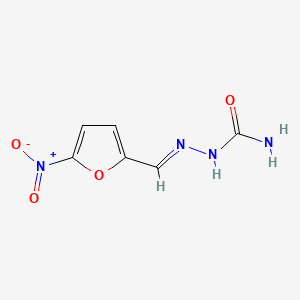

1. Furacilin
2. Furacillin
3. Furacin
4. Nitrofural
5. Nitrofurazone, Calcium (2:1) Salt
1. Nitrofural
2. 59-87-0
3. Furacilin
4. Furacin
5. Furacillin
6. Actin-n
7. 5-nitro-2-furaldehyde Semicarbazone
8. Aldomycin
9. Furacine
10. Furaldon
11. Nifuzon
12. Babrocid
13. Chemofuran
14. Furacinetten
15. Furacoccid
16. Furacycline
17. Furaplast
18. Furaziline
19. Furazone
20. Mastofuran
21. Monafuracin
22. Nitrofurazan
23. Nitrozone
24. Otofuran
25. Alfucin
26. Amifur
27. Furesol
28. Mammex
29. Nefco
30. Furazol W
31. 5-nitrofurfural Semicarbazone
32. Becafurazone
33. Biofuracina
34. Dermofural
35. Furametral
36. Furaseptyl
37. Furatsilin
38. Fuvacillin
39. Monafuracis
40. Monofuracin
41. Nitrofurol
42. Biofurea
43. Cocafurin
44. Coxistat
45. Dynazone
46. Eldezol
47. Fedacin
48. Flavazone
49. Fracine
50. Furacort
51. Furaderm
52. Furagent
53. Furalone
54. Furaskin
55. Furazin
56. Furazina
57. Furazyme
58. Furfurin
59. Furosem
60. Hemofuran
61. Ibiofural
62. Nifucin
63. Nifurid
64. Otofural
65. Sanfuran
66. Vabrocid
67. Vadrocid
68. Yatrocin
69. Chixin
70. 5-nitrofurazone
71. Furan-ofteno
72. Spray-dermis
73. Spray-foral
74. Furacin-hc
75. Nitrofuralum
76. Eldezol F-6
77. Furacilinum
78. Nitrofurane
79. (5-nitro-2-furfurylidenamino)urea
80. Furacin-e
81. Nitrofuraldehyde Semicarbazone
82. 5-nitrofuraldehyde Semicarbazide
83. Usaf Ea-4
84. Rivafurazon
85. Fura-septin
86. Veterinary Nitrofurazone
87. Nsc-2100
88. Nitrofuran (bactericide)
89. Nf-7
90. 6-nitrofuraldehyde Semicarbazide
91. Nitrofural [inn]
92. 5-nitro-2-furfural Semicarbazone
93. 1-(5-nitro-2-furfurylidene)semicarbazide
94. 5-nitrofuran-2-aldehyde Semicarbazone
95. 5-nitro-2-furfuraldehyde Semicarbazone
96. Nci-c56064
97. 5-nitro-2-furancarboxaldehyde Semicarbazone
98. Semikarbazon 5-nitrofurfuralu
99. Nfz
100. Hydrazinecarboxamide, 2-[(5-nitro-2-furanyl)methylene]-
101. Nsc-1602
102. U-6421
103. 2-furaldehyde, 5-nitro-, Semicarbazone
104. 5-nitrofuran-2-carbaldehyde Semicarbazone
105. 2-[(5-nitro-2-furanyl)methylene]-hydrazinecarboxamide
106. X8xi70b5z6
107. Nfs
108. 2-furancarboxaldehyde, 5-nitro-, Semicarbazone
109. Nsc1602
110. Nsc2100
111. [(e)-(5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methylideneamino]urea
112. Component Of Furea
113. (5-nitro-2-furfurylideneamino)urea
114. Nitrofural (inn)
115. Component Of Furadex
116. 2-[(5-nitro-2-furanyl)methylene]hydrazinecarboxamide
117. Component Of Furacort
118. 112574-44-4
119. Hydrazinecarboxamide, 2-((5-nitro-2-furanyl)methylene)-
120. Ncgc00090686-04
121. Ncgc00090686-07
122. Nitrofurazonum
123. Dsstox_cid_944
124. Dsstox_rid_75881
125. Dsstox_gsid_20944
126. 2-((5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinecarboxamide
127. Wln: T5oj Bnw E1unmvz
128. (2e)-2-[(5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methylidene]hydrazinecarboxamide
129. Dymazone
130. Furalcyn
131. Acutol
132. 2-furancarboxaldehyde, Semicarbazone
133. Rivopon-5
134. (e)-2-((5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinecarboxamide
135. Sr-05000002027
136. Mfcd00003225
137. 2-((5-nitro-2-furanyl)methylene)hydrazinecarboxamide
138. Nitrofuralum [inn-latin]
139. Chebi:44368
140. Unii-x8xi70b5z6
141. Ccris 1195
142. Nitrofurazone [usp:inn:ban]
143. Nfz Mix
144. Hsdb 3136
145. Cas-59-87-0
146. Nsc 1602
147. Nsc 2100
148. Prestwick_806
149. 2-[(5-nitro-2-furyl)methylene]hydrazinecarboxamide
150. Einecs 200-443-1
151. Furacin (tn)
152. 2((5-nitro-2-furanyl)methylene)hydrazinecarboxamide
153. Nitrofurazone (usp)
154. Semikarbazon 5-nitrofurfuralu [polish]
155. Brn 0086403
156. Ai3-17333
157. [(e)-(5-nitro-2-furyl)methyleneamino]urea
158. Prestwick2_000492
159. Prestwick3_000492
160. Spectrum5_001160
161. Nitrofural [iarc]
162. Nitrofurazone (nitrofural)
163. Nitrofurazone [mi]
164. Chembl869
165. Nitrofural [who-dd]
166. Nitrofurazone [hsdb]
