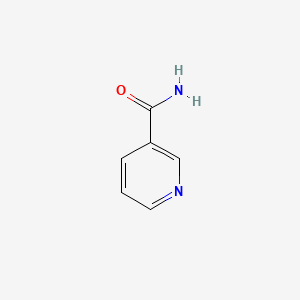

1. 3 Pyridinecarboxamide
2. 3-pyridinecarboxamide
3. B 3, Vitamin
4. B3, Vitamin
5. Enduramide
6. Jenapharm, Nicotinsureamid
7. Niacinamide
8. Nicobion
9. Nicotinsureamid Jenapharm
10. Papulex
11. Vitamin B 3
12. Vitamin B3
13. Vitamin Pp
1. Niacinamide
2. 98-92-0
3. 3-pyridinecarboxamide
4. Pyridine-3-carboxamide
5. Nicotinic Acid Amide
6. Vitamin Pp
7. Papulex
8. Aminicotin
9. Amixicotyn
10. Nicobion
11. Nicotylamide
12. Nikotinamid
13. Savacotyl
14. Benicot
15. Dipegyl
16. Endobion
17. Hansamid
18. Pelmine
19. Nicotinic Amide
20. Delonin Amide
21. Pelonin Amide
22. Vi-nicotyl
23. Austrovit Pp
24. Inovitan Pp
25. Nicosylamide
26. Nicotilamide
27. Nicotililamido
28. Amnicotin
29. Niacevit
30. Nicamina
31. Nicamindon
32. Nicofort
33. Nicomidol
34. Nicotamide
35. Nicovitina
36. Nicovitol
37. Nicozymin
38. Niocinamide
39. Niozymin
40. Niamide
41. Nicasir
42. Nicogen
43. Nicota
44. Nicotol
45. Nicovit
46. Niko-tamin
47. 3-carbamoylpyridine
48. Nicotine Acid Amide
49. Nandervit-n
50. Pyridine-3-carboxylic Acid Amide
51. Vitamin B
52. Niavit Pp
53. Nicotinamidum
54. Nicosan 2
55. Nicotine Amide
56. Beta-pyridinecarboxamide
57. Nikotinsaeureamid
58. Nicotylamidum
59. Mediatric
60. Nicotinsaureamid
61. Pyridine, 3-carbamoyl-
62. 3-pyridinecarboxylic Acid Amide
63. M-(aminocarbonyl)pyridine
64. Acid Amide
65. Factor Pp
66. Nicotinamida
67. Nicovel
68. Vitamin B (van)
69. Pelmin
70. Amid Kyseliny Nikotinove
71. Witamina Pp
72. Pp-faktor
73. Amide Pp
74. Nicotinsaureamid [german]
75. Nikotinsaeureamid [german]
76. Amid Kyseliny Nikotinove [czech]
77. Nicotinamidum [inn-latin]
78. Nicotinamida [inn-spanish]
79. Nam
80. Niacinamid
81. Nictoamide
82. Ccris 1901
83. Dipigyl
84. Hsdb 1237
85. Vi-noctyl
86. Ai3-02906
87. Nsc 13128
88. B-pyridinecarboxamide
89. Niacinamide [usp]
90. Nicotinamide [inn]
91. 3-(aminocarbonyl)pyridine
92. Mfcd00006395
93. Nsc-13128
94. Nsc-27452
95. .beta.-pyridinecarboxamide
96. Nicotinamide (vitamin B3)
97. Chembl1140
98. Mls000069714
99. Chebi:17154
100. 25x51i8rd4
101. Nsc13128
102. Niacinamide (usp)
103. Ncgc00093354-03
104. Ncgc00093354-05
105. Smr000058212
106. Nicotinamide 10 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
107. Dsstox_cid_929
108. Niacinamide;nicotinic Acid Amide;vitamin B3
109. Wln: T6nj Cvz
110. Dsstox_rid_75873
111. Dsstox_gsid_20929
112. Niacinamide [usan]
113. Enduramide
114. Cas-98-92-0
115. B3, Vitamin
116. Vitamin B 3
117. B 3, Vitamin
118. 3 Pyridinecarboxamide
119. Sr-01000721872
120. Nicotinsaureamid Jenapharm
121. Einecs 202-713-4
122. Jenapharm, Nicotinsaureamid
123. Niacotinamide
124. Nicotinamid
125. Nicotin-amide
126. Unii-25x51i8rd4
127. Nicotinsaeureamid
128. 3-amidopyridine
129. Dea No. 1405
130. Nicotinamide,(s)
131. Vitamin B3 Amide
132. 3-yridinecarboxamide
133. Mediatric (salt/mix)
134. Niacin - Vitamin B3
135. 1yc5
136. Opera_id_775
137. Niacin (as Niacinamide)
138. Niacinamide [ii]
139. Niacinamide(vitamin B3)
140. Niacinamide [fcc]
141. Nicotinamide [mi]
142. Niacinamide [hsdb]
143. Niacinamide [inci]
144. Nicotinamide [jan]
145. Bmse000281
146. Molmap_000061
147. Ec 202-713-4
148. Niacinamide [vandf]
149. Schembl2926
150. Nicotinamide (jp17/inn)
151. Nicotinamidum [hpus]
152. Niacinamide [usp-rs]
153. Nicotinamide [mart.]
154. Mls001424246
155. Nicotinamide [who-dd]
