

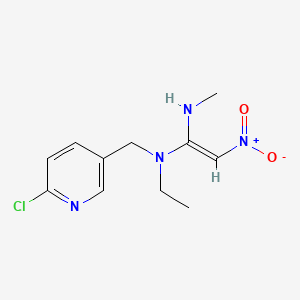

1. (1e)-n-((6-chloro-3-pyridinyl)methyl)-n-ethyl-n'-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine
2. (e)-n-(6-chloro-3-pyridylmethyl)-n-ethyl-n'-methyl-2-nitrovinylidenediamine
1. 150824-47-8
2. (e)-nitenpyram
3. 120738-89-8
4. Niterndipoine
5. Bestguard
6. Capstar
7. (e)-n-((6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl)-n-ethyl-n'-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine
8. Nitenpyram [iso]
9. Ti 304
10. Chebi:39170
11. (1e)-n-((6-chloro-3-pyridinyl)methyl)-n-ethyl-n'-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine
12. N-((6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl)-n-ethyl-n-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine
13. (e)-n-[(6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl]-n-ethyl-n'-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine
14. (e)-1-n'-[(6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl]-1-n'-ethyl-1-n-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine
15. 3a837vz81y
16. Ncgc00166149-01
17. (e)-n-(6-chloro-3-pyridylmethyl)-n-ethyl-n'-methyl-2-nitrovinylidenediamine
18. N-((6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl)-n-ethyl-n'-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine
19. Dsstox_cid_21080
20. Dsstox_rid_79622
21. Dsstox_gsid_41080
22. (1e)-n-[(6-chloro-3-pyridinyl)methyl]-n-ethyl-n'-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine
23. 1,1-ethenediamine, N-((6-chloro-3-pyridinyl)methyl)-n-ethyl-n'-methyl-2-nitro-, (1e)-
24. 1,1-ethenediamine, N-[(6-chloro-3-pyridinyl)methyl]-n-ethyl-n'-methyl-2-nitro-, (1e)-
25. Cas-150824-47-8
26. Unii-3a837vz81y
27. N-[(6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl]-n-ethyl-n'-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine
28. Nitenpyram [mi]
29. Schembl25788
30. Schembl25789
31. Chembl259728
32. Nitenpyram [green Book]
33. Dtxsid8041080
34. Chebi:39171
35. Hsdb 8491
36. Hms3885b06
37. Hy-b0820
38. Zinc2381598
39. Tox21_112342
40. Bdbm50486236
41. Mfcd01631161
42. Ti-304
43. (e)-n-(6-chloro-3-pyridylmethyl)-n-ethyl-n2-methyl-2-nitrovinylidenediamine
44. Akos015914907
45. Nitenpyram 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
46. Tox21_112342_1
47. Ccg-267169
48. Db11438
49. Ks-5369
50. (1e)-n-((6-chloro-3-pyridinyl)methyl]-n-ethyl-n2-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine
51. (e)-n-(6-chloro-3-pyridylmethyl)-n-ethyl-n'-methyl-2-nitroethylene-1,1-diamine
52. Nitenpyram 1000 Microg/ml In Methanol
53. Ncgc00166149-02
54. Nitenpyram 10 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
55. Cs-0012837
56. S4422
57. Nitenpyram, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
58. A14229
59. C18511
60. 738n898
61. A804578
62. A809078
63. Q-201476
64. Q3817186
65. Q27119765
66. N-ethyl-n-[1-(methylamino)-2-nitroethenyl]-6-chloropyridine-3-methanamine
67. (e)-n-((6-chloro-3-pyridinyl)methyl)-n-ethyl-n'-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine
68. (e)-n-((6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl)-n-ethyl-n-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine
69. [(e)-1-{[(6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl](ethyl)amino}-2-nitroethenyl](methyl)amine
70. 1,1-ethenediamine, N-((6-chloro-3-pyridinyl)methyl)-n-ethyl-n-methyl-2-nitro-
71. N-[(6-chloro-3-pyridinyl)methyl]-n-ethyl-n'-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine
72. N1-[(6-chloro-3-pyridyl)methyl]-n1'-ethyl-n1'-methyl-2-nitro-ethene-1,1-diamine
73. (e)-n1'-[(6-chloro-3-pyridyl)methyl]-n1'-ethyl-n1-methyl-2-nitro-ethene-1,1-diamine;nitenpyram
| Molecular Weight | 270.71 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H15ClN4O2 |
| XLogP3 | 2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 270.0883534 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 270.0883534 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 74 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 306 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
VET: Nitenpyram inhibits the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. It is used to treat Ctenocephalides spp in dogs and cats ... . It is toxic to fleas for only 24-48 hr and is normally used in combination with an insect growth regulator to provide continuous flea control.
