

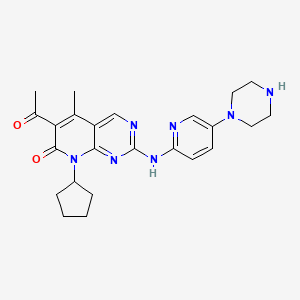

1. 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-(5-piperazin-1-ylpyridin-2-ylamino)-8h-pyrido(2,3-d)pyrimidin-7-one
2. Ibrance
3. Pd 0332991
4. Pd-0332991
5. Pd0332991
1. 571190-30-2
2. Pd-0332991
3. Ibrance
4. Pd0332991
5. Pd 0332991
6. Palbociclib Free Base
7. Unii-g9zf61le7g
8. 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-((5-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)amino)pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7(8h)-one
9. Pd-332991
10. 571190-30-2 (free Base)
11. Mfcd11840850
12. 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-[(5-piperazin-1-ylpyridin-2-yl)amino]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7(8h)-one
13. 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-[[5-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]amino]-8h-pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one
14. G9zf61le7g
15. Palbociclib(pd0332991)
16. Pd 332991
17. 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-(5-piperazin-1-ylpyridin-2-ylamino)-8h-pyrido(2,3-d)pyrimidin-7-one
18. Chebi:85993
19. 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-[(5-piperazin-1-ylpyridin-2-yl)amino]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one
20. Lqq
21. 2euf
22. 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-{[5-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]amino}pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7(8h)-one
23. Pyrido(2,3-d)pyrimidin-7(8h)-one, 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-((5-(1-piperazinyl)-2-pyridinyl)amino)-
24. Palbociclib [usan]
25. 571190-30-2 Pound Not827022-32-2
26. Palbociclib [usan:inn]
27. [d8]-palbociclib
28. 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-((5-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)amino)-8h-pyrido(2,3-d)pyrimidin-7-one
29. Ibrance (tn)
30. Palbociclib- Bio-x
31. Kinome_3823
32. Kinome_3824
33. Palbociclib [mi]
34. 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-(5-piperazin-1-yl-pyridin-2-ylamino)-8h-pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one Hydrochloride
35. Palbociclib [inn]
36. Palbociclib [jan]
37. Palbociclib (jan/usan)
38. Palbociclib [who-dd]
39. Schembl462630
40. Bdbm6309
41. Chembl189963
42. Gtpl7380
43. Pd 0332991 (palbociclib)
44. Dtxsid40972590
45. Ex-a408
46. Palbociclib [orange Book]
47. 2euf; Pd 0332991
48. Otava-bb 1115529
49. Bcpp000125
50. Hms3265m09
51. Hms3265m10
52. Hms3265n09
53. Hms3265n10
54. Hms3744g13
55. Amy14886
56. Bcp09274
57. Bcp18381
58. Zinc3938686
59. Nsc758247
60. Nsc772256
61. Nsc800815
62. S4482
63. Akos022205241
64. Bcp9001058
65. Db09073
66. Nsc-758247
67. Nsc-772256
68. Nsc-800815
69. Sb40426
70. Pyrido-[2,3-d]-pyrimidin-7-one 43
71. Ncgc00263129-01
72. Ncgc00263129-08
73. Ncgc00263129-21
74. Ncgc00263129-22
75. Ac-25485
76. As-17016
77. Bp166224
78. Hy-50767
79. Sy026143
80. Ft-0697059
81. A14427
82. D10372
83. 190p302
84. Pd 0332991,pd0332991
85. Pd-0332991, Pd0332991
86. Brd-k51313569-001-01-1
87. P-0332991
88. Q15269707
89. 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-((5-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)amino(pyrido(2,3-d)pyrimidin-7(8h)-one
90. 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-(5-piperazin-1-yl-pyridin-2-ylamino)-8h-pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one
91. 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-[(5-piperazin-1-ylpyridin-2-yl)amino]pyrido[6,5-d]pyrimidin-7-one
92. 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-[[5-(1-piperazinyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7(8h)-one
93. 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-[[5-(piperazin-1-yl)-pyridin-2-yl]amino]-8h-pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one
94. 8-cyclopentyl-6-acetyl-5-methyl-2-{[5-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]amino}-7h,8h-pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one
| Molecular Weight | 447.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H29N7O2 |
| XLogP3 | 1.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 447.23827319 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 447.23827319 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 103 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 775 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Palbociclib is indicated in combination with [letrozole] as initial endocrine-based therapy for the treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 (HER2)-negative and hormone receptor(HR)-positive tumors in adult patients with advanced/metastatic breast cancer. It is as well approved in combination with [fulvestrant] in patients with disease progression with prior endocrine therapy. In the official labeling, the use of palbociclib should be accompanied with either an aromatase inhibition, no restricted to letrozole, as initial endocrine-based therapy in postmenopausal women or in man. The breast cancer starts as a group of cancer cells that grow into and destroy the nearby breast tissue. This growth can spread into other parts of the body which is called metastasis. According to the location of the cancer cells, it can be categorized in ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma. However, other types of breast cancer include inflammatory breast cancer, Paget disease of the breast, triple negative breast cancer non-Hodgkin lymphoma and soft tissue sarcoma. In males, breast cancer is usually treated as the cases of postmenopausal women and almost all the cases are ductal carcinoma.