156. Nicotinamide [who-ip]
157. Nicotinamide-(amide-[15n])
158. Schembl6278767
159. Sgcut00176
160. Zinc5878
161. Tpn Component Niacinamide
162. Dtxsid2020929
163. Schembl19978192
164. Bdbm27507
165. Niacinamide [orange Book]
166. Nicotinamide, Niacin, Vitamin B3
167. Hms2052m21
168. Hms2090b05
169. Hms2093h03
170. Hms2236j03
171. Hms3370f21
172. Hms3394m21
173. Hms3655m20
174. Hms3713b22
175. Hms3884a16
176. Nicotinamide [ep Impurity]
177. Pharmakon1600-01505397
178. Niacinamide [usp Monograph]
179. Nicotinamide [ep Monograph]
180. Bcp07322
181. Hy-b0150
182. Niacinamide Component Of Tpn
183. Nicotinamide (vitamin B3) Solution
184. Nsc27452
185. To_000073
186. Nicotinamide 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
187. Nicotinamide, >=98.5% (hplc)
188. Nicotinamide, >=99.5% (hplc)
189. Tox21_111202
190. Tox21_201716
191. Tox21_302776
192. Nicotinamidum [who-ip Latin]
193. Nsc759115
194. S1899
195. Stl163867
196. Akos005715850
197. Tox21_111202_1
198. Ccg-101149
199. Cs-1968
200. Db02701
201. Nc00399
202. Nsc-759115
203. Sb74497
204. Nicotinamide 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
205. Nicotinamide, >=98% (hplc), Powder
206. Ncgc00093354-04
207. Ncgc00093354-06
208. Ncgc00093354-09
209. Ncgc00256432-01
210. Ncgc00259265-01
211. Niacin (as Niacinamide) [vandf]
212. As-13845
213. Bn166252
214. Nicotinamide, Puriss., 99.0-101.0%
215. Sy024804
216. Nicotinamide, Tested According To Ph.eur.
217. Sbi-0206826.p001
218. Db-057754
219. Ft-0631517
220. Ft-0672696
221. Ft-0773644
222. N0078
223. N1651
224. Sw197779-3
225. En300-15612
226. Niacinamide, Meets Usp Testing Specifications
227. C00153
228. D00036
229. Nicotinamide (niacinamide), Analytical Standard
230. Ab00373895-13
231. Ab00373895_15
232. Ab00373895_16
233. Nicotinamide, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, >=98%
234. A845925
235. Ac-907/25014114
236. Q192423
237. Q-201470
238. Sr-01000721872-3
239. Sr-01000721872-4
240. Sr-01000721872-5
241. Z33546463
242. F2173-0513
243. Niacinamide;nicotinic Acid Amide;vitamin B3; Vitamin Pp
244. Nicotinamide, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
245. A186b02e-6c70-4e54-9739-79398d439aaa
246. Nicotinamide, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
247. Niacinamide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
248. Niacinamide, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
249. Nicotinamide, Bioreagent, Suitable For Cell Culture, Suitable For Insect Cell Culture
250. Nicotinamide (vitamin B3) Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 122.12 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H6N2O |
| XLogP3 | -0.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 122.048012819 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 122.048012819 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 56 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 9 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 114 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Vitamin B Complex
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Niacinamide. Online file (MeSH, 2018). Available from, as of June 1, 2018: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2017/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
/CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Nicotinamide is included in the database.