Kahn, C.M (ed.).; The Merck Veterinary Manual 10th Edition. Merck & Co. Whitehouse Station NJ. 2010, p. 2197
VET: Nitenpyram is indicated as a flea adulticide in dogs and cats that are, at a minimum, 2 pounds in weight and 4 weeks old. It does not repel fleas or ticks and does not reliably kill ticks, flea eggs, larvae or immature fleas. Nitenpyram may be effective for treating fly larvae (maggots) of various species. Fleas begin to fall from treated animals about 30 minutes after dosing and a single dose can protect animals for 1-2 days.
Plumb D.C. Veterinary Drug Handbook. 8th ed. (pocket). Ames, IA: Wiley-Blackwell, 2015., p. 1048
VET: The following adverse events are based on post-approval adverse drug experience reporting. Not all adverse reactions are reported to FDA CVM. It is not always possible to reliably estimate the adverse event frequency or establish a causal relationship to product exposure using this data. The following adverse events are listed in decreasing order of reporting frequency. Cats: hyperactivity, panting, lethargy, itching, vocalization, vomiting, fever, decreased appetite, nervousness, diarrhea, difficulty breathing, salivation, incoordination, seizures, pupil dilation, increased heart rate, and trembling. Dogs: lethargy/depression, vomiting, itching, decreased appetite, diarrhea, hyperactivity, incoordination, trembling, seizures, panting, allergic reactions including hives, vocalization, salivation, fever, and nervousness. The frequency of serious signs, including neurologic signs and death, was greater in animals under 2 pounds of body weight, less than 8 weeks of age, and/or reported to be in poor body condition. In some instances, birth defects and fetal/neonatal loss were reported after treatment of pregnant and/or lactating animals.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Capstar-nitenpyram capsule (Updated: October 17, 2018). Available from, as of November 27, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=71454d3d-6bd3-49ef-89c2-bd930adcb421
Insecticides
Pesticides designed to control insects that are harmful to man. The insects may be directly harmful, as those acting as disease vectors, or indirectly harmful, as destroyers of crops, food products, or textile fabrics. (See all compounds classified as Insecticides.)
Nitenpyram is rapidly and practically completely absorbed after oral administration. Peak levels occur approximately 80 minutes after dosing in dogs; approximately 40 minutes in cats. Elimination half-lives are: approximately 3 hours for dogs; 8 hours for cats. Nitenpyram is excreted primarily as conjugated metabolites in the urine and excretion is complete within 48 hours of dosing. In dogs, approximately 3% of a dose is excreted in feces; in cats approximately 5% is excreted in the feces.
Plumb D.C. Veterinary Drug Handbook. 8th ed. (pocket). Ames, IA: Wiley-Blackwell, 2015., p. 1048
Nitenpyram is administered PO in pill form to kill fleas in both dogs and cats. It is absorbed rapidly, with maximal blood concentrations reached within 1.2 hr and 0.6 hr in dogs and cats, respectively. ... The compound is rapidly eliminated, with >90% excreted in the urine within 24-48 hr, primarily as unchanged nitenpyram.
Kahn, C.M (ed.).; The Merck Veterinary Manual 10th Edition. Merck & Co. Whitehouse Station NJ. 2010, p. 2360
BACKGROUND: Nitenpyram is a member of the economically important neonicotinoid class of insecticides. The in vivo metabolism of nitenpyram is not well characterized, but cytochrome P450 activity is the major mechanism of resistance to neonicotinoids identified in insect pests, and P450s metabolize other neonicotinoids including imidacloprid. RESULTS: Here, we used the GAL4-UAS targeted expression system to direct RNA interference (RNAi) against the cytochrome P450 redox partners to interrupt P450 functions in specific tissues in Drosophila melanogaster. RNAi of the mitochondrial redox partner defective in the avoidance of repellents (dare) in the digestive tissues reduced nitenpyram mortality, suggesting an activation step in the metabolism of nitenpyram carried out by a mitochondrial P450. RNAi of the mitochondrial cytochrome P450 Cyp12a5, which is expressed in the digestive tissues, resulted in the same phenotype, and transgenic overexpression of Cyp12a5 increased nitenpyram sensitivity. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that in vivo metabolism of nitenpyram by the mitochondrial P450 CYP12A5 results in the formation of a product with higher toxicity than the parent compound.
PMID:29316188 Harrop TW et al; Pest Manag Sci 74 (7): 1616-1622 (2018)
Elimination half-lives /after oral dosing/ are: approximately 3 hours for dogs; 8 hours for cats.
Plumb D.C. Veterinary Drug Handbook. 8th ed. (pocket). Ames, IA: Wiley-Blackwell, 2015., p. 1048
Nitenpyram is in the class of neonicotinoid insecticides. It enters the systemic circulation of the adult flea after consuming blood from a treated animal. It binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the postsynaptic membranes and blocks acetylcholine-mediated neuronal transmission causing paralysis and death of the flea. Nitenpyram is 3500x more selective for insect alpha-4beta-2 nicotinic receptors than in vertebrate receptors. It does not inhibit acetylcholinesterase.
Plumb D.C. Veterinary Drug Handbook. 8th ed. (pocket). Ames, IA: Wiley-Blackwell, 2015., p. 1048
