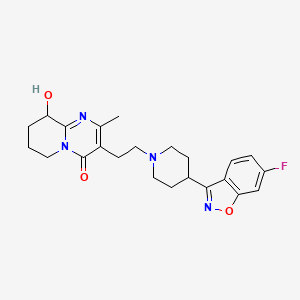

1. 3-(2-(4-(6-fluoro-3-(1,2-benzisoxazolyl))-1-piperidinyl)ethyl)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-4h-pyrido(1,2-a)pyrimidin-4-one
2. 9 Hydroxy Risperidone
3. 9 Hydroxyrisperidone
4. 9 Oh Risperidone
5. 9-hydroxy-risperidone
6. 9-hydroxyrisperidone
7. 9-oh-risperidone
8. Invega
9. Invega Sustenna
10. Paliperidone Palmitate
11. Palmitate, Paliperidone
12. R 76477
13. R-76477
14. R76477
15. Sustenna, Invega
1. 144598-75-4
2. 9-hydroxyrisperidone
3. Invega
4. 9-oh-risperidone
5. 3-(2-(4-(6-fluorobenzo[d]isoxazol-3-yl)piperidin-1-yl)ethyl)-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-4h-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one
6. Ro76477
7. C23h27fn4o3
8. R-76477
9. 3-[2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzoxazol-3-yl)piperidin-1-yl]ethyl]-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-6,7,8,9-tetrahydropyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one
10. Ro-76477
11. 3-[2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-4h-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one
12. Chembl1621
13. 4h-pyrido(1,2-a)pyrimidin-4-one, 3-(2-(4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl)ethyl)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-
14. Chebi:83804
15. 144598-75-4 (free Base)
16. Nsc-759623
17. (9rs)-3-(2-(4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)piperidin-1-yl))ethyl)-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-4h-pyrido(1,2-a)pyrimidin-4-one
18. 4h-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one, 3-[2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-
19. 838f01t721
20. Paliperidone [inn]
21. 3-{2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzoxazol-3-yl)piperidin-1-yl]ethyl}-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-4h,6h,7h,8h,9h-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one
22. Palliperidone
23. 9-hydroxy Risperidone
24. R 76477
25. Hsdb 8148
26. Rac 9-hydroxy Risperidone
27. Unii-838f01t721
28. 3-(2-(4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl)ethyl)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-4h-pyrido(1,2-a)pyrimidin-4-one
29. 3-{2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzoxazol-3-yl)piperidin-1-yl]ethyl}-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-6,7,8,9-tetrahydropyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one
30. Paliperidone [usan:inn:ban:jan]
31. Invega (tn)
32. Mfcd00871802
33. Paliperidone- Bio-x
34. Risperidone-m 9-hydroxy
35. Paliperidone [mi]
36. Paliperidone [jan]
37. Paliperidone [usan]
38. Paliperidone [vandf]
39. Paliperidone [mart.]
40. Jns-007er
41. Mls004773953
42. Paliperidone [usp-rs]
43. Paliperidone [who-dd]
44. Schembl436689
45. Paliperidone (jan/usp/inn)
46. Gtpl7258
47. Paliperidone [ema Epar]
48. Dtxsid7049059
49. 9-hydroxyrisperidone-d4 Solution
50. Paliperidone, >=98% (hplc)
51. Bcpp000132
52. Hms3261b06
53. Hms3743m09
54. Hms3887k15
55. Paliperidone [orange Book]
56. Amy24885
57. Bcp02338
58. Hy-a0019
59. Paliperidone [usp Monograph]
60. Tox21_500562
61. Bdbm50252513
62. S1724
63. Akos005266713
64. Akos016339656
65. Akos025392164
66. Ac-1282
67. Bcp9001047
68. Ccg-221866
69. Cs-0386
70. Db01267
71. Ks-1279
72. Lp00562
73. Nsc 759623
74. Pb27526
75. Sdccgsbi-0633730.p001
76. Ncgc00186014-01
77. Ncgc00186014-12
78. Ncgc00261247-01
79. 4h-pyrido(1,2-a)pyrimidin-4-one, 3-(2-(4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl)ethyl)-6,7,8-tetrahydro-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-
80. 4h-pyrido(2,1-a)pyrimidin-4-one, 6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-3-(2-(4-(6-fluro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl)ethyl)-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-
81. As-13860
82. Bp164223
83. Smr001456280
84. Risperidone Impurity, 9-hydroxyrisperidone-
85. 9-hydroxy Risperidone-d4 (paliperidone D4)
86. 9-hydroxyrisperidone 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
87. Ft-0600425
88. Ft-0670101
89. Ft-0670102
90. P1897
91. Risperidone Impurity C [ep Impurity]
92. C21516
93. D05339
94. 598p754
95. L023985
96. Q423292
97. Sr-02000000862
98. Q-101425
99. Sr-02000000862-3
100. Brd-a99888680-001-04-6
101. Paliperidone, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
102. Risperidone Impurity, 9-hydroxyrisperidone- [usp Impurity]
103. (+/-)-3-[2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-4h-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one
104. (9rs)-3-[2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)piperidin-1-yl]ethyl]-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-4h-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one (9-hydroxyrisperidone)
105. 3-(2-(4-(6-fluorobenzo[d]isoxazol-3-yl)piperidin-1-yl)ethyl)-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-6,7,8,9-tetrahydropyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one
106. 3-[ 2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-4h-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one
107. 3-[ 2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-4h-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin4-one
108. 3-[2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol- 3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-9-hy Droxy-2-methyl-4h-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one
109. 3-[2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-4h-pyrido[1,2-a]-pyrimidin-4-one