167. Nitrofurazone [inci]
168. Schembl25416
169. Schembl25417
170. Bspbio_000383
171. Bspbio_002075
172. Nitrofurazone [vandf]
173. Mls002153843
174. Nitrofurazone [mart.]
175. Spectrum1500434
176. Nitrofurazone [usp-rs]
177. Bpbio1_000423
178. Component Of Furea (salt/mix)
179. Component Of Furadex (salt/mix)
180. Hms502g20
181. Nitrofural [ep Monograph]
182. (e)-2-((5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine-1-carboxamide
183. Hms1569d05
184. Hms1920b04
185. Hms2091j04
186. Hms2096d05
187. Hms3713d05
188. Nitrofurazone [green Book]
189. Pharmakon1600-01500434
190. Nitrofurazone [orange Book]
191. Hy-b0226
192. Zinc4802968
193. Tox21_110997
194. Tox21_202988
195. Tox21_400035
196. Bdbm50420350
197. Ccg-39642
198. Nitrofurazone [usp Monograph]
199. Nsc757244
200. S1644
201. Stk741625
202. 1-(5-nitrofurfurylidene)semicarbazide
203. 5-nitro-2-furaldehyde, Semicarbazone
204. 5-nitro-2-furfurylidene Semicarbazone
205. Akos000304771
206. Tox21_110997_1
207. Db00336
208. Nsc-757244
209. Idi1_000778
210. Ncgc00090686-01
211. Ncgc00090686-02
212. Ncgc00090686-03
213. Ncgc00090686-05
214. Ncgc00090686-06
215. Ncgc00090686-08
216. Ncgc00090686-11
217. Ncgc00260533-01
218. Nitrofurazone 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
219. Ac-10331
220. Bs-42205
221. Semioxamazide, 1-(5-nitrofurfurylidene)-
222. Smr000059012
223. Sbi-0051458.p003
224. Ab00373885
225. N0200
226. C08042
227. D00862
228. Ab00373885-04
229. Ab00373885_05
230. Ab00373885_06
231. Structure Of 5-nitro-2-furaldehyde-semicarbazone
232. [(e)-[(5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methylidene]amino]urea
233. Q-201480
234. Sr-05000002027-1
235. Sr-05000002027-3
236. Brd-k79092138-001-05-2
237. Brd-k79092138-001-06-0
238. 5-nitro-2-furaldehyde Semicarbazone, >=97.0% (hplc)
239. Nitrofural, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
240. Hydrazinecarboxamide, 2-((5-nitro-2-furanyl)methylene)
241. Nitrofurazone, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
242. Nitrofural For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
243. Nitrofurazone Solution, 100 Mug/ml In Acetonitrile, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
244. Nitrofurazone, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 198.14 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H6N4O4 |
| XLogP3 | 0.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 198.03890469 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 198.03890469 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 126 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 261 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anti-Infective Agents, Local; Anti-Infective Agents, Urinary; Trypanocidal Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
/NITROFURAZONE/ IS BACTERICIDAL FOR MANY GRAM POSITIVE & GRAM NEGATIVE ORGANISMS PRESENT IN SURFACE INFECTIONS ... IT HAS BEEN USED TOPICALLY TO TREAT INFECTIONS OF SKIN & MUCOUS MEMBRANES.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations. 4th ed. Chicago: American Medical Association, 1980., p. 1026
NITROFURAZONE MAY BE TRIED IN ... /LATE-STAGE TRYPANOSOMIASIS/ WITH SOME CHANCE OF SUCCESS. SINGLE COURSE OF TREATMENT ... AT 6 HR INTERVALS FOR 1 WK. 3 COURSES MAY BE GIVEN WITH A WEEK'S REST BETWEEN EACH.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1074
IT FINDS USE, ESP, IN TREATMENT OF 2ND & 3RD DEGREE BURNS & IN SKIN GRAFTING IN WHICH THERE ARE COMPLICATIONS FROM BACTERIAL INFECTIONS THAT ARE REFRACTORY TO USUAL DRUGS OF CHOICE BUT IN WHICH SENSITIVITY TO NITROFURAZONE IS DEMONSTRABLE. ... NITROFURAZONE IS USED IN MGMNT OF SUSCEPTIBLE INFECTIONS OF EYE, EAR, NOSE, URETHRA & VAGINA. ... /IT/ RETAINS ITS ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY IN BLOOD, SERUM & PUS; PHAGOCYTOSIS IS NOT INHIBITED & NITROFURAZONE DOES NOT INTERFERE WITH HEALING.
