

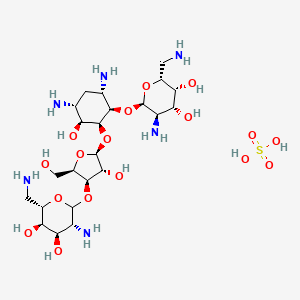

1. Neomycin
2. Neomycin Palmitate
3. Neomycin Sulfate
1. Neomycin Sulfate
2. 1405-10-3
3. Neomycin Trisulfate Hydrate
4. Akos016010116
| Molecular Weight | 712.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H48N6O17S |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 15 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 23 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 712.27966526 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 712.27966526 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 436 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 47 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 953 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 18 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Neomycin sulfate |
| Drug Label | Neomycin Sulfate Tablets, USP, for oral administration, contain neomycin which is an antibiotic obtained from the metabolic products of the actinomycete Streptomycesfradiae. Structurally, neomycin sulfate may be represented as follows:Chemically, i... |
| Active Ingredient | Neomycin sulfate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Oman Pharm Products; Teva; X Gen Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Neomycin sulfate |
| Drug Label | Neomycin Sulfate Tablets, USP, for oral administration, contain neomycin which is an antibiotic obtained from the metabolic products of the actinomycete Streptomycesfradiae. Structurally, neomycin sulfate may be represented as follows:Chemically, i... |
| Active Ingredient | Neomycin sulfate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Oman Pharm Products; Teva; X Gen Pharms |
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
Compounds which inhibit the synthesis of proteins. They are usually ANTI-BACTERIAL AGENTS or toxins. Mechanism of the action of inhibition includes the interruption of peptide-chain elongation, the blocking the A site of ribosomes, the misreading of the genetic code or the prevention of the attachment of oligosaccharide side chains to glycoproteins. (See all compounds classified as Protein Synthesis Inhibitors.)