
1. Dl 8280
2. Dl-8280
3. Dl8280
4. Dr 3355
5. Dr-3355
6. Dr3355
7. Hoe 280
8. Hoe-280
9. Hoe280
10. Ofloxacin Hydrochloride
11. Ofloxacine
12. Orf 28489
13. Orf-28489
14. Orf28489
15. Ru 43280
16. Ru-43280
17. Ru43280
18. Tarivid
1. 82419-36-1
2. Floxin
3. Tarivid
4. Ofloxacine
5. Oxaldin
6. Ocuflox
7. Hoe-280
8. Oflx
9. Dl-8280
10. Ofloxacino
11. Ofloxacinum
12. Exocin
13. Hoe 280
14. Floxin Otic
15. Dextrofloxacin
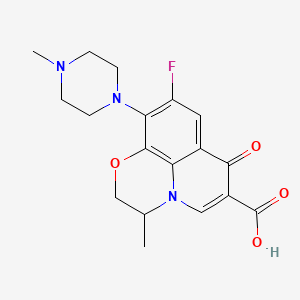
16. 9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7h-[1,4]oxazino[2,3,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic Acid
17. 9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-7-oxo-3,7-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazino[2,3,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic Acid
18. Chebi:7731
19. Oflocet
20. Visiren
21. Chembl4
22. J01ma01
23. Nsc-727071
24. Nsc-758178
25. A4p49jaz9h
26. Mls000028749
27. Ofloxacina
28. Ofloxacin Otic
29. Ofloxacina [dcit]
30. Ofloxacine [french]
31. Ofloxacinum [latin]
32. Exocine
33. Flobacin
34. Ofloxacin 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
35. Smr000058192
36. Zanocin
37. Floxil
38. Ofloxacino [spanish]
39. Dsstox_cid_21085
40. Dsstox_rid_79623
41. Dsstox_gsid_41085
42. 8-fluoro-3-methyl-9-(4-methyl-piperazin-1-yl)-6-oxo-2,3-dihydro-6h-1-oxa-3a-aza-phenalene-5-carboxylic Acid
43. Ofx
44. Floxin In Dextrose 5%
45. Dl 8280
46. Pt 01
47. Orf 18489
48. (-)-(s)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7h-pyrido[1,2,3-de]-1;(-)-(s)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7h-pyrido[1,2,3-de]-1
49. 9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7h-pyrido[1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid
50. Floxin (tn)
51. Ccris 5233
52. (+/-)-floxin
53. Sr-01000076050
54. Mfcd00226105
55. Unii-a4p49jaz9h
56. Floxin In Dextrose 5% In Plastic Container
57. Brn 3657947
58. Monoflocet
59. Dl-ofloxacin
60. Hsdb 8030
61. Ofloxacin,(s)
62. Ncgc00016948-01
63. Ofloxacin (floxin)
64. Cas-82419-36-1
65. Dl8280
66. Exocin (eye Drops)
67. Ofloxacin [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
68. (+-)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7h-pyrido(1,2,3-de)-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid
69. 83380-47-6
70. Wp-0405
71. Spectrum_001186
72. Ofloxacin [inn]
73. Ofloxacin [jan]
74. Ofloxacin [mi]
75. (r)-ofloxacin-[d3]
