

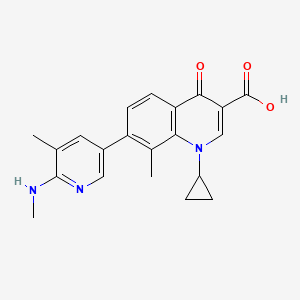

1. 1-cyclopropyl-8-methyl-7-(5-methyl-6-(methylamino)-3-pyridinyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
2. Ozanex
3. Xepi
1. 245765-41-7
2. Xepi
3. T-3912
4. T 3912
5. 1-cyclopropyl-8-methyl-7-[5-methyl-6-(methylamino)pyridin-3-yl]-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
6. Gf-001001-00
7. V0lh498rfo
8. 1-cyclopropyl-8-methyl-7-(5-methyl-6-(methylamino)pyridin-3-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
9. Ozenoxacin Cream
10. Ozenoxacin [inn]
11. Ozenoxacin [inn:jan]
12. Unii-v0lh498rfo
13. Ozadub
14. Xepi (tn)
15. Ozenoxacin [mi]
16. Ozenoxacin; T-3912
17. Ozenoxacin [jan]
18. Ozenoxacin [usan]
19. Ozenoxacin [who-dd]
20. Ozenoxacin (jan/usan/inn)
21. Schembl1711829
22. Chembl3990047
23. Ozenoxacin [orange Book]
24. Gtpl10841
25. Dtxsid00947446
26. Chebi:136050
27. Bcp16621
28. Ex-a2693
29. Vja76541
30. Who 8788
31. Zinc1483896
32. S6582
33. Akos032947315
34. At18754
35. Db12924
36. Sb16801
37. Ncgc00532517-01
38. Bs-16742
39. Da-31712
40. Hy-14957
41. Ozenoxacin 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
42. Cs-0003657
43. Ft-0701296
44. D09544
45. Q17125399
46. Gf-001001-00; M-5120; T-3912; Gf-00100100;t3912;t 3912
47. 1-cyclopropyl-8-methyl-7-(5-methyl-6-(methylamino)-3-pyridinyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
48. 3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid, 1-cyclopropyl-1,4-dihydro-8-methyl-7-(5-methyl-6-(methylamino)-3-pyridinyl)-4-oxo-
| Molecular Weight | 363.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H21N3O3 |
| XLogP3 | 4.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 363.15829154 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 363.15829154 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 82.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 645 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Ozenoxacin cream is indicated for the topical treatment of impetigo caused by *Staphylococcus aureus* or *Streptococcus pyogenes* in patients aged 2 months of age and older.
FDA Label
Treatment of impetigo
Although the exposure response relationship for ozenoxacin after it has been applied topically has not yet been studied, a formal relationship is unlikely because systemic exposure of ozenoxacin following its topical application has been measured to be negligible.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
Topoisomerase Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit the activity of DNA TOPOISOMERASES. (See all compounds classified as Topoisomerase Inhibitors.)
D - Dermatologicals
D06 - Antibiotics and chemotherapeutics for dermatological use
D06A - Antibiotics for topical use
D06AX - Other antibiotics for topical use
D06AX14 - Ozenoxacin
Absorption
Four studies were performed in which varying strengths of ozenoxacin cream, up to 2% (twice the concentration of the marketed formulation), were administered to 110 patients. Three of the studies examined systemic absorption in healthy subjects and in subjects having impetigo. The studies were performed with either single or repeated application of up to 1 g ozenoxacin cream to intact or abraded skin (up to 200 cm squared surface area). No systemic absorption was seen in 84 of 86 subjects, and negligible systemic absorption was seen at the level of detection (0.489 ng/mL) in 2 subjects.
Route of Elimination
Studies regarding elimination and excretion have not yet been investigated in humans due to the negligible systemic absorption observed in clinical studies.
Volume of Distribution
Ozenoxacin undergoes negligible systemic absorption after its topical administration. Subsequently, since negligible systemic absorption of ozenoxacin was observed in clinical studies, tissue distribution has not been investigated in humans either.
Clearance
Ozenoxacin undergoes negligible systemic absorption after its topical administration.
Studies have demonstrated that ozenoxacin is not metabolized in the presence of fresh human skin discs and is minimally metabolized in human hepatocytes.
Ozenoxacin is a quinolone antibiotic drug. And, like most quinolones, ozenoxacin predominately executes its mechanism of action by entering into bacterial cells and acting to inhibit the bacterial DNA replication enzymes DNA gyrase A and topoisomerase IV. As DNA gyrase A and topoisomerase IV are essential to bacterial DNA replication activities including supercoiling, supercoil relaxation, chromosomal condensation, chromosomal decatenation and more, their inhibition is the principal action of ozenoxacin's mechanism and it has been demonstrated to be bactericidal against *S. aureus* and *S. pyogenes* organisms.