impurity]
172. Nalidixic Acid [orange Book]
173. Nsc757432
174. Stk735579
175. Nalidixic Acid [usp Impurity]
176. 1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylicacid, 1-ethyl-1,4-dihydro-7-methyl-4-oxo-
177. 1-ethyl-1,4-dihydro-7-methyl-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxilic Acid
178. Akos000120074
179. Tox21_110835_1
180. Db00779
181. Nc00494
182. Nsc-757432
183. Sdccgsbi-0050814.p004
184. Idi1_000058
185. Ncgc00018181-01
186. Ncgc00018181-02
187. Ncgc00018181-03
188. Ncgc00018181-04
189. Ncgc00018181-05
190. Ncgc00018181-06
191. Ncgc00018181-07
192. Ncgc00018181-09
193. Ncgc00018181-10
194. Ncgc00018181-12
195. Ncgc00018181-13
196. Ncgc00021730-03
197. Ncgc00021730-04
198. Ncgc00021730-05
199. Ncgc00021730-06
200. Ncgc00021730-07
201. Ncgc00256581-01
202. Ncgc00259028-01
203. As-13289
204. Nci60_041807
205. Smr004703506
206. Wln: T66 Bn Ev Jnj B2 Dvq I1
207. Sbi-0050814.p003
208. Db-049349
209. Nalidixic Acid 1000 Microg/ml In Methanol
210. 1, 1-ethyl-1,4-dihydro-7-methyl-4-oxo-
211. Bb 0242389
212. Ft-0603390
213. N0490
214. S2328
215. Sw219624-1
216. 1-ethyl-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxilic Acid
217. 1-ethyl-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
218. Vu0239598-6
219. C05079
220. D00183
221. D91720
222. Nalidixic Acid 1000 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
223. Nalidixic Acid, Meets Usp Testing Specifications
224. 389n082
225. Q281082
226. Sr-01000003086-4
227. Sr-01000003086-6
228. Brd-k47886988-323-03-0
229. Nalidixic Acid, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
230. Sr-01000003086-10
231. F0850-6751
232. Z256708444
233. 1-ethyl-7-methyl-1,8-naphthyridin-4-one-3-carboxylic Acid
234. 1-ethyl-7-methyl-4-oxo-[1,8]naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
235. Nalidixic Acid, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
236. Nalidixic Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
237. 1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid,1-ethyl-1,4-dihydro-7-methyl-4-oxo-
238. 1-ethyl-7-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-[1,8]naph Thyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
239. N-benzyl-4-[(5-cyclobutyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)methyl]-n-ethyl-3-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,4-benzoxazine-6-sulfonamide
| Molecular Weight | 232.23 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H12N2O3 |
| XLogP3 | 1.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 232.08479225 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 232.08479225 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 70.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 378 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anti-Infective Agents, Quinolone /SRP: Antibacterial/
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
IN US, NALIDIXIC ACID IS APPROVED ONLY FOR TREATMENT OF URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS CAUSED BY SUSCEPTIBLE MICROORGANISMS. EFFECTIVENESS AGAINST INDOLE-POSITIVE PROTEUS IS ESP IMPORTANT. APPARENT CURES...IN 30-50% OF UNCOMPLICATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1007
...BRUCELLOSIS HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY MANAGED WITH ORAL NALIDIXIC ACID. DRUG HAS BEEN GIVEN IV TO TREAT GRAM-NEGATIVE SEPTICEMIAS.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1008
...BACTERICIDAL TO MOST OF COMMON GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA THAT CAUSE URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS. ...99% OF STRAINS OF E COLI, 98% OF PROTEUS MIRABILIS & 75-97% OF OTHER PROTEUS SPECIES, 92% OF KLEBSIELLA-ENTEROBACTER, & 80% OF OTHER COLIFORM BACTERIA ARE SENSITIVE TO DRUG. ... SOME STRAINS OF SALMONELLA & SHIGELLA...SENSITIVE.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1007
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for NALIDIXIC ACID (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
BECAUSE...MAY ACCUMULATE IN PT WITH RENAL OR HEPATIC INSUFFICIENCY, IT SHOULD BE USED VERY CAUTIOUSLY IN THESE PT, ESP IF NEUROLOGIC DAMAGE IS PRESENT. ... CAUTION IS INDICATED IF THIS DRUG IS USED DURING PREGNANCY, ALTHOUGH SOME... HAVE TAKEN IT DURING 2ND & 3RD TRIMESTERS WITHOUT ADVERSELY AFFECTING MOTHER OR FETUS.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 793
BY ORAL ROUTE IT IS DIFFICULT TO ACHIEVE EFFECTIVE PLASMA LEVELS. FUTHERMORE, BINDING TO PLASMA PROTEIN INHIBITS ACTIVITY. ... 4% THAT PASSES INTO BOWEL IS INSUFFICIENT TO BE EFFICACIOUS IN TREATMENT OF INTESTINAL SHIGELLOSIS...
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1152
PSEUDOMONAS SPECIES ARE RESISTANT. ... ACQUIRED RESISTANCE TO DRUG OCCURS, BUT IT DOES NOT SEEM TO BE TRANSFERABLE.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1007
DETERMINATION OF URINARY LEVELS OF 17-KETOSTEROIDS & 17-KETOGENIC STEROIDS MAY BE FALSELY ELEVATED WHEN NALIDIXIC ACID HAS BEEN PRESCRIBED.
