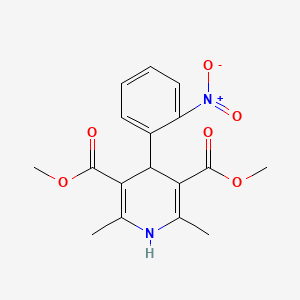

1. Adalat
2. Bay 1040
3. Bay A 1040
4. Bay-1040
5. Bay-a-1040
6. Bay1040
7. Baya1040
8. Cordipin
9. Cordipine
10. Corinfar
11. Fenigidin
12. Korinfar
13. Monohydrochloride, Nifedipine
14. Nifangin
15. Nifedipine Gtis
16. Nifedipine Monohydrochloride
17. Nifedipine-gtis
18. Procardia
19. Procardia Xl
20. Vascard
1. 21829-25-4
2. Adalat
3. Procardia
4. Procardia Xl
5. Adalat Cc
6. Cordipin
7. Corinfar
8. Fenihidine
9. Citilat
10. Oxcord
11. Dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
12. Bay-a-1040
13. Coracten
14. Fenihidin
15. Afeditab Cr
16. Adalate
17. Nifediac
18. Hexadilat
19. Introcar
20. Kordafen
21. Nifedical
22. Nifedipinum
23. Tibricol
24. Adapine
25. Anifed
26. Pidilat
27. Sepamit
28. Zenusin
29. Orix
30. Adalat La
31. Bay A 1040
32. Nifedipino
33. 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid Dimethyl Ester
34. Adipine Xl
35. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, Dimethyl Ester
36. C17h18n2o6
37. Mfcd00057326
38. Nifedipine (adalat)
39. Ccris 6074
40. Chebi:7565
41. Nifedipine Slow Release
42. 3,5-dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
43. Chembl193
44. Nsc-757242
45. I9zf7l6g2l
46. Mls000028521
47. Dimethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2'-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
48. Dimethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(o-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
49. Ncgc00015748-11
50. Chronadalate
51. Dignokonstant
52. Adapress
53. Afeditab
54. Aldipin
55. Alfadal
56. Angipec
57. Aprical
58. Bonacid
59. Calcibloc
60. Calcigard
61. Calcilat
62. Cardifen
63. Cardilat
64. Cardionorm
65. Cordafen
66. Cordaflex
67. Cordalat
68. Cordicant
69. Cordilan
70. Corotrend
71. Corynphar
72. Dilafed
73. Dipinkor
74. Duranifin
75. Ecodipi
76. Ecodipin
77. Fenamon
78. Hadipin
79. Macorel
80. Megalat
81. Myogard
82. Nifecard
83. Nifecor
84. Nifedicor
85. Nifedin
86. Nifedipres
87. Nifelan
88. Nifelat
89. Nificard
90. Smr000058291
91. Alonix
92. Anpine
93. Camont
94. Fedcor
95. Glopir
96. Coral
97. Depin
98. Alat
99. Adalat Retard
100. Cas-21829-25-4
101. Fedcor Retard
102. Adalat Crono
103. Chronadalate Lp
104. Adalat Oros
105. 4-(2'-nitrophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-dicarbomethoxy-1,4-dihydropyridine
106. Dsstox_cid_5715
107. Ecodipin E
108. Apo-nifed
109. Nifensar Xl
110. Alonix S
111. Fenamon Sr
112. Dimethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
113. Adalat Cr
114. Adalat Ft
115. Adalat Lp
116. Adalat Pa
117. Adalat Gits
118. Dsstox_rid_77889
119. Adalat 5
120. Dsstox_gsid_25715
121. Adalat 10
122. Adalat 20
123. Adalat Gits 30
124. Alpha-nifedipine Retard
125. Emaberin
126. Dilcor
127. Aprical Long
128. Slofedipine Xl
129. Fortipine La
130. Nifedical Xl
131. Nifedipinum [inn-latin]
132. Tensipine Mr
133. 4-(2-nitrophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-dicarbomethoxy-1,4-dihydropyridine
134. Adalate Lp
135. Nifedipino [inn-spanish]
136. Adalat Xl
137. 4-(2'-nitrophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridin-3,5-dicarbonsaeuredimethylester
