

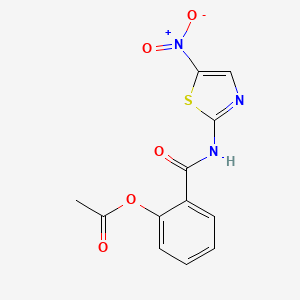

1. 2-(acetolyloxy)-n-(5-nitro-2-thiazolyl)benzamide
2. Alinia
3. Colufase
4. Cryptaz
5. Daxon
6. Heliton
7. Ntz
8. Taenitaz
1. 55981-09-4
2. Alinia
3. 2-((5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)carbamoyl)phenyl Acetate
4. Nitazoxamide
5. Daxon
6. Nitazoxanidum [inn-latin]
7. Nitazoxanida [inn-spanish]
8. 2-[(5-nitro-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)carbamoyl]phenyl Acetate
9. Benzamide, 2-(acetyloxy)-n-(5-nitro-2-thiazolyl)-
10. [2-[(5-nitro-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)carbamoyl]phenyl] Acetate
11. 2-(acetolyloxy)-n-(5-nitro-2-thiazolyl)benzamide
12. Nsc 697855
13. Nsc697855
14. Ntz
15. 2-acetyloxy-n-[(5-nitro-2-thiazolyl)]benzamide
16. Nsc-697855
17. Nsc-760057
18. N-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)salicylamide Acetate Ester
19. Ph 5776
20. Ph-5776
21. Nitazoxanide (alinia, Annita)
22. Soa12p041n
23. Nitazoxanida
24. Cryptaz
25. [2-[(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)carbamoyl]phenyl] Acetate
26. Ncgc00090774-01
27. Nitazoxanid
28. Nitazoxanidum
29. Colufase
30. Heliton
31. Dsstox_cid_13757
32. Dsstox_rid_79095
33. Dsstox_gsid_33757
34. Phavic-1
35. Smr000466367
36. Alinia (tn)
37. Azt + Nitazoxanide
38. Cas-55981-09-4
39. Einecs 259-931-8
40. Nitazoxanide (usan/inn)
41. (2-((5-nitro-2-thiazolyl)carbamoyl)phenyl)acetat
42. Brn 1225475
43. Unii-soa12p041n
44. N-(5-nitro-2-thiazolyl)salicylamide Acetate (ester)
45. Nitrazoxanide
46. Pacovanton
47. Dexidex
48. Kidonax
49. Nitazox
50. Paramix
51. Nitax
52. Toza
53. Nitazoxanide [usan:inn:ban]
54. Alinia(tm)
55. Mfcd00416599
56. O-(n-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)carbamoyl)phenyl Acetate
57. Nitazoxanide- Bio-x
58. Salicylamide, N-(5-nitro-2-thiazolyl)-, Acetate (ester)
59. Cpd000466367
60. Nitazoxanide [mi]
61. Nitazoxanide [inn]
62. Ncimech_000843
63. Nitazoxanide [usan]
64. Chembl1401
65. Nitazoxanide [vandf]
66. 2-(acetyloxy)-n-(5-nitro-2-thiazolyl)benzamide
67. Oprea1_263587
68. Schembl40981
69. Nitazoxanide [mart.]
70. Mls000759492
71. Mls001424074
72. Mls006010127
73. Nitazoxanide [usp-rs]
74. Nitazoxanide [who-dd]
75. Dtxsid5033757
76. Chebi:94807
77. Nitazoxanide [green Book]
78. Nitazoxanide, >=98% (hplc)
79. Ntz;nsc 697855
80. Hms2051l04
81. Hms3393l04
82. Hms3655m11
83. Hms3715f10
84. Nitazoxanide [orange Book]
85. Pharmakon1600-01503843
86. Bcp13918
87. Hy-b0217
88. Zinc3956788
89. Tox21_111018
90. Tox21_201226
91. Bdbm50075050
92. Ccg-35851
93. Mmv688991
94. Nsc760057
95. Stk395664
96. Akos015915393
97. Tox21_111018_1
98. Ac-1302
99. Db00507
100. Ks-1160
101. Nc00246
102. Ncgc00090774-02
103. Ncgc00090774-03
104. Ncgc00090774-04
105. Ncgc00090774-05
106. Ncgc00258778-01
107. Bn164151
108. Nci60_034935
109. Ft-0601547
110. N1031
111. Nitrazoxanide 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
112. S1627
113. Sw197626-2
114. 2-(5-nitrothiazol-2-ylcarbamoyl)phenyl Acetate
115. D02486
116. Ab00639988-07
117. Ab00639988-09
118. Ab00639988_10
119. Ab00639988_11
120. 2-(acetyloxy)-n-(5-nitro-2-thiazolyl)-benzamide
121. 981n094
122. A830877
123. Sr-01000759418
124. Q-201475
125. Q2943789
126. Sr-01000759418-9
127. Salicylamide, N-(5-nitro-2-thiazolyl)- Acetate (ester)
128. Z1514087129
129. Nitazoxanide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
130. Acetic Acid [2-[[(5-nitro-2-thiazolyl)amino]-oxomethyl]phenyl] Ester
131. Zox
| Molecular Weight | 307.28 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H9N3O5S |
| XLogP3 | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 307.02629157 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 307.02629157 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 142 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 428 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Alinia |
| PubMed Health | Nitazoxanide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiprotozoal |
| Drug Label | Alinia Tablets and Alinia for Oral Suspension contain the active ingredient, nitazoxanide, a synthetic antiprotozoal agent for oral administration. Nitazoxanide is a light yellow crystalline powder. It is poorly soluble in ethanol and practically ins... |
| Active Ingredient | Nitazoxanide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; For suspension |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 100mg/5ml; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Romark |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Alinia |
| PubMed Health | Nitazoxanide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiprotozoal |
| Drug Label | Alinia Tablets and Alinia for Oral Suspension contain the active ingredient, nitazoxanide, a synthetic antiprotozoal agent for oral administration. Nitazoxanide is a light yellow crystalline powder. It is poorly soluble in ethanol and practically ins... |
| Active Ingredient | Nitazoxanide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; For suspension |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 100mg/5ml; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Romark |
For the treatment of diarrhea in adults and children caused by the protozoa Giardia lamblia, and for the treatment of diarrhea in children caused by the protozoan, Cryptosporidium parvum. Nitazoxanide has not been shown to be superior to placebo medication for the management of diarrhea caused by Cryptosporidium parvum in patients with HIV/immunodeficiency.
