

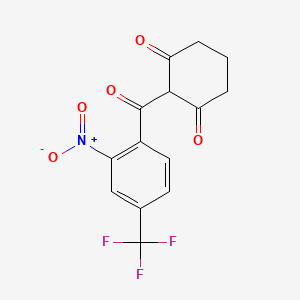

1. 2-(2-nitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl)cyclohexane-1,3-dione
2. 2-(2-nitro-4-trifluoromethylbenzoyl)-1,3-cyclohexanedione
3. Ntbc Cpd
4. Orfadin
1. 104206-65-7
2. Orfadin
3. 2-(2-nitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl)cyclohexane-1,3-dione
4. Nitisone
5. Ntbc
6. 2-(2-nitro-4-trifluoromethylbenzoyl)-1,3-cyclohexanedione
7. 2-[2-nitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl]cyclohexane-1,3-dione
8. 2-(2-nitro-4-trifluoromethylbenzoyl)cyclohexane-1,3-dione
9. Sc 0735
10. Sc-0735
11. 2-(alpha,alpha,alpha-trifluoro-2-nitro-p-tuluoyl)-1,3-cyclohexanedione
12. 1,3-cyclohexanedione, 2-[2-nitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl]-
13. 2-{[2-nitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbonyl}cyclohexane-1,3-dione
14. Chembl1337
15. Chebi:50378
16. 1,3-cyclohexanedione, 2-(2-nitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl)-
17. Mfcd01752192
18. Sc0735
19. K5bn214699
20. Nitisinone [inn]
21. Nitisinone [usan:inn]
22. Nitisinona
23. Nitisinonum
24. Smr002529592
25. Orfadin (tn)
26. Nitisinone (jan/usan/inn)
27. Unii-k5bn214699
28. Nityr
29. Fe-0200
30. 2-[2-nitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl]-1,3-cyclohexanedione
31. Nitisinone [mi]
32. Nitisinone [jan]
33. Nitisinone [usan]
34. Nitisinone [vandf]
35. Nitisinone [mart.]
36. Nitisinone [who-dd]
37. Bidd:pxr0129
38. Mls004774025
39. Mls006011955
40. Nitisinone [ema Epar]
41. Schembl338795
42. Ambz0071
43. Gtpl6834
44. Dtxsid9042673
45. Nitisinone [orange Book]
46. Nitisinone, >=95% (hplc)
47. Schembl15996621
48. Hms3740a15
49. Hms3870k03
50. Bcp15276
51. Hy-b0607
52. Bdbm50088804
53. Nsc773149
54. Rb3134
55. S5325
56. Akos015891363
57. Akos015994590
58. Zinc100014475
59. Am62666
60. Ccg-222085
61. Db00348
62. Ex-6233
63. Nsc-773149
64. Sb19017
65. Ncgc00185778-01
66. Ncgc00185778-02
67. Ncgc00185778-04
68. Ncgc00185778-07
69. Ac-26934
70. Sy047291
71. Db-014936
72. Ft-0672739
73. D05177
74. A800922
75. Sr-01000940576
76. J-505680
77. Q3877355
78. Sr-01000940576-2
79. Ntbc; Nitisone; Sc0735; Sc 0735; Sc-0735
80. Z1514110653
81. 1,3-cyclohexanedione,2-[2-nitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl]-
82. 2-(2-nitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-benzoyl)cyclohexane-1,3-dione
83. 2-[2-nitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl]cyclohexane-1,3-dione;nitisinone
84. 2-(.alpha.,.alpha.,.alpha.-trifluoro-2-nitro-p-tuluoyl)-1,3-cyclohexanedione
| Molecular Weight | 329.23 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H10F3NO5 |
| XLogP3 | 2.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 329.05110691 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 329.05110691 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 97 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 524 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Orfadin |
| PubMed Health | Nitisinone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Drug Label | Orfadin contains nitisinone, which is a hydroxyphenyl-pyruvate dioxygenase inhibitor indicated as an adjunct to dietary restriction of tyrosine and phenylalanine in the treatment of hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 (HT-1). Nitisinone occurs as white to... |
| Active Ingredient | Nitisinone |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg; 2mg; 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Swedish Orphan |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Orfadin |
| PubMed Health | Nitisinone (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Drug Label | Orfadin contains nitisinone, which is a hydroxyphenyl-pyruvate dioxygenase inhibitor indicated as an adjunct to dietary restriction of tyrosine and phenylalanine in the treatment of hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 (HT-1). Nitisinone occurs as white to... |
| Active Ingredient | Nitisinone |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg; 2mg; 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Swedish Orphan |
Used as an adjunct to dietary restriction of tyrosine and phenylalanine in the treatment of hereditary tyrosinemia type 1.
FDA Label
Hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 (HT 1)
Orfadin is indicated for the treatment of adult and paediatric (in any age range) patients with confirmed diagnosis of hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 (HT 1) in combination with dietary restriction of tyrosine and phenylalanine.
Alkaptonuria (AKU)
Orfadin is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with alkaptonuria (AKU).
Treatment of adult and paediatric patients with confirmed diagnosis of hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 (HT-1) in combination with dietary restriction of tyrosine and phenylalanine.
Treatment of adult and paediatric (in any age range) patients with confirmed diagnosis of hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 (HT 1) in combination with dietary restriction of tyrosine and phenylalanine.
Treatment of tyrosinemia type 1
Hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 occurs due to a deficiency in fumarylacetoacetase (FAH), the final enzyme in the tyrosine catabolic pathway. Nitisinone inhibits catabolism of tyrosine by preventing the catabolic intermediates. In patients with HT-1, these catabolic intermediates are converted to the toxic metabolites succinylacetone and succinylacetoacetate, which are responsible for the observed liver and kidney toxicity. Succinylacetone can also inhibit the porphyrin synthesis pathway leading to the accumulation of 5-aminolevulinate, a neurotoxin responsible for the porphyric crises characteristic of HT-1.
Enzyme Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme combination and the catalytic reaction. (See all compounds classified as Enzyme Inhibitors.)
A16AX04
A16AX04
A16AX04
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A16 - Other alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16A - Other alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16AX - Various alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16AX04 - Nitisinone
Absorption
The capsule and liquid formulations are bioequivalent in both the plasma concentration-time curve and maximum plasma concentration (Cmax).
~54 hours
Nitisinone is a competitive inhibitor of 4-hydroxyphenyl-pyruvate dioxygenase, an enzyme upstream of fumarylacetoacetate hydrolyase (FAH) in the tyrosine catabolic pathway. By inhibiting the normal catabolism of tyrosine in patients with hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 (HT-1), nitisinone prevents the accumulation of the catabolic intermediates maleylacetoacetate and fumarylacetoacetate.