138. Dimethyl 4-(2-nitrophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
139. Procardia (tn)
140. 193689-82-6
141. Adalat (tn)
142. Afeditab Cr (tn)
143. 1173023-46-5
144. Sr-01000075332
145. Baya1040
146. Nifedipine,(s)
147. Bay 1040
148. Kb-1712p
149. Prestwick_357
150. Einecs 244-598-3
151. Dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
152. Brn 0497773
153. Nifedipine-[13c8]
154. Spectrum_000979
155. Tocris-1075
156. Nifedipine [mi]
157. Nifedipine [inn]
158. Nifedipine [jan]
159. Opera_id_1816
160. Prestwick0_000063
161. Prestwick1_000063
162. Prestwick2_000063
163. Prestwick3_000063
164. Spectrum2_001058
165. Spectrum3_000516
166. Spectrum4_000074
167. Spectrum5_001278
168. Lopac-n-7634
169. Nifedipine [hsdb]
170. Nifedipine [inci]
171. Nifedipine [usan]
172. Nifedipine [vandf]
173. Unii-i9zf7l6g2l
174. N 7634
175. Cid_4485
176. Nifedipine [mart.]
177. Schembl3968
178. Nifedipine [usp-rs]
179. Nifedipine [who-dd]
180. Nifedipine [who-ip]
181. Bidd:pxr0034
182. Cbiol_001826
183. Lopac0_000819
184. Oprea1_788617
185. Bspbio_000245
186. Bspbio_001391
187. Bspbio_002071
188. Kbiogr_000111
189. Kbiogr_000627
190. Kbiogr_002400
191. Kbioss_000111
192. Kbioss_001459
193. Kbioss_002405
194. Mls000758222
195. Mls001148146
196. Mls001401371
197. Bidd:gt0442
198. Divk1c_000313
199. Spectrum1500431
200. Spbio_001016
201. Spbio_002166
202. Bpbio1_000271
203. Gtpl2514
204. Nifedipine (jp17/usp/inn)
205. Bay-a 1040
206. Dtxsid2025715
207. Nifedipine [orange Book]
208. Bcbcmap01_000046
209. Hms500p15
210. Hsdb 7775
211. Kbio1_000313
212. Kbio2_000111
213. Kbio2_001459
214. Kbio2_002400
215. Kbio2_002679
216. Kbio2_004027
217. Kbio2_004968
218. Kbio2_005247
219. Kbio2_006595
220. Kbio2_007536
221. Kbio3_000221
222. Kbio3_000222
223. Kbio3_001571
224. Kbio3_002879
225. Nifedipine [ep Monograph]
226. Nifedipine [usp Impurity]
227. Cmap_000042
228. Nifedipine-d4(2-nitrophenyl-d4)
229. Ninds_000313
230. Bio1_000112
231. Bio1_000601
232. Bio1_001090
233. Bio2_000111
234. Bio2_000591
235. Hms1361f13
236. Hms1568m07
237. Hms1791f13
238. Hms1920p19
239. Hms1989f13
240. Hms2051o03
241. Hms2089h11
242. Hms2091h20
243. Hms2095m07
244. Hms2233b22
245. Hms3262d19
246. Hms3267g06
247. Hms3393o03
248. Hms3412e17
249. Hms3651m19
250. Hms3676e17
251. Hms3712m07
252. Hms3748o21
253. Nifedipine [usp Monograph]
254. Pharmakon1600-01500431
255. Nifedipinum [who-ip Latin]
256. Act02669
257. Bcp21147
258. Hy-b0284
259. L-type Calcium Channel Blocker Iii
260. Tox21_110212
261. Tox21_200304
262. Tox21_500819
263. Bbl023163
264. Bdbm50000778
265. Bdbm50101817
266. Ccg-40115
267. Nsc757242
268. Nsc786036
269. S1808
270. Stk735567
271. Zinc85205448
272. Akos002942507
273. Akos037515769
274. Nifedipine - Cas 21829-25-4
275. Nifedipine 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
276. Nifedipine, >=98% (hplc), Powder
277. Tox21_110212_1
278. Ac-8061
279. Ccg-100758
280. Db01115
281. Ks-1456
282. Lp00819
283. Nc00008
284. Nifedipine [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
285. Nsc 757242
286. Nsc-786036
287. Sdccgsbi-0050796.p005
288. 4-(2'-nitrophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridin-3,5-dicarbonsaeuredimethylester [german]
289. Idi1_000313
290. Idi1_033861
291. Bay-1040;bay 1040;bay1040
292. Ncgc00015748-01
293. Ncgc00015748-02
294. Ncgc00015748-03
295. Ncgc00015748-04
296. Ncgc00015748-05
297. Ncgc00015748-06
298. Ncgc00015748-07
299. Ncgc00015748-08
300. Ncgc00015748-09
301. Ncgc00015748-10
302. Ncgc00015748-12
303. Ncgc00015748-13
304. Ncgc00015748-14
305. Ncgc00015748-15
306. Ncgc00015748-17
307. Ncgc00015748-33
308. Ncgc00021710-02
309. Ncgc00024983-01
310. Ncgc00024983-02
311. Ncgc00024983-03
312. Ncgc00024983-04
313. Ncgc00024983-05
314. Ncgc00024983-06
315. Ncgc00024983-07
316. Ncgc00024983-08
317. Ncgc00091707-01
318. Ncgc00091707-02
319. Ncgc00091707-03
320. Ncgc00257858-01
321. Ncgc00261504-01
322. Bn166183
323. Cpd000058291
324. Sy074220
325. Sbi-0050796.p004
326. Eu-0100819
327. Ft-0630478
328. Ft-0653833
329. Ft-0672727
330. N0528
331. Sw219724-1
332. 29n254
333. Bim-0050796.0001
334. C07266
335. D00437
336. Q39111
337. Ab00052051-05
338. Ab00052051_06
339. Ab00052051_07
340. 5-22-04-00268 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
341. A899873
342. L001054
343. Q-201471
344. Sr-01000075332-1
345. Sr-01000075332-3
346. Sr-01000075332-4
347. Sr-01000075332-6
348. Brd-k96354014-001-01-3
349. Brd-k96354014-001-10-4
350. Z90350374
351. F2173-0802
352. Nifedipine, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