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1105
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for NITROFURAZONE (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
... /TREATMENT AS IN LATE-STAGE TRYPANOSOMIASIS/ IS UNSUITABLE FOR FEBRILE OR DEBILITATED PATIENTS. ... IT PRODUCES HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA IN PATIENTS WITH GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE DEFICIENCY.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1074
WHEN USED TOPICALLY IN EAR ... /NITROFURAZONE/ MAY PRODUCE CUTANEOUS SENSITIVITY REACTIONS. ... THIS TYPE OF REACTION ... FREQUENTLY MIMICS DISEASE BEING TREATED. ... /THIS DRUG REACTION/ CAN USUALLY BE RECOGNIZED BECAUSE THE INFLAMMATORY PROCESS BEGINS TO SPREAD TO LOBULE OF EAR & INFECTION DOES NOT RESPOND TO TREATMENT.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 1000
... STRAINS OF PSEUDOMONAS & PROTEUS ARE OFTEN RESISTANT.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations. 4th ed. Chicago: American Medical Association, 1980., p. 1026
IT HAS NOT YET BEEN SHOWN TO BE USEFUL IN TREATMENT OF MINOR BURNS, WOUNDS, OR CUTANEOUS ULCERS WHICH ARE INFECTED. IT IS PROBABLY NOT EFFECTIVE IN TREATMENT OF PYODERMA. ... APPROX 0.5-2% OF PATIENTS BECOME SENSITIZED TO DRUG, SOMETIMES WITHIN 5 DAYS OF INITIATION OF TREATMENT. ... FOR ALL NITROFURAZONE DOSAGE FORMS, AVOID EXPOSURE AT ALL TIMES TO DIRECT SUNLIGHT, EXCESSIVE HEAT & ALKALINE MATERIALS.
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1105
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for NITROFURAZONE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of bacterial skin infections including pyodermas, infected dermatoses and infections of cuts, wounds, burns and ulcers due to susceptible organisms.
Nitrofurazone is a topical antibacterial agent indicated as an adjunctive therapy for second and third degree burns when resistance to other agents is a real or potential problem. Nitrofurazone is also indicated in skin grafting when bacterial contamination may cause graft rejection or donor site infection, especially in hospitals with a history of resistant bacteria.
Anti-Infective Agents
Substances that prevent infectious agents or organisms from spreading or kill infectious agents in order to prevent the spread of infection. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Infective Agents.)
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B05 - Blood substitutes and perfusion solutions
B05C - Irrigating solutions
B05CA - Antiinfectives
B05CA03 - Nitrofural
D - Dermatologicals
D08 - Antiseptics and disinfectants
D08A - Antiseptics and disinfectants
D08AF - Nitrofuran derivatives
D08AF01 - Nitrofural
D - Dermatologicals
D09 - Medicated dressings
D09A - Medicated dressings
D09AA - Medicated dressings with antiinfectives
D09AA03 - Nitrofural
P - Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents
P01 - Antiprotozoals
P01C - Agents against leishmaniasis and trypanosomiasis
P01CC - Nitrofuran derivatives
P01CC02 - Nitrofural
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01A - Antiinfectives
S01AX - Other antiinfectives
S01AX04 - Nitrofural
S - Sensory organs
S02 - Otologicals
S02A - Antiinfectives
S02AA - Antiinfectives
S02AA02 - Nitrofural
Absorption
Well absorbed.
