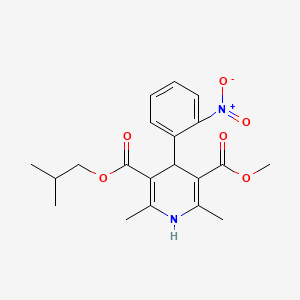

1. Bay K 5552
1. 63675-72-9
2. Sular
3. Nisocor
4. Baymycard
5. Nisoldipin
6. Zadipina
7. Bay K 5552
8. Nisoldipinum
9. Syscor
10. 3-isobutyl 5-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
11. Nisoldipinum [inn-latin]
12. Nisoldipino [inn-spanish]
13. Bay-k-5552
14. Bay-k 5552
15. Geomatrix 16e
16. Nisoldipine (stn)
17. Chebi:76917
18. Methyl 2-methylpropyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
19. 3-o-methyl 5-o-(2-methylpropyl) 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
20. Nsc-759106
21. 4i8hab65sz
22. Chembl441428
23. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, Methyl 2-methylpropyl Ester
24. Nisoldipino
25. Nisoldipine 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
26. Ncgc00164633-01
27. Dsstox_cid_3371
28. Dsstox_rid_76999
29. Dsstox_gsid_23371
30. 3-methyl 5-(2-methylpropyl) 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
31. Smr000466370
32. Cas-63675-72-9
33. Sular (tn)
34. Sr-05000002009
35. Einecs 264-407-7
36. Mfcd00478055
37. Unii-4i8hab65sz
38. Brn 0454188
39. Nisoldipine (jan/usan/inn)
40. Nisoldipine;
41. Nisoldipine,(s)
42. Nisoldipine [usan:inn:ban:jan]
43. (+-)-isobutyl Methyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(o-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
44. Isobutyl 1,4-dihydro-5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3-pyridincarboxylat
45. Nisoldipine, ~97%
46. Nisoldipine [mi]
47. Nisoldipine [inn]
48. Nisoldipine [jan]
49. (.+/-.)-nisoldipine
50. Nisoldipine [usan]
51. Nisoldipine [vandf]
52. Baymycard, Norvasc, Syscor
53. Chembl1726
54. Nisoldipine [mart.]
55. Schembl39779
56. (+/-)-nisoldipine
57. Nisoldipine [usp-rs]
58. Nisoldipine [who-dd]
59. 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid Methyl 2-methylpropyl Ester
60. Mls000759498
61. Mls001424102
62. Mls002153943
63. Bidd:gt0684
64. Gtpl2524
65. Chembl3192341
66. Dtxsid0023371
67. Nisoldipine, >=98% (hplc)
68. Nisoldipine [orange Book]
69. Hms2051o18
70. Hms2089k20
71. Hms2093f15
72. Hms2097e13
73. Hms2231l20
74. Hms3393o18
75. Hms3651k17
76. Hms3714e13
77. Hms3744o19
78. Hms3884i08
79. Pharmakon1600-01505390
80. Bcp22696
81. Tox21_112251
82. Tox21_302365
83. Ac-987
84. Bbl028683
85. Bdbm50101963
86. Bdbm50227259
87. Dl-255
88. Nsc759106
89. S1748
90. Stk631543
91. Akos005563632
92. Akos037515714
93. Tox21_112251_1
94. Ccg-100894
95. Ccg-213412
96. Cs-1131
97. Db00401
98. Ks-5188
99. Nc00144
100. Nsc 759106
101. Bay K 5552;bay-k 5552;sular
102. Isobutyl Methyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
103. O5-isobutyl O3-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
104. Ncgc00164633-02
105. Ncgc00164633-03
106. Ncgc00255136-01
107. 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid Isobutyl Methyl Ester
108. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, Methyl 2-methylpropyl Ester, (+-)-
109. 6-bromo-2,3-dimethoxybenzoicacid
110. Bn164147
111. Hy-17402
112. (+/-)-bay-k-5552
113. Sbi-0206830.p001
114. ((c)i)-nisoldipine-d4(2-nitrophenyl-d4)
115. Ft-0601599
116. N0900
117. Sw219237-1
118. C07699
119. D00618
120. Ab01275444-01
121. Ab01275444_02
122. 675n729
123. A834466
124. Q3342150
125. Sr-05000002009-1
126. Sr-05000002009-2
127. Sr-05000002009-3
128. Brd-a84465106-001-01-2
129. Z277942268
130. 3-isobutyl5-methyl2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
131. Isobutyl Methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
132. (.+/-.)-isobutyl Methyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(o-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
133. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, 3-methyl 5-(2-methylpropyl) Ester
134. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, Methyl 2-methylpropyl Ester, (+/-)-
135. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, Methyl 2-methylpropyl Ester, (.+/-.)-
136. 3-isobutyl 5-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate #
137. Methyl 2-methylpropyl-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate, Dl-
138. O5-isobutyl O3-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate;nisoldipine
139. O5-methyl O3-(2-methylpropyl) 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
| Molecular Weight | 388.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H24N2O6 |
| XLogP3 | 3.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 388.16343649 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 388.16343649 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 110 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 704 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Nisoldipine |
| PubMed Health | Nisoldipine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Nisoldipine is an extended-release tablet dosage form of the dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker nisoldipine. Nisoldipine is ()-Isobutyl methyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(o-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate, C20H24N2O6, and has the struct... |
| Active Ingredient | Nisoldipine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 34mg; 8.5mg; 30mg; 25.5mg; 17mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Sular |