353. Nifedipine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
354. Nifedipine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
355. 2,6-dimethyl-3,5-dicarbomethoxy-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine
356. 4-(2'-nitrophenyl)-2,6 Dimethyl-3,5-dicarbmethoxy-1,4-dihydropyridine
357. 4-(2'-nitrophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-dicarbmethoxy-1,4-dihydropyridine
358. Nifedipine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
359. 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylicaciddimethylester
360. 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic Acid 3,5-dimethyl Ester
361. Dimethyl (4-(2-nitrophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate)
362. Dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate #
363. Dimethyl2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
364. 101539-70-2
365. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, Dimethyl Ester (9ci)
366. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(o-nitrophenyl)-, Dimethyl Ester (8ci)
| Molecular Weight | 346.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H18N2O6 |
| XLogP3 | 2.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 346.11648630 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 346.11648630 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 110 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 608 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Adalat cc |
| PubMed Health | Nifedipine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Adalat CC is an extended release tablet dosage form of the calcium channel blocker nifedipine. Nifedipine is 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-dimethyl ester, C17H18N2O6, and has the structural formula:Nifedi... |
| Active Ingredient | Nifedipine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 60mg; 30mg; 90mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bayer Hlthcare |
| 2 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Afeditab cr |
| PubMed Health | Nifedipine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Afeditab CR is an extended release tablet dosage form of the calcium channel blocker nifedipine. Nifedipine is 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2- nitrophenyl)-dimethyl ester, C H N O , and has the structural formula: 1718... |
| Active Ingredient | Nifedipine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 60mg; 30mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs |
| 3 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Nifedipine |
| PubMed Health | Nifedipine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Nifedipine is a drug belonging to a class of pharmacological agents known as the calcium channel blockers. Nifedipine is 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, dimethyl ester, C17H18N2O6, and has the structural fo... |
| Active Ingredient | Nifedipine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release; Capsule |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 90mg; 60mg; 10mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Twi Pharms; Valeant Intl; Osmotica Pharm; Par Pharm; Intergel Pharm; Matrix Labs; Actavis Elizabeth; Martec Usa; Emcure Pharms Usa; Mylan |
| 4 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Procardia |
| PubMed Health | Nifedipine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | PROCARDIA (nifedipine) is an antianginal drug belonging to a class of pharmacological agents, the calcium channel blockers. Nifedipine is 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, dimethyl ester, C17H18N2O6, and ha... |
| Active Ingredient | Nifedipine |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 5 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Procardia xl |
| Drug Label | Nifedipine is a drug belonging to a class of pharmacological agents known as the calcium channel blockers. Nifedipine is 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, dimethyl ester, C17H18N2O6, and has the structural fo... |
| Active Ingredient | Nifedipine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 90mg; 60mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 6 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Adalat cc |
| PubMed Health | Nifedipine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Adalat CC is an extended release tablet dosage form of the calcium channel blocker nifedipine. Nifedipine is 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-dimethyl ester, C17H18N2O6, and has the structural formula:Nifedi... |