NIH/NLM; ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available from, as of June 1, 2018: https://clinicaltrials.gov/
Niacin and niacinamide are used to prevent niacin deficiency and to treat pellagra. Some clinicians prefer niacinamide for the treatment of pellagra because it lacks vasodilating effects. Pellagra may result from dietary deficiency, isoniazid therapy, or from decreased conversion of tryptophan to niacin in Hartnup disease or carcinoid tumors. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017
Although niacin and niacinamide have not been shown by well-controlled trials to have therapeutic value, the drugs have been used for the management of schizophrenic disorder, drug-induced hallucinations, chronic brain syndrome, hyperkinesis, unipolar depression, motion sickness, alcohol dependence, livedoid vasculitis, acne, and leprosy. /NOT included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Nicotinamide (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Blood glucose concentration should be monitored periodically in patients receiving niacin or niacinamide, especially early in the course of therapy. Dosage requirements for antidiabetic agents (e.g., insulin, oral sulfonylureas) may change in diabetic patients.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017
Potential adverse effects on fetus: Higher levels in fetus than mother, but no fetal anomalies reported. Potential side effects on breast-fed infant: No adverse effects known . FDA Category: C (C = Studies in laboratory animals have revealed adverse effects on the fetus (teratogenic, embryocidal, etc.), but there are no controlled studies in pregnant women. The benefits from use of the drug in pregnant women may be acceptable despite its potential risks, or there are no laboratory animal studies or adequate studies in pregnant women.) /from table II/
Stockton, D.L. and A.S. Paller. J Am Acad Dermatol 23 (1):87-103 (1990)
Niacinamide /was administered/ daily as a liquid formulation to head and neck cancer patients receiving a 5- to 7-week course of radiotherapy. Niacinamide was administered orally 1.5 hr before irradiation. The daily dose was 80 mg/kg bw to a maximum of 6 g. A dose reduction to 60 mg/kg was introduced for patients with severe side-effects. ... Side-effects of niacinamide were monitored. In all patients, peak concentrations greater than 700 nM/mL could be obtained 0.25-3 hr after drug intake. During the first week of treatment, plasma concentrations at the time of irradiation were adequate in 82% of the samples. Nausea, with or without vomiting, occurred in 65% of patients. Tolerance improved after a 25% reduction of the dose in six of seven patients but plasma concentrations at the time of irradiation decreased below 700 nM/mL in four out of six patients. Other niacinamide side effects included gastrointestinal symptoms, flushing, dizziness, sweating, fatigue, and headache. The most powerful single predictor for severe niacinamide toxicity was the mean of the plasma concentration measured at the time of irradiation during the first week.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Expert Panel; Final Report of the Safety Assessment of Niacinamide and Niacin p.6; Intl J of Toxicology 24 (Suppl 5): 1-31 (2005). Available from, as of June 4, 2018: https://www.cir-safety.org/ingredients
Abnormal liver function test results (including increased serum concentrations of bilirubin, AST [SGOT], ALT [SGPT], and LDH), jaundice, and chronic liver damage have occurred during niacin and niacinamide therapy. Abnormal prothrombin time and hypoalbuminemia have also been reported.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Nicotinamide (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Vitamin B Complex
A group of water-soluble vitamins, some of which are COENZYMES. (See all compounds classified as Vitamin B Complex.)