| PubMed Health | Nisoldipine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | SULAR (nisoldipine) is an extended release tablet dosage form of the dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker nisoldipine. Nisoldipine is 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, methyl 2-methylpropyl ester, C20H24... |
| Active Ingredient | Nisoldipine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 34mg; 8.5mg; 17mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Shionogi |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Nisoldipine |
| PubMed Health | Nisoldipine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Nisoldipine is an extended-release tablet dosage form of the dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker nisoldipine. Nisoldipine is ()-Isobutyl methyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(o-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate, C20H24N2O6, and has the struct... |
| Active Ingredient | Nisoldipine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 34mg; 8.5mg; 30mg; 25.5mg; 17mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Sular |
| PubMed Health | Nisoldipine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antihypertensive, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | SULAR (nisoldipine) is an extended release tablet dosage form of the dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker nisoldipine. Nisoldipine is 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, methyl 2-methylpropyl ester, C20H24... |
| Active Ingredient | Nisoldipine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 34mg; 8.5mg; 17mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Shionogi |
For the treatment of hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
Nisoldipine, a dihydropyridine calcium-channel blocker, is used alone or with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, to treat hypertension, chronic stable angina pectoris, and Prinzmetal's variant angina. Nisoldipine is similar to other peripheral vasodilators. Nisoldipine inhibits the influx of extra cellular calcium across the myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes possibly by deforming the channel, inhibiting ion-control gating mechanisms, and/or interfering with the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The decrease in intracellular calcium inhibits the contractile processes of the myocardial smooth muscle cells, causing dilation of the coronary and systemic arteries, increased oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue, decreased total peripheral resistance, decreased systemic blood pressure, and decreased afterload.
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)
Calcium Channel Blockers
A class of drugs that act by selective inhibition of calcium influx through cellular membranes. (See all compounds classified as Calcium Channel Blockers.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C08 - Calcium channel blockers
C08C - Selective calcium channel blockers with mainly vascular effects
C08CA - Dihydropyridine derivatives
C08CA07 - Nisoldipine
Absorption
Relatively well absorbed into the systemic circulation with 87% of the radiolabeled drug recovered in urine and feces. The absolute bioavailability of nisoldipine is about 5%.
Route of Elimination
Although 60-80% of an oral dose undergoes urinary excretion, only traces of unchanged nisoldipine are found in urine.
Pre-systemic metabolism in the gut wall, and this metabolism decreases from the proximal to the distal parts of the intestine. Nisoldipine is highly metabolized; 5 major urinary metabolites have been identified. The major biotransformation pathway appears to be the hydroxylation of the isobutyl ester. A hydroxylated derivative of the side chain, present in plasma at concentrations approximately equal to the parent compound, appears to be the only active metabolite and has about 10% of the activity of the parent compound. Cytochrome P450 enzymes are believed to play a major role in the metabolism of nisoldipine. The particular isoenzyme system responsible for its metabolism has not been identified, but other dihydropyridines are metabolized by cytochrome P450 IIIA4.
Nisoldipine has known human metabolites that include 2,6-Dimethyl-5-(2-methylpropoxycarbonyl)-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid, 5-O-(1-hydroxy-2-methylpropyl) 3-O-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, and Dehydro Nisoldipine.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
7-12 hours
By deforming the channel, inhibiting ion-control gating mechanisms, and/or interfering with the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, Nisoldipine inhibits the influx of extracellular calcium across the myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes The decrease in intracellular calcium inhibits the contractile processes of the myocardial smooth muscle cells, causing dilation of the coronary and systemic arteries, increased oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue, decreased total peripheral resistance, decreased systemic blood pressure, and decreased afterload.