

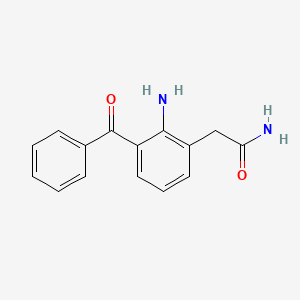

1. 2-amino-3-benzoylbenzeneacetamide
2. Nevanac
1. 78281-72-8
2. Nevanac
3. 2-(2-amino-3-benzoylphenyl)acetamide
4. 2-amino-3-benzoylbenzeneacetamide
5. Ahr-9434
6. Ilevro
7. Al 6515
8. Al-6515
9. Ahr 9434
10. Benzeneacetamide, 2-amino-3-benzoyl-
11. Chebi:75922
12. 0j9l7j6v8c
13. Ahr 9434;al 6515
14. Ncgc00185741-01
15. Dsstox_cid_28564
16. Dsstox_rid_82836
17. Dsstox_gsid_48638
18. Nepafenac [usan]
19. Amfenac Amide
20. Smr002529588
21. Cas-78281-72-8
22. Nepafenaco
23. Nepafenacum
24. Unii-0j9l7j6v8c
25. Nepafena
26. Nepafenac [usan:inn:ban:jan]
27. Nevanac (tn)
28. Mfcd08067732
29. 2-(2-amino-3-benzoyl-phenyl)acetamide
30. 2-[2-amino-3-(benzoyl)phenyl]acetamide
31. Nepafenac [inn]
32. Nepafenac [jan]
33. Nepafenac [mi]
34. Nepafenac [vandf]
35. Nepafenac [mart.]
36. Nepafenac [usp-rs]
37. Nepafenac [who-dd]
38. Chembl1021
39. Schembl93835
40. Nepafenac [ema Epar]
41. Mls003915618
42. Mls004774140
43. Mls006010644
44. Nepafenac (jan/usan/inn)
45. Gtpl7564
46. Nepafenac [orange Book]
47. Dtxsid0048638
48. Nepafenac, >=98% (hplc)
49. 2-amino-3-benzoyl-phenylacetamide
50. Hms3654p07
51. Hms3884e07
52. Act02914
53. Amy10899
54. Bcp21333
55. Ex-a1350
56. Wzb81453
57. Zinc5162311
58. Tox21_112985
59. Bdbm50228731
60. S1255
61. Stl451069
62. Akos005146108
63. Tox21_112985_1
64. Ac-6949
65. Ccg-267004
66. Cs-0899
67. Db06802
68. Ncgc00185741-02
69. 2-(2-amino-3-benzoyl-phenyl)-acetamide
70. As-19176
71. Hy-17357
72. 2-amino-3-benzoylbenzeneacetamide;nepafenac
73. Ft-0603701
74. N0932
75. Sw219197-1
76. 2-[2-amino-3-(phenylcarbonyl)phenyl]acetamide
77. A26218
78. D05143
79. Ab01274763-01
80. Ab01274763_02
81. 281n728
82. A890381
83. Q684379
84. Sr-01000931908
85. J-507774
86. Sr-01000931908-2
87. Brd-k04112579-001-02-1
| Molecular Weight | 254.28 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H14N2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 254.105527694 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 254.105527694 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 86.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 337 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Nevanac |
| Drug Label | NEVANAC (nepafenac ophthalmic suspension) 0.1% is a sterile, topical, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) prodrug for ophthalmic use. Each mL of NEVANAC suspension contains 1 mg of nepafenac. Nepafenac is designated chemically as 2-amino-3-ben... |
| Active Ingredient | Nepafenac |
| Dosage Form | Suspension/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | 0.1% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alcon Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Nevanac |
| Drug Label | NEVANAC (nepafenac ophthalmic suspension) 0.1% is a sterile, topical, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) prodrug for ophthalmic use. Each mL of NEVANAC suspension contains 1 mg of nepafenac. Nepafenac is designated chemically as 2-amino-3-ben... |
| Active Ingredient | Nepafenac |
| Dosage Form | Suspension/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | 0.1% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alcon Pharms |
For the treatment of pain and inflammation associated with cataract surgery.
FDA Label
Nevanac is indicated for:
- prevention and treatment of postoperative pain and inflammation associated with cataract surgery;
- reduction in the risk of postoperative macular oedema associated with cataract surgery in diabetic patients.
Low but quantifiable plasma concentrations of nepafenac and amfenac were observed in the majority of subjects 2 and 3 hours postdose, respectively, following bilateral topical ocular TID dosing of nepafenac ophthalmic suspension, 0.1%. The mean steady-state Cmax for nepafenac and for amfenac were 0.310 0.104 ng/ml and 0.422 0.121 ng/ml, respectively, following ocular administration.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
S01BC10
S01BC10
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01B - Antiinflammatory agents
S01BC - Antiinflammatory agents, non-steroids
S01BC10 - Nepafenac
Absorption
Nepafenac rapidly cross the cornea (6 times faster than diclofenac in vitro).
Route of Elimination
After oral administration of 14C-nepafenac to healthy volunteers, urinary excretion was found to be the major route of radioactivity elimination, accounting for approximately 85% of the dose, while fecal excretion represented approximately 6% of the dose. Nepafenac (prodrug) and amfenac (active compound) were not quantifiable in the urine.
Nepafenac (prodrug) is deaminated to amfenac (active compound) in the ciliary body epithelium, retina, and choroid by intraocular hydrolases. Subsequently, amfenac undergoes extensive metabolism to more polar metabolites involving hydroxylation of the aromatic ring leading to glucuronide conjugate formation.
Nepafenac is a prodrug. After penetrating the cornea, nepafenac undergoes rapid bioactivation to amfenac, which is a potent NSAID that uniformly inhibits the COX1 and COX2 activity.