76. Ofloxacin [usan]
77. Opera_id_1114
78. Prestwick0_000237
79. Prestwick1_000237
80. Prestwick2_000237
81. Prestwick3_000237
82. Spectrum2_001464
83. Spectrum3_001499
84. Spectrum4_000324
85. Spectrum5_001063
86. Ofloxacin [vandf]
87. Epitope Id:116889
88. Ofloxacin [mart.]
89. O 8757
90. Ofloxacin [usp-rs]
91. Ofloxacin [who-dd]
92. Lopac0_000904
93. Oprea1_242882
94. Schembl24373
95. Bspbio_000313
96. Bspbio_003117
97. Kbiogr_000667
98. Kbioss_001666
99. Fluoro-methyl-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-oxo-[?]carboxylic Acid
100. Mls001074203
101. Mls006011774
102. Divk1c_000721
103. Spectrum1502044
104. Spbio_001387
105. Spbio_002234
106. (s)-ofloxacin;levaquin;quixin
107. Ofloxacin (jp17/usp/inn)
108. Bpbio1_000345
109. Ofloxacin [orange Book]
110. Dtxsid3041085
111. Ofloxacin [ep Monograph]
112. Schembl14163982
113. Gtpl10918
114. Hms502e03
115. Kbio1_000721
116. Kbio2_001666
117. Kbio2_004234
118. Kbio2_006802
119. Kbio3_002617
120. Ofloxacin [usp Monograph]
121. Chebi:194135
122. Ninds_000721
123. Hms1568p15
124. Hms1921h12
125. Hms2090f07
126. Hms2092b10
127. Hms2095p15
128. Hms2235c05
129. Hms3259g07
130. Hms3262f10
131. Hms3369b01
132. Hms3393k06
133. Hms3604b17
134. Hms3712p15
135. Pharmakon1600-01502044
136. (3r)-9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7h-[1,4]oxazino[2,3,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic Acid
137. (s)-9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-7-oxo-3,7-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazino[2,3,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic Acid
138. Amy22220
139. Bcp14346
140. Bcp22048
141. Hy-b0125
142. Rkl10083
143. Ofloxacin, Fluoroquinolone Antibiotic
144. Tox21_110703
145. Tox21_500904
146. Bbl005605
147. Bdbm50045004
148. Ccg-39210
149. Nsc727071
150. Nsc758178
151. S1463
152. Stk256723
153. Ofloxacin 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
154. Akos001033517
155. Akos016042783
156. Ofloxacine; Dl-8280; Hoe-280
157. Tox21_110703_1
158. Ac-7616
159. Bcp9000851
160. Cs-1891
161. Db01165
162. Ks-5011
163. Lp00904
164. Nc00466
165. Nsc 727071
166. Nsc 758178
167. Sdccgsbi-0050879.p004
168. Idi1_000721
169. Ncgc00015772-02
170. Ncgc00015772-03
171. Ncgc00015772-04
172. Ncgc00015772-05
173. Ncgc00015772-06
174. Ncgc00015772-07
175. Ncgc00015772-08
176. Ncgc00015772-09
177. Ncgc00015772-10
178. Ncgc00015772-12
179. Ncgc00015772-13
180. Ncgc00015772-22
181. Ncgc00094219-01
182. Ncgc00094219-02
183. Ncgc00094219-03
184. Ncgc00094219-04
185. Ncgc00094219-05
186. Ncgc00094219-06
187. Ncgc00178284-01
188. Ncgc00178284-02
189. Ncgc00261589-01
190. (+-)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7h-pyrido(1,2,3-de)(1,4)benzoxazin-6-carbonsaeure
191. (+/-)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7h-pyrido[1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid
192. 7h-pyrido(1,2,3-de)-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid, 2,3-dihydro-9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-, (+-)-
193. 7h-pyrido(1,2,3-de)-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid, 9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-, (+-)-
194. 9-fluoro-3,7-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-2h-[1,4]oxazino[2,3,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic Acid
195. Sy007392
196. Sbi-0050879.p003
197. Db-056608
198. Ab00513820
199. Eu-0100904
200. Ft-0627808
201. Ft-0630905
202. Ft-0670773
203. Ft-0673216
204. O0403
205. Ofloxacin, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
206. Vu0243192-7
207. 86o854
208. C07321
209. D00453
210. O-2800
211. Ab00052263-12
212. Ab00052263-13
213. Ab00052263_14
214. Ab00052263_15
215. Ofloxacin, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
216. A864414
217. Q411447
218. Sr-01000076050-1
219. Sr-01000076050-4
220. Sr-01000076050-7
221. Brd-a24228527-001-05-9
222. Brd-a24228527-001-19-0
223. Sr-01000076050-16
224. Z56761309
225. F0020-0095
226. F0472-0226
227. 7-chloro-4-hydroxy-8-methylquinoline-3-carboxylicethylester
228. Ofloxacin, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
229. Ofloxacin, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
230. (+/-)-9-fluoro-2,2,3-de)-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid
231. 8-methyl-2,3-dihydrofuro[3,2-e]imidazo-[1,2-c]pyrimidine-9-carboxylicacid
232. Ofloxacin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
233. (+/-)-9-fluoro-2, 3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7h-pyrido[1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid
234. 7-fluoro-2-methyl-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-10-oxo-4-oxa-1-azatricyclo[7.3.1.0^{5,13}]trideca-5(13),6,8,11-tetraene-11-carboxylic Acid
235. 7-fluoro-2-methyl-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-10-oxo-4-oxa-1-azatricyclo[7.3.1.05,13]trideca-5,7,9(13),11-tetraene-11-carboxylic Acid
236. 7h-pyrido(1,2,3-de)-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid, 9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-
237. 7h-pyrido(1,2,3-de)-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid, 9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-, (+/-)-
238. 9-fluoro-10-(4-methylpiperazino)-3-methyl-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7h-pyrido[1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzooxazine-6-carboxylic Acid
239. 9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7h-pyrido(1,2,3-de)(1,4)benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid, Dl-
240. 9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7h-pyrido [1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazin-6-carboxylic Acid
241. 9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7h-pyrido[1,2,3-de][1,4]benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid
242. 9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-7-oxo-3,7-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazino[2,3,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylicacid
243. 9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methylpiperazino)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7h-[1,4]oxazino[2,3,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 361.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H20FN3O4 |
| XLogP3 | -0.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 361.14378429 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 361.14378429 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 73.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 634 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Floxin otic |