110. 3-[2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-4h-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one, 9-hydroxyrisperidone
111. 3-[2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]-9-hydroxy-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-2-methyl-4h-pyrido[1,2-a]-pyrimidin-4-one
112. 3-{2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzoisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl}-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-pyrido[1,2-alpha]pyrimidin-4-one
113. 3-{2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzoxazol-3-yl)piperidin-1-yl]ethyl}-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-4h-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one
114. 3-{2-[4-(6-fluoro-benzo[d]isoxazol-3-yl)-piperidin-1-yl]-ethyl}-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-6,7,8,9- Tetrahydro-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one
115. 6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-3-(2-(4-(6-fluro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl)ethyl)-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-4h-pyrido[2,1-a]pyrimidin-4-one
116. 9-hydroxyrisperidone Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 426.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H27FN4O3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 426.20671890 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 426.20671890 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 82.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 764 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Invega |
| PubMed Health | Paliperidone |
| Drug Classes | Antipsychotic |
| Drug Label | Paliperidone, the active ingredient in INVEGA Extended-Release Tablets, is a psychotropic agent belonging to the chemical class of benzisoxazole derivatives. INVEGA contains a racemic mixture of (+)- and (-)- paliperidone. The chemical name is (... |
| Active Ingredient | Paliperidone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 9mg; 1.5mg; 12mg; 6mg; 3mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Janssen Pharms; Janssen |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Invega sustenna |
| PubMed Health | Paliperidone (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antipsychotic |
| Active Ingredient | Paliperidone palmitate |
| Dosage Form | Suspension, extended release |
| Route | Intramuscular |
| Strength | 234mg/1.5ml (156mg/ml); 156mg/ml (156mg/ml); 117mg/0.75ml (117mg/0.75ml); 39mg/0.25ml (39mg/0.25ml); 78mg/0.5ml (78mg/0.5ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Janssen Pharms |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Invega |
| PubMed Health | Paliperidone |
| Drug Classes | Antipsychotic |
| Drug Label | Paliperidone, the active ingredient in INVEGA Extended-Release Tablets, is a psychotropic agent belonging to the chemical class of benzisoxazole derivatives. INVEGA contains a racemic mixture of (+)- and (-)- paliperidone. The chemical name is (... |
| Active Ingredient | Paliperidone |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 9mg; 1.5mg; 12mg; 6mg; 3mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Janssen Pharms; Janssen |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Invega sustenna |
| PubMed Health | Paliperidone (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antipsychotic |
| Active Ingredient | Paliperidone palmitate |
| Dosage Form | Suspension, extended release |
| Route | Intramuscular |
| Strength | 234mg/1.5ml (156mg/ml); 156mg/ml (156mg/ml); 117mg/0.75ml (117mg/0.75ml); 39mg/0.25ml (39mg/0.25ml); 78mg/0.5ml (78mg/0.5ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Janssen Pharms |
Antipsychotic Agent
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Paliperidone. Online file (MeSH, 2014). Available from, as of November 19, 2013: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2014/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
Invega (paliperidone) Extended-Release Tablets are indicated for the treatment of schizophrenia. The efficacy of Invega in schizophrenia was established in three 6-week trials in adults and one 6-week trial in adolescents, as well as one maintenance trial in adults. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for INVEGA (paliperidone) tablet, extended release (June 2011). Available from, as of November 12, 2013: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=7b8e5b26-b9e4-4704-921b-3c3c0d159916
Invega (paliperidone) Extended-Release Tablets are indicated for the treatment of schizoaffective disorder as monotherapy and an adjunct to mood stabilizers and/or antidepressant therap. The efficacy of Invega in schizoaffective disorder was established in two 6-week trials in adults. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for INVEGA (paliperidone) tablet, extended release (June 2011). Available from, as of November 12, 2013: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=7b8e5b26-b9e4-4704-921b-3c3c0d159916
Invega Sustenna (paliperidone palmitate) is indicated for the treatment of schizophrenia. Efficacy was established in four short-term studies and one longer-term study in adults. /Paliperidone palmitate; Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for IINVEGA SUSTENNA (paliperidone palmitate) injection (October 2012). Available from, as of November 15, 2013: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=1af14e42-951d-414d-8564-5d5fce138554