| Active Ingredient | Nifedipine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 60mg; 30mg; 90mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bayer Hlthcare |
| 7 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Afeditab cr |
| PubMed Health | Nifedipine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Afeditab CR is an extended release tablet dosage form of the calcium channel blocker nifedipine. Nifedipine is 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2- nitrophenyl)-dimethyl ester, C H N O , and has the structural formula: 1718... |
| Active Ingredient | Nifedipine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 60mg; 30mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs |
| 8 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Nifedipine |
| PubMed Health | Nifedipine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Nifedipine is a drug belonging to a class of pharmacological agents known as the calcium channel blockers. Nifedipine is 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, dimethyl ester, C17H18N2O6, and has the structural fo... |
| Active Ingredient | Nifedipine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release; Capsule |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 90mg; 60mg; 10mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Twi Pharms; Valeant Intl; Osmotica Pharm; Par Pharm; Intergel Pharm; Matrix Labs; Actavis Elizabeth; Martec Usa; Emcure Pharms Usa; Mylan |
| 9 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Procardia |
| PubMed Health | Nifedipine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | PROCARDIA (nifedipine) is an antianginal drug belonging to a class of pharmacological agents, the calcium channel blockers. Nifedipine is 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, dimethyl ester, C17H18N2O6, and ha... |
| Active Ingredient | Nifedipine |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 10 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Procardia xl |
| Drug Label | Nifedipine is a drug belonging to a class of pharmacological agents known as the calcium channel blockers. Nifedipine is 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, dimethyl ester, C17H18N2O6, and has the structural fo... |
| Active Ingredient | Nifedipine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 90mg; 60mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
Calcium Channel Blockers; Tocolytic Agents; Vasodilator Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2009)
Nifedipine extended-release tablets are indicated for the management of vasospastic angina confirmed by any of the following criteria: 1) classical pattern of angina at rest accompanied by ST segment elevation, 2) angina or coronary artery spasm provoked by ergonovine, or 3) angiographically demonstrated coronary artery spasm. In those patients who have had angiography, the presence of significant fixed obstructive disease is not incompatible with the diagnosis of vasospastic angina, provided that the above criteria are satisfied. Nifedipine extended-release may also be used where the clinical presentation suggests a possible vasospastic component but where vasospasm has not been confirmed, eg, where pain has a variable threshold on exertion or in unstable angina where electrocardiographic findings are compatible with intermittent vasospasm, or when angina is refractory to nitrates and/or adequate doses of beta blockers. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Nifedipine (nifedipine) tablet, film coated, extended release (May 2006). Available from, as of October 15, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=1158
Nifedipine extended-release tablets are indicated for the management of chronic stable angina (effort-associated angina) without evidence of vasospasm in patients who remain symptomatic despite adequate doses of beta blockers and/or organic nitrates or who cannot tolerate those agents. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Nifedipine (nifedipine) tablet, film coated, extended release (May 2006). Available from, as of October 15, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=1158
Nifedipine extended-release tablets (ADALAT CC) is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ADALAT CC (nifedipine) tablet, film coated (June 2009). Available from, as of October 15, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=10098