| PubMed Health | Ofloxacin (Into the ear) |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial |
| Drug Label | OCUFLOX (ofloxacin ophthalmic solution) 0.3% is a sterile ophthalmic solution. It is a fluorinated carboxyquinolone anti-infective for topical ophthalmic use.... |
| Active Ingredient | Ofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Otic |
| Strength | 0.3% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Daiichi |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ocuflox |
| PubMed Health | Ofloxacin (Into the eye) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of ofloxacin tablets and other antibacterial drugs, ofloxacin tablets should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be c... |
| Active Ingredient | Ofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | 0.3% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Allergan |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ofloxacin |
| PubMed Health | Ofloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial, Antibiotic |
| Active Ingredient | Ofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops; Tablet |
| Route | Ophthalmic; Oral; Otic |
| Strength | 200mg; 400mg; 300mg; 0.3% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva; Cadila Pharms; Apotex; Altaire Pharms; Hi Tech Pharma; Bausch And Lomb; Alcon Pharms; Fera Pharms; Dr Reddys Labs; Fdc; Akorn |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Floxin otic |
| PubMed Health | Ofloxacin (Into the ear) |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial |
| Drug Label | OCUFLOX (ofloxacin ophthalmic solution) 0.3% is a sterile ophthalmic solution. It is a fluorinated carboxyquinolone anti-infective for topical ophthalmic use.... |
| Active Ingredient | Ofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Otic |
| Strength | 0.3% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Daiichi |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ocuflox |
| PubMed Health | Ofloxacin (Into the eye) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of ofloxacin tablets and other antibacterial drugs, ofloxacin tablets should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be c... |
| Active Ingredient | Ofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | 0.3% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Allergan |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ofloxacin |
| PubMed Health | Ofloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial, Antibiotic |
| Active Ingredient | Ofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops; Tablet |
| Route | Ophthalmic; Oral; Otic |
| Strength | 200mg; 400mg; 300mg; 0.3% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva; Cadila Pharms; Apotex; Altaire Pharms; Hi Tech Pharma; Bausch And Lomb; Alcon Pharms; Fera Pharms; Dr Reddys Labs; Fdc; Akorn |
Anti-Bacterial Agents; Anti-Infective Agents, Urinary; Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2012)
Ofloxacin is used in the treatment of acute pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) caused by susceptible C. trachomatis or N. gonorrhoeae, but should not be used if QRNG may be involved or if in vitro susceptibility cannot be tested. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 407
Ofloxacin is used in adults for the treatment of nongonococcal urethritis and cervicitis caused by Chlamydia trachomatis. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 407
Ofloxacin is used in adults for the treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs) (cystitis) caused by susceptible gram-negative bacteria, including Citrobacter diversus, ... Enterobacter aerogenes, ... Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, ... Proteus mirabilis, or Pseudomonas aeruginosa. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 406
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Ofloxacin (36 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: Fluoroquinolones, including ofloxacin, are associated with an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all ages. This risk is further increased in older patients usually over 60 years of age, in patients taking corticosteroid drugs, and in patients with kidney, heart or lung transplants.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for OFLOXACIN tablet, film coated (January 2012). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=95b9fc17-9c94-4762-910c-df0bb0b2aa85
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: Fluoroquinolones, including ofloxacin, may exacerbate muscle weakness in persons with myasthenia gravis. Avoid ofloxacin in patients with known history of myasthenia gravis.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for OFLOXACIN tablet, film coated (January 2012). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=95b9fc17-9c94-4762-910c-df0bb0b2aa85
Some quinolones, including ofloxacin, have been associated with prolongation of the QT interval on the electrocardiogram and infrequent cases of arrhythmia. Rare cases of torsade de pointes have been spontaneously reported during postmarketing surveillance in patients receiving quinolones, including ofloxacin.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for OFLOXACIN tablet, film coated (January 2012). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=95b9fc17-9c94-4762-910c-df0bb0b2aa85
Rare cases of sensory or sensorimotor axonal polyneuropathy affecting small and/or large axons resulting in paresthesias, hypoesthesias, dysesthesias and weakness have been reported in patients receiving quinolones, including ofloxacin. Ofloxacin should be discontinued if the patient experiences symptoms of neuropathy including pain, burning, tingling, numbness, and/or weakness or other alterations of sensation including light touch, pain, temperature, position sense, and vibratory sensation in order to prevent the development of an irreversible condition.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for OFLOXACIN tablet, film coated (January 2012). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=95b9fc17-9c94-4762-910c-df0bb0b2aa85
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Ofloxacin (28 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of infections (respiratory tract, kidney, skin, soft tissue, UTI), urethral and cervical gonorrhoea.
