

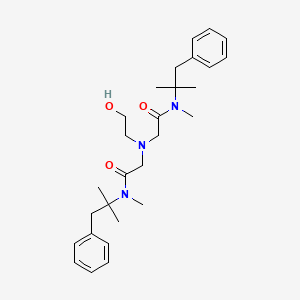

1. 2,2'-((2-hydroxyethyl)imino)bis(n-alpha,alpha-dimethylphenethyl)-n-methylacetamide
2. Mucaine
3. Muthesa
4. Oxaine
5. Oxetacain
6. Oxethazaine Hydrochloride
7. Oxethazaine Monohydrochloride
8. Oxethazine
9. Robercain R
10. Tepilta
1. Oxetacaine
2. 126-27-2
3. Oxethacaine
4. Mucaine
5. Oxaethacainum
6. Betalgil
7. Strocain
8. Emoren
9. Oxethazine
10. Oxetacaine [inn]
11. Wy-806
12. Acetamide, 2,2'-((2-hydroxyethyl)imino)bis(n-(1,1-dimethyl-2-phenylethyl)-n-methyl-
13. Nsc-758444
14. Chembl127592
15. Ip8qt76v17
16. 2-[2-hydroxyethyl-[2-[methyl-(2-methyl-1-phenylpropan-2-yl)amino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-n-methyl-n-(2-methyl-1-phenylpropan-2-yl)acetamide
17. Chebi:31947
18. Oxetacaine (inn)
19. 2,2'-((2-hydroxyethyl)imino)bis(n-(1,1-dimethyl-2-phenylethyl)-n-methylacetamide)
20. Acetamide, 2,2'-[(2-hydroxyethyl)imino]bis[n-(1,1-dimethyl-2-phenylethyl)-n-methyl-
21. Ncgc00016382-01
22. Cas-126-27-2
23. Dsstox_cid_5818
24. Dsstox_rid_77936
25. Dsstox_gsid_25818
26. Oxethacaina [italian]
27. Milzine
28. Oxetacainum [inn-latin]
29. Oxetacaina [inn-spanish]
30. Ccris 4692
31. Sr-05000001851
32. Einecs 204-780-5
33. Fh 099
34. Wy 806
35. Oxethazaine [usan:jan]
36. Brn 2404063
37. Unii-ip8qt76v17
38. Prestwick_767
39. Spectrum_001657
40. 2-di(n-methyl-n-phenyl-tert-butyl-carbamoylmethyl)aminoethanol
41. Oxethazaine [mi]
42. Prestwick0_000058
43. Prestwick1_000058
44. Prestwick2_000058
45. Prestwick3_000058
46. Spectrum2_001987
47. Spectrum3_001751
48. Spectrum4_000202
49. Spectrum5_001269
50. Oxethazaine [jan]
51. N,n-bis(n-methyl-n-phenyl-tert-butylacetamido)-beta-hydroxyethylamine
52. Oxethazaine [usan]
53. Cid_4621
54. Oxetacaine [mart.]
55. 2,2'-((2-hydroxyethyl)imino)bis(n-(alpha,alpha-dimethylphenethyl)-n-methylacetamide)
56. Oxetacaine [who-dd]
57. Oxethazaine (jp17/usan)
58. Schembl24489
59. Bspbio_000215
60. Bspbio_003482
61. Kbiogr_000803
62. Kbioss_002137
63. 4-12-00-02822 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
64. Mls002154188
65. Divk1c_000715
66. Spectrum1503279
67. Spbio_002136
68. Spbio_002173
69. Bpbio1_000237
70. Oxethazaine, Analytical Standard
71. Dtxsid0025818
72. Hms502d17
73. Kbio1_000715
74. Kbio2_002137
75. Kbio2_004705
76. Kbio2_007273
77. Kbio3_002702
78. Ninds_000715
79. Hms1568k17
80. Hms1922a04
81. Hms2093c15
82. Hms2095k17
83. Hms2236a03
84. Hms3370m13
85. Hms3712k17
86. Hms3885p21
87. Pharmakon1600-01503279
88. Bcp07626
89. Hy-b0955
90. Zinc3874585
91. Tox21_110407
92. Bdbm50017672
93. Ccg-39525
94. Nsc758444
95. Akos024284189
96. Tox21_110407_1
97. Cs-4432
98. Db12532
99. Nsc 758444
100. Acetamide, 2,2'-((2-hydroxyethyl)imino)bis(n-(alpha,alpha-dimethylphenethyl)-n-methyl-
101. Idi1_000715
102. Ncgc00016382-02
103. Ncgc00016382-03
104. Ncgc00016382-04
105. Ncgc00016382-07
106. Ncgc00016382-09
107. Ncgc00095039-01
108. Ncgc00095039-02
109. Ncgc00095039-03
110. N-(1,1-dimethyl-2-phenyl-ethyl)-2-[[2-[(1,1-dimethyl-2-phenyl-ethyl)-methyl-amino]-2-oxo-ethyl]-(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]-n-methyl-acetamide
111. Smr001233479
112. Sbi-0051816.p002
113. Db-041818
114. Ab00052348
115. Ft-0603332
116. Sw196906-3
117. D01152
118. Ab00052348_08
119. Ab00052348_09
120. 126o272
121. J-005353
122. Q2412605
123. Sr-05000001851-1
124. Sr-05000001851-3
125. Brd-k56940463-001-05-4
126. Brd-k56940463-001-08-8
127. 2-hydroxyethyliminobis(n-[alpha,alpha-dimethylphenethyl]-n-methylacetamide)
128. 2,2'-(2-hydroxyethylazanediyl)bis(n-methyl-n-(2-methyl-1-phenylpropan-2-yl)acetamide)
129. 2,2'-((2-hydroxyethyl)imino)bis(n-(.alpha.,.alpha.-dimethylphenethyl)-n-methylacetamide)
130. N-(1,1-dimethyl-2-phenyl-ethyl)-2-[{[(1,1-dimethyl-2-phenyl-ethyl)-methyl-carbamoyl]-methyl}-(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-amino]-n-methyl-acetamide