FDA Label
The general effect of this medication is the prevention of microbe activity through disruption of important energy pathways for survival and proliferation. Nitazoxanide exhibits antiprotozoal activity by interfering with the pyruvate ferredoxin/flavodoxin oxidoreductase dependent electron transfer reaction, an essential reaction need for anaerobic energy metabolism of various microorganisms. Sporozoites of Cryptosporidium parvum and trophozoites of Giardia lamblia are therefore inhibited, relieving symptoms of diahrrea. Interference with the PFOR enzyme-dependent electron transfer reaction may only be one of the many pathways by which nitazoxanide exhibits antiprotozoal activity.
Antiparasitic Agents
Drugs used to treat or prevent parasitic infections. (See all compounds classified as Antiparasitic Agents.)
P - Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents
P01 - Antiprotozoals
P01A - Agents against amoebiasis and other protozoal diseases
P01AX - Other agents against amoebiasis and other protozoal diseases
P01AX11 - Nitazoxanide
Absorption
The relative bioavailability of the suspension compared to the tablet was 70%. When administered with food the AUC and Cmax increased by two-fold and 50%, respectively, for the tablet and 45 to 50% and ≤ 10%, respectively, for the oral suspension.
Route of Elimination
Tizoxanide is excreted in the urine, bile and feces, and tizoxanide glucuronide is excreted in urine and bile. Approximately 2/3 of the oral dose of nitazoxanide is excreted in the faeces and 1/3 in the urine.
Clearance
Nitazoxanide is cleared in the urine and feces. The metabolite, tizoxanide, is also found in the urine, plasma, and breastmilk. The drug is not found unchanged in the urine.
The active metabolite of this drug is tizoxanide (desacetyl-nitazoxanide). The initial reaction in the metabolic pathway of Nitazoxanide is hydrolysis to tizoxanide, followed by conjugation, primarily by glucuronidation to tizoxanide glucuronide. The oral suspension bioavailability of this drug is not equivalent to that of the oral tablets. Compared to the to the tablet, the bioavailability of the suspension was 70%. When administered with food, the AUCt of tizoxanide and tizoxanide glucuronide in plasma is increased to almost two-fold and the maximum concentration is increased by almost 50% compared to when ingested without food. When the oral suspension was ingested with food, the AUC of tizoxanide and tizoxanide glucuronide increased by approximately 50% and the Cmax increased by less than 10%.
7.3h
The most widely accepted mechanism of NTZ is believed to be the disruption of the energy metabolism in anaerobic microbes by inhibition of the pyruvate: ferredoxin/flavodoxin oxidoreductase (PFOR) cycle. In parasitic-protozoa, Nitazoxanide also induces lesions in the cell membranes and depolarizes the mitochondrial membrane while inhibiting quinone oxidoreductase NQO1, nitroreductase-1 and protein disulphide isomerase enzymes. In addition, this drug also inhibits the glutathione-S-transferase (a major detoxifying enzyme) and modulates the Avr-14 gene, encoding for the alpha-type subunit of glutamate-gated chloride ion channel present in nematodes. Aside from its well understood non-competitive inhibition of the PFOR in anaerobic bacteria, NTZ also demonstrates various other antibacterial mechanisms. It inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase in E Coli, disrupts the membrane potential and pH homeostasis in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis, suppresses the chaperone/usher (CU) pathway of the gram-negative bacteria, and stimulates host macrophage autophagy in tuberculosis patients. NTZ also suppresses viral replication by inhibiting the maturation of the viral hemagglutinin and the viral transcription factor immediate early 2 (IE2) as well as by activating the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (an antiviral intracellular protein). Lastly, NTZ exhibits an inhibitory effect on tumor cell progression by altering drug detoxification (glutathione-S-transferase P1), unfolded protein response, autophagy, anti-cytokines activity, and c-Myc inhibition.