FDA Label
Ofloxacin is a quinolone/fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Ofloxacin is bactericidal and its mode of action depends on blocking of bacterial DNA replication by binding itself to an enzyme called DNA gyrase, which allows the untwisting required to replicate one DNA double helix into two. Notably the drug has 100 times higher affinity for bacterial DNA gyrase than for mammalian. Ofloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Anti-Infective Agents, Urinary
Substances capable of killing agents causing urinary tract infections or of preventing them from spreading. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Infective Agents, Urinary.)
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
Topoisomerase II Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit the activity of DNA TOPOISOMERASE II. Included in this category are a variety of ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS which target the eukaryotic form of topoisomerase II and ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS which target the prokaryotic form of topoisomerase II. (See all compounds classified as Topoisomerase II Inhibitors.)
Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors
Drugs and compounds which inhibit or antagonize the biosynthesis or actions of CYTOCHROME P-450 CYP1A2. (See all compounds classified as Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors.)
J01MA01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01M - Quinolone antibacterials
J01MA - Fluoroquinolones
J01MA01 - Ofloxacin
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01A - Antiinfectives
S01AE - Fluoroquinolones
S01AE01 - Ofloxacin
S - Sensory organs
S02 - Otologicals
S02A - Antiinfectives
S02AA - Antiinfectives
S02AA16 - Ofloxacin
Absorption
Bioavailability of ofloxacin in the tablet formulation is approximately 98%
Route of Elimination
Ofloxacin is mainly eliminated by renal excretion, where between 65% and 80% of an administered oral dose of ofloxacin is excreted unchanged via urine within 48 hours of dosing. About 4-8% of an ofloxacin dose is excreted in the feces and the drug is minimally subject to biliary excretion.
Ofloxacin is distributed into bone, cartilage, bile, skin, sputum, bronchial secretions, pleural effusions, tonsils, saliva, gingival mucosa, nasal secretions, aqueous humor, tears, sweat, lung, blister fluid, pancreatic fluid, ascitic fluid, peritoneal fluid, gynecologic tissue, vaginal fluid, cervix, ovary, semen, prostatic fluid, and prostatic tissue. For most of these tissues and fluids, ofloxacin concentrations are approximately 0.5-1.7 times concurrent serum concentrations. Ofloxacin is concentrated within neutrophils, achieving concentrations in these cells that may be up to 8 times greater than extracellular concentrations.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 417
Ofloxacin is widely distributed into body tissues and fluids following oral administration. In healthy adults, the apparent volume of distribution of ofloxacin averages 1-2.5 L/kg. Impaired renal function does not appear to affect the volume of distribution of ofloxacin; the apparent volume of distribution of the drug averages 1.1-2 L/kg in patients with impaired renal function, including those with severe renal failure undergoing hemodialysis.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 417
Pharmacokinetic parameters in geriatric patients receiving ofloxacin generally are similar to those in younger adults. Although results of pharmacokinetic studies in geriatric individuals 65-81 years of age indicate that the rate of absorption, volume of distribution, and route of excretion in geriatric individuals are similar to those in younger adults, peak serum concentrations are slightly higher (9-21% higher) and half-life more prolonged in geriatric patients than in younger adults. There also is evidence that peak plasma concentration are higher in geriatric women than geriatric men (114% higher following single doses or 54% higher following multiple doses).