FDA Label
Ibrance is indicated for the treatment of hormone receptor (HR) positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer :
- in combination with an aromatase inhibitor;
- in combination with fulvestrant in women who have received prior endocrine therapy.
In pre- or perimenopausal women, the endocrine therapy should be combined with a luteinizing hormone releasing hormone (LHRH) agonist.
Treatment of breast malignant neoplasms
Treatment of Ewing sarcoma
Due to its mechanism of action, palbociclib inhibits cell growth and suppresses DNA replication in retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene (RB) proficient cancer cells. As expected, these RB cells present a significant increase in the proportion of cells in G1 state and the presence of palbociclib produces effective dephosphorylation of RB, reduce proliferation and induce senescence causing cell-cycle arrest. In vitro studies showed the potential for palbociclib to reduce cellular proliferation of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cell lines through the inhibition of the cell-cycle progression from G1 to S phase. In this study, it was demonstrated that the sensitivity of the cells significantly increased with the expression of _RB1_ and _CCND1_ and low expression of _CDKN2A_. As well, palbociclib, combined with antiestrogens, enhanced _in vivo_ antitumor activity in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer mouse models. In clinical trials, palbociclib, in combination with letrozole, was shown to significantly increase the progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with metastatic breast cancer without prior endocrine treatment. In the results, the PFS increased from 4.5 to 9.5 months with an overall response rate (ORR) of 24.6%.
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit PROTEIN KINASES. (See all compounds classified as Protein Kinase Inhibitors.)
L01XE33
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EF - Cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk) inhibitors
L01EF01 - Palbociclib
Absorption
Palbociclib presents a linear pharmacokinetic profile and its peak plasma concentration was observed 6-12 hours after oral administration. The oral bioavailability is reported to be of 46% with a steady-state reached after 8 days and a median accumulation ratio of 2.4. The absorption of palbociclib is significantly reduced under fasting conditions and hence, food intake is recommended when this drug is administered.
Route of Elimination
The main route of elimination of palbociclib is through feces after hepatic metabolism while renal clearance seems to play a minor role accounting only for 17.5% of the eliminated dose.
Volume of Distribution
The mean apparent distribution of palbociclib is 2583 L which suggests that palbociclib penetrates extensively into peripheral tissues.
Clearance
The mean apparent oral clearance of palbociclib is of 63.1 L/h.
Palbociclib is mainly hepatically transformed. the metabolism is mainly performed by the activities of the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme 3A and the sulfotransferase 2A1. The metabolism of palbociclib is represented mainly by reactions of oxidation and sulfonation followed by acylation and glucuronidation as minor reactions. After its metabolism, palbociclib forms mainly inactive glucuronide and sulfamic acid conjugates. The major circulating metabolite, accounting for 1.5% of the dose in excreta is is the glucuronide conjugate.
The mean plasma elimination half-life of palbociclib is 29 hours.
Palbociclib is a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor that acts by binding to the ATP pocket with an IC50 in the range of 9-15 nmol/L. It is important to consider that it presents low to absent activity against other kinases. The CDK4/6 kinase is involved, with coregulatory partner cyclin D, in the G1-S transition. Hence, inhibition of this step prevents cell cycle progression in cells in whose this pathway is functioning. This step includes the pathways of the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein and the E2F family of transcription factors.