ABOUT 1% OF (14)C WAS RECOVERED FROM URINE, FECES & BILE AS UNCHANGED 5-NITRO-2-FURALDEHYDE SEMICARBAZONE, SUGGESTING SUBSTANTIAL METABOLISM OF THIS SUBSTANCE IN RAT /AFTER ORAL DOSAGE OF 100 MG/KG/.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V7 177 (1974)
RATS DOSED WITH 100 MG/KG 5-NITRO-2-FURALDEHYDE SEMICARBAZONE- [FORMYL-(14)C] ... EXCRETED ABOUT 66%, 35% & 1% OF ACTIVITY IN URINE, FECES & IN RESPIRED AIR AS CO2, RESPECTIVELY, WITHIN 96 HR, & MAJORITY OF (14)C ACTIVITY WAS ELIMINATED WITHIN 48 HR. RECOVERY OF (14)C IN BILE WAS ABOUT 27% AFTER 48 HR.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V7 177 (1974)
IN RATS DOSED WITH 100 MG/KG, PLASMA LEVELS OF 4.5 MG/L ... WERE FOUND AFTER 4 HR, 34% OF WHICH WAS BOUND TO PROTEINS. RATS DOSED WITH 200 MG/KG ... EXCRETED ABOUT 4.6% IN URINE & 0.5% IN FECES WITHIN 48 HR. ORALLY ADMIN 5-NITRO-2-FURALDEHYDE SEMICARBAZONE WAS DETECTED IN CEREBROSPINAL FLUID OF DOGS WITHIN 2 HR.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V7 177 (1974)
Nitrofurans, including nitrofural, undergo metabolic reduction at the nitro group to generate reactive species which can covalently bind to cellular macromolecules (Polnaszek et al., 1984; Kutcher & McCalla, 1984; McCalla 1979; McCalla et al., 1975).
/NITROFURAZONE HAS/ BEEN SHOWN TO BE REDUCED BY ENZYMES & PREPN FROM MAMMALIAN LIVER. ... ISOLATION OF A HYDROXYLAMINE INTERMEDIATE IS NOT UNCOMMON IN IN VITRO STUDIES.
Testa, B. and P. Jenner. Drug Metabolism: Chemical & Biochemical Aspects. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc., 1976., p. 123
The disposition of the antibiotic nitrofurazone was studied in the singlepass isolated perfused rat liver. Both the effects of the steady state level of drug and the composition of the perfusate were evaluated. The higher level (120 ug/ml) of nitrofurazone in a perfusion medium lacking the glutathione precursors, glycine, glutamic acid and cysteine, caused a marked increase in bile flow (from 1.01 + or - 0.07 to 2.33 + or - 1.07 ul/min/g), massiv biliary efflux of glutathione disulfide (from 0.55 + or - 0.07 to 60.6 + or - 25.4 nmol/min/g) and a sharp decline in the caval efflux of glutathione (to undetectable levels) and the tissue level of glutathione (from 5.74 + or - 0.20 to 2.68 + or - 0.13 umol/g). Even after the drug was discontinued, these parameters were not restored to control levels. The lower level (30 ug/ml) of nitrofurazone with or without amino acid supplementatio and the higher level with supplementation induced less dramatic effects. Using (35)S methionine, a new conjugated metabolite of nitrofurazone and glutathione was detected. The data suggest that the toxicity of the reactive oxygen species generated by the redox cycling of the nitro group and the reactive metabolites generated by further reduction of nitrofurazone can be mitigated by adequate glutathione levels, but that livers lacking sufficient glutathione to scavenge these reactive species may be damaged.
PMID:3358793 Hoener BA; Biochem Pharmacol 37 (8): 1629-36 (1988)
5 hours
The exact mechanism of action is unknown. Nitrofurazone inhibits several bacterial enzymes, especially those involved in the aerobic and anaerobic degradation of glucose and pyruvate. This activity is believed also to affect pyruvate dehydrogenase, citrate synthetase, malate dehydrogenase, glutathione reductase, and pyruvate decarboxylase.
MECHANISM OF ANTIBACTERIAL ACTION OF FURAN DERIV IS UNKNOWN, BUT IT IS PRESUMED THAT THE COMPD INTERFERES WITH ENZYMATIC PROCESSES ESSENTIAL TO BACTERIAL GROWTH. /FURAN DERIV/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1003
The exact mechanism of action of nitrofurazone is not known. It appears, howeverthat the drug acts by inhibiting bacterial enzymes involved in carbohydrage metabolism. Oragnic matter (eg, blood pus, serum) and aminobenzoic acid (p-aminobenzoic acid) inhibit the antibacterial action of nitrofurazone.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 93. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1993 (Plus Supplements, 1993)., p. 2212