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 417
The oral bioavailability of ofloxacin is 85-100% in healthy, fasting adults, and peak serum concentrations of the drug generally are attained within 0.5-2 hours. In patients with normal renal and hepatic function, peak serum concentrations and AUCs increase in proportion to the dose over the oral dosage range of 100-600 mg and generally are unaffected by age. Following oral administration of a single 100-, 200-, 300-, or 400-mg dose of ofloxacin in healthy, fasting adults, peak serum concentrations average 1-1.3, 1.5-2.7, 2.4-4.6, or 2.9-5.6 ug/mL, respectively. Some accumulation occurs following multiple doses. Steady-state serum concentrations of ofloxacin are achieved after 4 doses of the drug and are approximately 40% higher than concentrations achieved following single oral doses.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 417
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Ofloxacin (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hepatic
Less than 10% of a single dose of ofloxacin is metabolized; approximately 3-6% of the dose is metabolized to desmethyl ofloxacin and 1-5% is metabolized to ofloxacin N-oxide. Desmethyl ofloxacin is microbiologically active, but is less active against susceptible organisms than is ofloxacin; ofloxacin N-oxide has only minimal antibacterial activity.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 417
Seven patients with end-stage renal disease on regular hemodialysis were treated orally with a loading dose of 200 mg ofloxacin and multiple maintenance doses of 100 mg per 24 hr for 10 days. The pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin and its metabolites were studied at the end of the treatment period. Plasma and dialysate concentrations of ofloxacin and ofloxacin metabolites were measured by HPLC. Peak (3.1 mg.L-1) and trough levels (1.6 mg.L-1) and the AUC of ofloxacin were comparable to the values in healthy volunteers given 300 to 400 mg ofloxacin p.o. The mean half-life, determined in the dialysis-free interval (t1/2 beta) and during the haemodialysis session (t1/2 HD), was 38.5 h and 9.9 h, respectively. Extrarenal clearance (32.7 mL.min-1) was unchanged as compared to that reported in healthy volunteers after a single dose of ofloxacin. The fractional removal by haemodialysis amounted to 21.5%. Two metabolites, ofloxacin-N-oxide and demethyl-ofloxacin, were detected in plasma. Despite prolonged t1/2 beta of both metabolites (66.1 and 50.9 hr) and multiple doses of ofloxacin the peak concentrations of the metabolites reached only 14% and 5% of that of the parent drug, respectively. It is concluded that in patients on regular hemodialysis treatment the dosage adjustment employed resulted in safe and therapeutically favourable plasma concentrations. The observed accumulation of ofloxacin metabolites does not appear to have any toxic or therapeutic significance.
PMID:1541323 Kampf D et al; Eur J Clin Pharmacol 42 (1): 95-9 (1992)
9 hours
In adults with creatinine clearances of 10-50 mL/minute, half-life of the drug averages 16.4 hours (range: 11-33.5 hours); in adults with creatinine clearances less than 10 mL/minute, half-life averages 21.7 hours (range: 16.9-28.4 hours). In patients with end-stage renal failure, half-life of the drug may range from 25-48 hours.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 417
In healthy adults with normal renal function, the elimination half-life of ofloxacin in the distribution phase averages 0.5-0.6 hours and the elimination half-life in the terminal phase averages 4-8 hours.In healthy geriatric adults 64-86 years of age with renal function normal for their age, half-life of the drug averages 6.4-8.5 hours.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 417
Following ocular instillation of 1 drop of ofloxacin 0.3% 4 times daily for 12 doses in healthy individuals, the elimination half-life of drug in tear film was approximately 226 minutes. In a study in rabbits, the terminal elimination half-life of ofloxacin in tear film following topical application to the eye was approximately 210 minutes. In adults with normal renal function, the serum elimination half-life of ofloxacin in the terminal phase averages 4-8 hours.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011
Ofloxacin acts on DNA gyrase and toposiomerase IV, enzymes which, like human topoisomerase, prevents the excessive supercoiling of DNA during replication or transcription. By inhibiting their function, the drug thereby inhibits normal cell division.