Miller, R. R., and D. J. Greenblatt. Handbook of Drug Therapy. New York: Elsevier North Holland, 1979., p. 182
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for NALIDIXIC ACID (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of urinary tract infections caused by susceptible gram-negative microorganisms, including the majority of E. Coli, Enterobacter species, Klebsiella species, and Proteus species.
FDA Label
Nalidixic acid is a quinolone antibacterial agent for oral administration. Nalidixic acid has marked antibacterial activity against gram-negative bacteria including Enterobacter species, Escherichia coli, Morganella Morganii; Proteus Mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, and Providencia rettgeri. Pseudomonas species are generally resistant to the drug. Nalidixic acid is bactericidal and is effective over the entire urinary pH range. Conventional chromosomal resistance to nalidixic acid taken in full dosage has been reported to emerge in approximately 2 to 14 percent of patients during treatment; however, bacterial resistance to nalidixic acid has not been shown to be transferable via R factor.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
Topoisomerase II Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit the activity of DNA TOPOISOMERASE II. Included in this category are a variety of ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS which target the eukaryotic form of topoisomerase II and ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS which target the prokaryotic form of topoisomerase II. (See all compounds classified as Topoisomerase II Inhibitors.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01M - Quinolone antibacterials
J01MB - Other quinolones
J01MB02 - Nalidixic acid
Absorption
Following oral administration, nalidixic acid is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Bioavailability is approximately 96%. Absorption may be delayed if taken with antacids.
Route of Elimination
Following oral administration, NegGram is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, partially metabolized in the liver, and rapidly excreted through the kidneys. Approximately four percent of NegGram is excreted in the feces.
ABSORPTION & ELIMINATION RATES OF NALIDIXIC ACID WERE SHOWN TO BE LOW IN NEWBORN CHILDREN COMPARED WITH ADULTS, & ADULT VALUES WERE NOT OBTAINED UNTIL ABOUT THIRD YR OF LIFE. RELATIVE DISTRIBUTION VOL, HOWEVER, WERE SIMILAR IN BOTH AGE GROUPS.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 437
IN RATS & MICE ORAL DOSES ARE RAPIDLY ABSORBED WITH PEAK BLOOD CONCN ABOUT 1 HR LATER. ...ELIMINATION IS VIA KIDNEYS, PEAKING @ ABOUT 6TH HR. 80% OF ADMIN DOSE IS ELIMINATED IN 1ST 8 HR. IN DOGS HIGHLY EFFECTIVE CONCN APPEAR IN URINE WITHIN 2-3 HR AFTER ORAL ADMIN.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 375
ABSORPTION EFFICIENCY & RATE OF ELIMINATION OF...NALIDIXIC ACID...DECR IN PT WITH SHIGELLOSIS. POOR ABSORPTION WAS GENERALLY OBSERVED IN YOUNGER PT WITH MARKED DIARRHEA BUT THERE WAS NO READY EXPLANATION FOR DELAYED EXCRETION.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 169
Rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract; bioavailability is approximately 96%. Absorption may be delayed if taken with antacids.
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 2092
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for NALIDIXIC ACID (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hepatic. 30% of administered dose is metabolized to the active metabolite, hydroxynalidixic acid. Rapid conjugation of parent drug and active metabolite to inactive metabolites. Metabolism may vary widely among individuals. In the urine, hydroxynalidixic acid represents 80 to 85% of the antibacterial activity.
WHEN NALIDIXIC ACID...IS INGESTED BY MAN, IT IS PARTLY EXCRETED AS FREE... /ACID/ BUT MUCH BIGGER PROPORTION IS EXCRETED AS MONOGLUCURONIDE...& CONSIDERABLE FRACTION AS 7-HYDROXYMETHYL METABOLITE...TOGETHER WITH SMALLER AMT OF LATTER IN CONJUGATED FORM. 3,7-DICARBOXYLIC ACID...IS MINOR METABOLITE.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 205
Nalidixic acid is partially metabolized in the liver to hydroxynalidixic acid and the glucuronic acid conjugates of nalidixic acid and hydroxynalidixic acid. The drug is also partially metabolized to the dicarboxylic acid derivative; there is some evidence suggesting that this metabolite is formed in the kidney.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 97. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1997 (Plus Supplements)., p. 593
1.1 to 2.5 hours in healthy adult patients, and up to 21 hours in patients with impaired renal function.
APPROX 96% OF ORALLY ADMIN...IS ABSORBED. PLASMA CONCN OF 20-50 UG/ML MAY BE ACHIEVED, BUT ACID IS 93-97% BOUND TO PLASMA PROTEINS. IN BODY SOME... CONVERTED TO ACTIVE HYDROXYNALIDIXIC ACID, & BOTH ARE EXCRETED INTO URINE. MOST...IS CONJUGATED IN LIVER. PLASMA T/2 IS...8 HR...MAY BE...21 HR IN...RENAL FAILURE.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1007
Evidence exists for Nalidixic acid that its active metabolite, hydroxynalidixic acid, binds strongly, but reversibly, to DNA, interfering with synthesis of RNA and, consequently, with protein synthesis.
IT APPEARS TO ACT BY INHIBITING DNA SYNTH.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1007