| Molecular Weight | 467.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C28H41N3O3 |
| XLogP3 | 3.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 |
| Exact Mass | 467.31479218 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 467.31479218 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 64.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 34 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 585 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Oxetacaine is available as an over-the-counter antacid and it is used to alleviate pain associated with gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, heartburn, esophagitis, hiatus hernia, and anorexia.
Oxetacaine improves common gastrointestinal symptoms. Oxetacaine is part of the anesthetic antacids which increase the gastric pH while providing relief from pain for a longer period of duration at a lower dosage. This property has been reported to relieve the symptoms of hyperacidity. Oxetacaine is reported to produce a reversible loss of sensation and to provide a prompt and prolonged relief of pain. In vitro, oxetacaine was showed to produce an antispasmodic action on the smooth muscle and block the action of serotonin. The local efficacy of oxetacaine has been proven to be 2000 times more potent than lignocaine and 500 times more potent than cocaine. Its anesthetic action produces the loss of sensation which can be explained by its inhibitory activity against the nerve impulses and de decrease in permeability of the cell membrane.
Anesthetics, Local
Drugs that block nerve conduction when applied locally to nerve tissue in appropriate concentrations. They act on any part of the nervous system and on every type of nerve fiber. In contact with a nerve trunk, these anesthetics can cause both sensory and motor paralysis in the innervated area. Their action is completely reversible. (From Gilman AG, et. al., Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 8th ed) Nearly all local anesthetics act by reducing the tendency of voltage-dependent sodium channels to activate. (See all compounds classified as Anesthetics, Local.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C05 - Vasoprotectives
C05A - Agents for treatment of hemorrhoids and anal fissures for topical use
C05AD - Local anesthetics
C05AD06 - Oxetacaine
Absorption
A peak plasma concentration of oxetacaine of approximately 20 ng/ml is attained about one hour after oral administration. LEss than 1/3 of the administered dose is absorbed as it undergoes extensive metabolism.
Route of Elimination
Less than 0.1% of the amdinistered dose is recovered in urine within 24 hours in the form of unchanged oxetacaine or its metabolites.
Volume of Distribution
This pharmacokinetic property has not been studied.
Clearance
This pharmacokinetic property has not been studied.
Oxetacaine is rapidly and extensively metabolized hepatically. After metabolism, there is a formation of primary metabolites such as beta-hydroxy-mephentermine and beta-hydroxy-phentermine. The major metabolites are found in the plasma in insignificant amounts.
Oxetacaine presents a very short half-life of approximately one hour.
Oxetacaine inhibits gastric acid secretion by suppressing gastrin secretion. Moreover, oxetacaine exerts a local anesthetic effect on the gastric mucosa. This potent local anesthetic effect of oxetacaine may be explained by its unique chemical characteristics in which, as a weak base, it is relatively non-ionized in acidic solutions whereas its hydrochloride salt is soluble in organic solvents and it can penetrate cell membranes. Oxetacaine diminishes the conduction of sensory nerve impulses near the application site which in order reduces the permeability of the cell membrane to sodium ions. This activity is performed by the incorporation of the unionized form into the cell membrane.