A11HA01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A11 - Vitamins
A11H - Other plain vitamin preparations
A11HA - Other plain vitamin preparations
A11HA01 - Nicotinamide
14(C)Niacinamide was incorporated into an oil-in-water (o/w) skin cream and into a 30% (w/w) soap base and applied to the skin of female Colworth Wistar rats. The final concentration of niacinamide in the soap solution was approximately 0.3% (w/v) and was 1% (w/w) in the skin cream. Application of the skin cream and soap paste was made to rat skin at approximately 20 mg/sq cm. The cream was carefully massaged over 10 sq cm of skin for up to 5 min before covering with polythene-lined occlusive protective patches. The rats were placed in metabolism cages for 48 hr during which time all excreta was collected. At 48 hr, the animals were killed and the patch, carcass, and treated area of skin were assayed for 14(C). Up to 32% 14(C) was recovered in excreta and in the carcasses from rats treated with skin cream containing 14(C)Niacinamide and up to 30% from those treated with soap paste.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Expert Panel; Final Report of the Safety Assessment of Niacinamide and Niacin p.5; Intl J of Toxicology 24 (Suppl 5): 1-31 (2005). Available from, as of June 4, 2018: https://www.cir-safety.org/ingredients
Nicotinamide is efficiently absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. At low doses, absorption is mediated via sodium-dependent facilitated diffusion. Passive diffusion is the principal mechanism of absorption at higher doses. Doses of up to three to four grams of nicotinamide are almost completely absorbed. Nicotinamide is transported via the portal circulation to the liver and via the systemic circulation to the various tissues of the body. Nicotinamide enters most cells by passive diffusion and enters erythrocytes by facilitated transport.
PDR for Nutritional Supplements 2nd ed. Thomson Reuters, Montvale, NJ 2008, p. 452
Niacinamide is widely distributed /throughout/ body tissues.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017
Niacin and niacinamide are readily absorbed from the GI tract following oral administration, and niacinamide (no longer commercially available in the US) is readily absorbed from subcutaneous and IM injection sites.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Nicotinamide (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
In amounts needed for physiologic function as a coenzyme (12-18 mg daily), niacin is converted to niacinamide; larger doses of niacin are converted to niacinamide to only a minor degree. Niacinamide is metabolized in the liver to N-methylniacinamide, other N-methylated derivatives, and nicotinuric acid (the glycine conjugate of niacin). These metabolites are excreted in urine. Following administration of physiologic doses of niacin or niacinamide, only a small amount of niacinamide is excreted unchanged in urine; however, following administration of larger doses, a greater proportion of niacin and niacinamide is excreted unchanged.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017
N1-Methyl-4-pyridone-3-carboxamide was detected on chromatograms of plasma extracts after oral administration of niacinamide to two human subjects.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Expert Panel; Final Report of the Safety Assessment of Niacinamide and Niacin p.6; Intl J of Toxicology 24 (Suppl 5): 1-31 (2005). Available from, as of June 4, 2018: https://www.cir-safety.org/ingredients
6-Hydroxynicotinamide and 6-hydroxynicotinic acid /were detected/ as urinary metabolites by comparison of ultraviolet, infrared, and mass spectra following intraperitoneal injections of 14(C)Niacin or 14(C)Niacinamide into rats.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Expert Panel; Final Report of the Safety Assessment of Niacinamide and Niacin p.8; Intl J of Toxicology 24 (Suppl 5): 1-31 (2005). Available from, as of June 4, 2018: https://www.cir-safety.org/ingredients
N1-methyl-4- pyridone-3-carboxamide is a major metabolite of niacin and niacinamide which has been found to be synthesized from N1- methylnicotinamide.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Expert Panel; Final Report of the Safety Assessment of Niacinamide and Niacin p.8; Intl J of Toxicology 24 (Suppl 5): 1-31 (2005). Available from, as of June 4, 2018: https://www.cir-safety.org/ingredients
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for Nicotinamide (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
The mean half life values were 2.7 hr, 5.9 hr, and 8.1 hr after taking 1, 3, or 6 g of Niacinamide, respectively.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Expert Panel; Final Report of the Safety Assessment of Niacinamide and Niacin p.6; Intl J of Toxicology 24 (Suppl 5): 1-31 (2005). Available from, as of June 4, 2018: https://www.cir-safety.org/ingredients