


1. Ahz-zinc
2. Beta-alanyl-l-histidinato Zinc
3. Z 103
4. Z-103
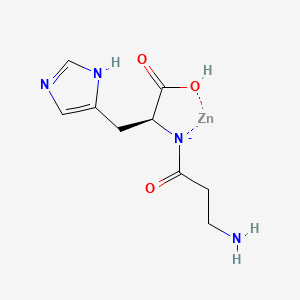
5. Zinc Carnosine
6. Zinc L-carnosine
7. Zinc L-carnosine Complex
8. Zinc N-(3-aminopropionyl)histidine
1. 107667-60-7
2. Zinc L-carnosine
3. Beta-alanyl-l-histidinato Zinc
4. Ncgc00181764-01
5. Dsstox_cid_28541
6. Dsstox_rid_82813
7. Dsstox_gsid_48615
8. Chembl3184454
9. Dtxsid7048615
10. Tox21_112950
11. Akos037515832
12. Db09221
13. Cas-107667-60-7
14. E76520
15. 667p607
| Molecular Weight | 290.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H13N4O3Zn- |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 289.027907 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 289.027907 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 110 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | -1 |
| Complexity | 265 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Peptic ulcer disease, dyspepsia.
Used to treat/manage peptic ulcer disease or irritation of the gastrointestinal tract by promoting tissue healing by the elimination of free radicals.
Anti-Ulcer Agents
Various agents with different action mechanisms used to treat or ameliorate PEPTIC ULCER or irritation of the gastrointestinal tract. This has included ANTIBIOTICS to treat HELICOBACTER INFECTIONS; HISTAMINE H2 ANTAGONISTS to reduce GASTRIC ACID secretion; and ANTACIDS for symptomatic relief. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Ulcer Agents.)
Absorption
Intestinal absorption of L-CAZ was studied in rats by Sano et al. using 14C- and 65Zn-labeled compounds. They suggested that L-CAZ dissociates to its components, L-carnosine and zinc, during intestinal absorption.
Route of Elimination
Intestinal absorption of the drug was examined using 14C- and 65Zn-labeled compounds. Polaprezinc metabolizes into its components, L-carnosine and zinc, during intestinal absorption. It was found that the excretion rates after one administration using 14C-labeled L-CAZ to rats were 4.1% in urine, 13.3% in feces, and 38.8% in exhalation. The study using 65Zn-labeled Paleprozinc were 0.3% in urine and 85.0% in the feces. The absorption rate of zinc is estimated to be approximately 11%.
Excretion rates of polaprezinc after a single administration using 14C-labeled drug to rats are 4.1% in urine, 13.3% in feces, and 38.8% in exhalation, and those using 65Zn-labeled L-CAZ are 0.3% in urine and 85.0% in feces. The absorption rate of zinc is estimated to be about 11%.
The half-life of polaprezinc has been studied in rats and found to be approximately 2 hours.
Polaprezinc increases the expression of various antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD-1), SOD-2, heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), glutathione S-transferase (GST), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-px), peroxidredoxin-1 (PRDX1; PRXI) and PRXD5 (PRXV). This process occurs in the gastric mucosa, defending mucosal cells against reactive oxygen species. This drug inhibits the activity of the transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kB) and decreases the expression of various inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin (IL) 1beta, IL-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-a). Polaprezinc also promotes the expression of numerous growth factors, including as platelet-derived growth factor-B (PDGF-B), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and nerve growth factor (NGF), in addition to various heat shock proteins (HSPs), including HSP90, HSP70, HSP60, HSP47, HSP27, and HSP10. This process promotes tissue growth and protects against damage the gastric mucosa.