


1. Methylphenylisoxazolyl Penicillin
2. Oxacillin Sodium
3. Oxacillin, Monosodium Salt, Anhydrous
4. Oxacillin, Monosodium Salt, Monohydrate
5. Oxacillin, Sodium
6. Oxazocilline
7. Penicillin, Methylphenylisoxazolyl
8. Prostaphlin
9. Sodium Oxacillin
10. Sodium, Oxacillin
1. Oxazocillin
2. 66-79-5
3. Oxazocilline
4. Mpi-penicillin
5. Oxacilina
6. Bactocill
7. Prostaphlin
8. Oxacillin Sodium
9. 5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl-penicillin
10. Oxacillin (inn)
11. Chebi:7809
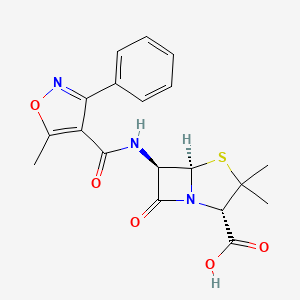
12. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-6-[(5-methyl-3-phenyl-1,2-oxazole-4-carbonyl)amino]-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
13. (5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)penicillin
14. Penicillin, (5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)-
15. 6beta-(5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)penicillanic Acid
16. Uh95vd7v76
17. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-6-{[(5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)carbonyl]amino}-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
18. Ossacillina
19. Oxacilline
20. Oxacillinum
21. Prostaphlyn
22. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-6-[[(5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)carbonyl]amino]-7-oxo-, (2s,5r,6r)-
23. Ossacillina [dcit]
24. Oxacillin [inn]
25. Mpi-pc
26. Oxacillin [inn:ban]
27. Oxacilina [inn-spanish]
28. Oxacilline [inn-french]
29. Oxacillinum [inn-latin]
30. 1173-88-2
31. Oxacilina (tn)
32. Einecs 200-635-5
33. Unii-uh95vd7v76
34. Oxacillin,(s)
35. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-6-[(5-methyl-3-phenyl-isoxazole-4-carbonyl)amino]-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
36. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-6-(((5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)carbonyl)amino)-7-oxo-, (2s-(2alpha,5alpha,6beta))-
37. Oxacillin [mi]
38. Oxacillin [vandf]
39. Chembl819
40. Epitope Id:181859
41. Oxacillin [mart.]
42. Oxacillin [who-dd]
43. Schembl3817
44. Dtxsid8023397
45. Gtpl10943
46. Hy-b0925a
47. Phenylisoxazole-4-carboxamido)-7-
48. Zinc3875439
49. Bdbm50350483
50. Db00713
51. 2,2-dimethyl-6beta-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-1,2-oxazole-4-carboxamido)penam-3alpha-carboxylic Acid
52. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-6-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-1,2-oxazole-4-amido)-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
53. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-6-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolecarboxamide)-7-oxo-
54. 5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isooxazolylpenicillin
55. Oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-
56. Cs-0013715
57. C07334
58. D08307
59. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-6-(5-methyl-3-
60. Q418725
61. Brd-k96786677-236-01-6
62. Brd-k96786677-236-02-4
63. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-6-(((5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)carbonyl)amino)-7-oxo-,(2s,5r,6r)-
64. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-6-(((5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)carbonyl)amino)-7-oxo-, (2s-(2.alpha.,5.alpha.,6.beta.))-
| Molecular Weight | 401.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H19N3O5S |
| XLogP3 | 2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 401.10454189 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 401.10454189 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 138 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 681 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Oxacillin sodium |
| Drug Label | Oxacillin for Injection, USP is a semisynthetic penicillin antibiotic derived from the penicillin nucleus, 6-amino-penicillanic acid. It is resistant to inactivation by the enzyme penicillinase (beta-lactamase). It is the sodium salt in parenteral do... |
| Active Ingredient | Oxacillin sodium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | eq 2gm base/vial; eq 10gm base/vial; eq 1gm base/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Aurobindo Pharma; Sandoz; Sagent Pharms; Agila Speclts |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Oxacillin sodium |
| Drug Label | Oxacillin for Injection, USP is a semisynthetic penicillin antibiotic derived from the penicillin nucleus, 6-amino-penicillanic acid. It is resistant to inactivation by the enzyme penicillinase (beta-lactamase). It is the sodium salt in parenteral do... |
| Active Ingredient | Oxacillin sodium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | eq 2gm base/vial; eq 10gm base/vial; eq 1gm base/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Aurobindo Pharma; Sandoz; Sagent Pharms; Agila Speclts |
Used in the treatment of resistant staphylococci infections.
Oxacillin is a penicillin beta-lactam antibiotic used in the treatment of bacterial infections caused by susceptible, usually gram-positive, organisms. The name "penicillin" can either refer to several variants of penicillin available, or to the group of antibiotics derived from the penicillins. Oxacillin has in vitro activity against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. The bactericidal activity of Oxacillin results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis and is mediated through Oxacillin binding to penicillin binding proteins (PBPs). Oxacillin is stable against hydrolysis by a variety of beta-lactamases, including penicillinases, and cephalosporinases and extended spectrum beta-lactamases.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01C - Beta-lactam antibacterials, penicillins
J01CF - Beta-lactamase resistant penicillins
J01CF04 - Oxacillin
Route of Elimination
Oxacillin Sodium is rapidly excreted as unchanged drug in the urine by glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion.
20 to 30 minutes
By binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, Oxacillin inhibits the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wall autolytic enzymes such as autolysins; it is possible that Oxacillin interferes with an autolysin inhibitor.