Quinolone(s) (QNs) is widely used in infection therapy due to its good antimicrobial characteristics. However, QNs-induced arthropathy of immature animals has led to restrictions on the therapeutic use of these antimicrobial agents. The exact mechanism(s) of QNs-induced chondrotoxicity remain unknown. In the present study, .../the authors/ investigated the possible mechanism of ofloxacin (one typical QNs)-induced injuries of chondrocytes. Juvenile rabbit joint chondrocytes cultured in alginate microspheres were incubated with ofloxacin at concentrations of 0, 2, 5, 10, 20, and 40 microg/mL for up to 96 hr. Concentration of 10 microg/mL ofloxacin induced apoptosis of chondrocyte with visible apoptotic signs, including degradation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, caspase-3 activation, and DNA ladder formation. Furthermore, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (phospho-ERK1/2) and growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (Grb2) were significantly reduced, and similar changes were also observed in the beta(1)-integrin receptor as assessed by immunoblotting. However, the mRNA level of beta(1)-integrin obtained from reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction remained unchanged. Results of beta(1)-integrin immunoprecipitation have also shown that beta(1)-integrin did not interact with activated intracellular signaling proteins. In addition, ofloxacin did not induce apoptosis and decrease beta(1)-integrin expression in chondrocytes supplemented with Mg(2+), and the ofloxacin-induced apoptosis was caspase-8-dependent, inhibition of which did not affect the expression mode of phospho-ERK1/2 and beta(1)-integrin. Our results demonstrate that ofloxacin affects beta(1)-integrin receptor functions and the ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway, causing caspase-8-dependent apoptosis after exposure of 48 hr.
PMID:17400890 Sheng ZG et al; J Pharmacol Exp Ther 322 (1): 155-65 (2007)
Quinolones are widely used in infection therapy due to their good antimicrobial characteristics. However, there potential joint chondrotoxicity on immature animals has stood in the way of the therapeutic application of these agents, the exact mechanism of which is still unclear. This study was undertaken to investigate the role of oxidative damage in ofloxacin (one typical quinolones)-induced arthropathy. Chondrocytes from juvenile rabbit joints were incubated with ofloxacin at concentrations of 0, 5, 10, 20, 40 and 80 ug/mL, respectively. The extent of oxidative damage was assessed by measuring the reactive oxygen species level, activities of antioxidant enzymes, and oxidative damage to some macromolecules. It was observed that ofloxacin induced a concentration-dependent increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species production, which may be an early mediator of ofloxacin cytotoxicity. Similarly, ofloxacin resulted in a significant lipid peroxidation, revealed by a concentration-dependent increase in the level of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances. At the same time, ofloxacin induced DNA damage in a concentration-dependent manner for 24 hr measured by comet assay, which may be a cause for overproduction of reactive oxygen species. Furthermore, antioxidant enzyme activities, such as glutathione peroxidase (GPx), catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD), were rapidly decreased after treatment with ofloxacin. In addition, SOD decline and reactive oxygen species production were strongly inhibited, and the loss in cell viability was partly abated by additional glutathione (GSH), N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and dithiothreitol (DTT). In conclusion, these results clearly demonstrated that ofloxacin could induce oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation and DNA oxidative damage to chondrocytes.
PMID:19818344 Li Q et al; Eur J Pharmacol 626 (2-3): 146-53 (2010)
Ofloxacin is a quinolone antimicrobial agent. The mechanism of action of ofloxacin and other fluoroquinolone antimicrobials involves inhibition of bacterial topoisomerase IV and DNA gyrase (both of which are type II topoisomerases), enzymes required for DNA replication, transcription, repair and recombination. Ofloxacin has in vitro activity against a wide range of gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms. Ofloxacin is often bactericidal at concentrations equal to or slightly greater than inhibitory concentrations. Fluoroquinolones, including ofloxacin, differ in chemical structure and mode of action from aminoglycosides, macrolides and beta-lactam antibiotics, including penicillins. Fluoroquinolones may, therefore, be active against bacteria resistant to these antimicrobials. Resistance to ofloxacin due to spontaneous mutation in vitro is a rare occurrence (range: 10(-9) to 10(-11)). Although cross-resistance has been observed between ofloxacin and some other fluoroquinolones, some microorganisms resistant to other fluoroquinolones may be susceptible to ofloxacin.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for OFLOXACIN tablet, film coated (January 2012). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=95b9fc17-9c94-4762-910c-df0bb0b2aa85
Fluoroquinolones prolong the QT interval by blocking voltage-gated potassium channels, especially the rapid component of the delayed rectifier potassium current I(Kr), expressed by HERG (the human ether-a-go-go-related gene). According to the available case reports and clinical studies, moxifloxacin carries the greatest risk of QT prolongation from all available quinolones in clinical practice and it should be used with caution in patients with predisposing factors for Torsades de pointes (TdP).
PMID:22156660 Briasoulis A et al; Cardiology 120 (2): 103-10 (2011)