The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) concluded from the apparent concordance of findings from observational studies in hypertensive patients and from randomized studies principally in acute myocardial infarction and unstable angina patients that it seems prudent and consistent with current evidence to recommend that short-acting nifedipine, especially at high doses, be used in the management of hypertension, angina, or myocardial infarction with great caution, if at all.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT), which compared long-term therapy with an ACE inhibitor (lisinopril) or dihydropyridine-derivative calcium-channel blocker (amlodipine) revealed no difference in the primary outcome of combined fatal coronary heart disease or nonfatal myocardial infarction among these therapies.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
Serious adverse reactions requiring discontinuance of nifedipine therapy or dosage adjustment are relatively rare. An increase in the frequency, intensity, and duration of angina, possibly resulting from hypotension, has occurred rarely during initiation of nifedipine therapy. Additional serious adverse effects including myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure or pulmonary edema, and ventricular arrhythmia or conduction defects have reportedly occurred in 4%, 2%, and less than 0.5% of patients receiving conventional nifedipine capsules, respectively, but these have not been directly attributed to the drug.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
Rarely, patients, usually receiving a beta blocker, have developed heart failure after beginning nifedipine. Patients with tight aortic stenosis may be at greater risk for such an event, as the unloading effect of nifedipine would be expected to be of less benefit to those patients, owing to their fixed impedance to flow across the aortic valve.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Nifedipine (nifedipine) tablet, film coated, extended release (May 2006). Available from, as of October 15, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=1158
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Nifedipine (32 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Nifedipine capsules are indicated to treat vasospastic angina and chronic stable angina. Extended release tablets are indicated to treat vasospastic angina, chronic stable angina, and hypertension.
FDA Label
Nifedipine is an inhibitor of L-type voltage gated calcium channels that reduces blood pressure and increases oxygen supply to the heart. Immediate release nifedipine's duration of action requires dosing 3 times daily. Nifedipine dosing is generally 10-120mg daily. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of excessive hypotension, angina, and myocardial infarction.
Calcium Channel Blockers
A class of drugs that act by selective inhibition of calcium influx through cellular membranes. (See all compounds classified as Calcium Channel Blockers.)
Tocolytic Agents
Drugs that prevent preterm labor and immature birth by suppressing uterine contractions (TOCOLYSIS). Agents used to delay premature uterine activity include magnesium sulfate, beta-mimetics, oxytocin antagonists, calcium channel inhibitors, and adrenergic beta-receptor agonists. The use of intravenous alcohol as a tocolytic is now obsolete. (See all compounds classified as Tocolytic Agents.)
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)
C08CA05
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C08 - Calcium channel blockers
C08C - Selective calcium channel blockers with mainly vascular effects
C08CA - Dihydropyridine derivatives
C08CA05 - Nifedipine
Absorption
Sublingual dosing leads to a Cmax of 10ng/mL, with a Tmax of 50min, and an AUC of 25ng\*h/mL. Oral dosing leads to a Cmax of 82ng/mL, with a Tmax of 28min, and an AUC of 152ng\*h/mL. Nifedipine is a Biopharmaceutics Classification System Class II drug, meaning it has low solubility and high intestinal permeability. It is almost completely absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract but has a bioavilability of 45-68%, partly due to first pass metabolism.
Route of Elimination
Nifedipine is 60-80% recovered in the urine as inactive water soluble metabolites, and the rest is eliminated in the feces as metabolites.
Volume of Distribution
The steady state volume of distribution of nifedipine is 0.62-0.77L/kg and the volume of distribution of the central compartment is 0.25-0.29L/kg.
Clearance
The total body clearance of nifedipine is 450-700mL/min.
Approximately 90% of an oral dose of nifedipine is rapidly absorbed from the GI tract following oral administration of the drug as conventional capsules. Only about 45-75% of an oral dose as conventional capsules reaches systemic circulation as unchanged drug since nifedipine is metabolized on first pass through the liver. Peak serum concentrations usually are reached within 0.5-2 hours after oral administration as conventional capsules. Food appears to decrease the rate but not the extent of absorption of nifedipine as conventional capsules.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
Plasma drug concentrations rise at a gradual, controlled rate after a nifedipine extended-release tablet dose and reach a plateau at approximately six hours after the first dose. For subsequent doses, relatively constant plasma concentrations at this plateau are maintained with minimal fluctuations over the 24-hour dosing interval. About a four-fold higher fluctuation index (ratio of peak to trough plasma concentration) was observed with the conventional immediate-release nifedipine capsule at t.i.d. dosing than with once daily nifedipine extended-release tablet.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Nifedipine (nifedipine) tablet, film coated, extended release (May 2006). Available from, as of October 15, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=1158
At steady-state the bioavailability of the nifedipine extended-release tablet is 86% relative to immediate-release nifedipine capsules. Administration of the nifedipine extended-release tablet in the presence of food slightly alters the early rate of drug absorption, but does not influence the extent of drug bioavailability. Markedly reduced GI retention time over prolonged periods (ie, short bowel syndrome), however, may influence the pharmacokinetic profile of the drug which could potentially result in lower plasma concentrations.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Nifedipine (nifedipine) tablet, film coated, extended release (May 2006). Available from, as of October 15, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=1158
The manufacturer states that relative oral bioavailability differs little if conventional nifedipine capsules are swallowed intact, bitten and swallowed, or bitten and held sublingually. However, some data indicate that the rate and extent of absorption of nifedipine following sublingual administration may be decreased substantially. Oral bioavailability of nifedipine may be increased up to twofold in patients with liver cirrhosis.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Nifedipine (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Nifedipine is predominantly metabolized by CYP3A4. Nifedipine is predominantly metabolized to 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-5-methoxycarbonyl-pyridine-3-carboxylic acid, and then further metabolized to 2-hydroxymethyl-pyridine carboxylic acid. Nifedipine is also minorly metabolized to dehydronifedipine.
The drug is extensively metabolized in the liver (to highly water-soluble, inactive metabolites) by the cytochrome P-450 microsomal enzyme system, including CYP3A.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
Nifedipine has known human metabolites that include Oxidized nifedipine.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The terminal elimination half life of nifedipine is approximately 2 hours.
In patients with normal renal and hepatic function, the plasma half-life of nifedipine is about 2 hours when administered as conventional capsules, and about 7 hours when administered as extended-release tablets (Adalat CC).
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
Nifedipine blocks voltage gated L-type calcium channels in vascular smooth muscle and myocardial cells. This blockage prevents the entry of calcium ions into cells during depolarization, reducing peripheral arterial vascular resistance and dilating coronary arteries. These actions reduce blood pressure and increase the supply of oxygen to the heart, alleviating angina.
The principal physiologic action of nifedipine is to inhibit the transmembrane influx of extracellular calcium ions across the membranes of myocardial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells, without changing serum calcium concentrations. Calcium plays important roles in the excitation-contraction coupling processes of the heart and vascular smooth muscle cells and in the electrical discharge of the specialized conduction cells of the heart. The membranes of these cells contain numerous channels that carry a slow inward current and that are selective for calcium. Activation of these slow calcium channels contributes to the plateau phase (phase 2) of the action potential of cardiac and vascular smooth muscle cells. The exact mechanism whereby nifedipine inhibits calcium ion influx across the slow calcium channels is not known, but the drug is thought to inhibit ion-control gating mechanisms of the channel, deform the slow channel, and/or interfere with release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. By inhibiting calcium influx, nifedipine inhibits the contractile processes of cardiac and vascular smooth muscle, thereby dilating the main coronary and systemic arteries.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
Nifedipine is a peripheral arterial vasodilator which acts directly on vascular smooth muscle. The binding of nifedipine to voltage-dependent and possibly receptor-operated channels in vascular smooth muscle results in an inhibition of calcium influx through these channels. Stores of intracellular calcium in vascular smooth muscle are limited and thus dependent upon the influx of extracellular calcium for contraction to occur. The reduction in calcium influx by nifedipine causes arterial vasodilation and decreased peripheral vascular resistance which results in reduced arterial blood pressure.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ADALAT CC (nifedipine) tablet, film coated (June 2009). Available from, as of October 15, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=10098