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS. Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Analyses of 17 placebo-controlled trials (modal duration of 10 weeks), largely in patients taking atypical antipsychotic drugs, revealed a risk of death in drug-treated patients of between 1.6 to 1.7 times the risk of death in placebo-treated patients. Over the course of a typical 10-week controlled trial, the rate of death in drug-treated patients was about 4.5%, compared to a rate of about 2.6% in the placebo group. Although the causes of death were varied, most of the deaths appeared to be either cardiovascular (e.g., heart failure, sudden death) or infectious (e.g., pneumonia) in nature. Observational studies suggest that, similar to atypical antipsychotic drugs, treatment with conventional antipsychotic drugs may increase mortality. The extent to which the findings of increased mortality in observational studies may be attributed to the antipsychotic drug as opposed to some characteristic(s) of the patients is not clear. Invega (paliperidone) Extended-Release Tablets is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for INVEGA (paliperidone) tablet, extended release (June 2011). Available from, as of November 12, 2013: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=7b8e5b26-b9e4-4704-921b-3c3c0d159916
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS: Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Invega Sustenna is not approved for use in patients with dementia-related psychosis. /Paliperidone palmitate/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for IINVEGA SUSTENNA (paliperidone palmitate) injection (October 2012). Available from, as of November 15, 2013: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=1af14e42-951d-414d-8564-5d5fce138554
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema, have been observed in patients receiving risperidone or paliperidone. Paliperidone is therefore contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to paliperidone, risperidone, or any ingredient in the paliperidone formulation.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013, p. 2504
An increased incidence of adverse cerebrovascular events (cerebrovascular accidents and transient ischemic attacks), including fatalities, has been observed in geriatric patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with certain atypical antipsychotic agents (aripiprazole, olanzapine, risperidone) in placebo-controlled studies. The manufacturer states that paliperidone is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013, p. 2504
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Paliperidone (32 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
As an oral extended-release tablet and a once-monthly extended-release suspension for intramuscular injection, paliperidone is indicated for the treatment of adults and adolescents with schizophrenia and in the treatment of schizoaffective disorder in combination with antidepressants or mood stabilizers. Paliperidone is also available in both an every-three-month and twice-yearly extended-release suspension for intramuscular injection for the treatment of schizophrenia.
Invega is indicated for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults and in adolescents 15 years and older.
Invega is indicated for the treatment of schizoaffective disorder in adults.
Paliperidone is an atypical antipsychotic developed by Janssen Pharmaceutica. Chemically, paliperidone is primary active metabolite of the older antipsychotic risperidone (paliperidone is 9-hydroxyrisperidone). The mechanism of action is unknown but it is likely to act via a similar pathway to risperidone.
Serotonin 5-HT2 Receptor Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate SEROTONIN 5-HT2 RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of SEROTONIN or SEROTONIN 5-HT2 RECEPTOR AGONISTS. Included under this heading are antagonists for one or more specific 5-HT2 receptor subtypes. (See all compounds classified as Serotonin 5-HT2 Receptor Antagonists.)
Antipsychotic Agents
Agents that control agitated psychotic behavior, alleviate acute psychotic states, reduce psychotic symptoms, and exert a quieting effect. They are used in SCHIZOPHRENIA; senile dementia; transient psychosis following surgery; or MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; etc. These drugs are often referred to as neuroleptics alluding to the tendency to produce neurological side effects, but not all antipsychotics are likely to produce such effects. Many of these drugs may also be effective against nausea, emesis, and pruritus. (See all compounds classified as Antipsychotic Agents.)
Dopamine D2 Receptor Antagonists
Compounds and drugs that bind to and inhibit or block the activation of DOPAMINE D2 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Dopamine D2 Receptor Antagonists.)
N05AX13
N - Nervous system
N05 - Psycholeptics
N05A - Antipsychotics
N05AX - Other antipsychotics
N05AX13 - Paliperidone
Absorption
The absolute oral bioavailability of paliperidone following paliperidone administration is 28%.
Route of Elimination
One week following administration of a single oral dose of 1 mg immediate-release 14C-paliperidone to 5 healthy volunteers, 59% (range 51% 67%) of the dose was excreted unchanged into urine, 32% (26% 41%) of the dose was recovered as metabolites, and 6% 12% of the dose was not recovered.
Volume of Distribution
487 L
The absolute oral bioavailability of paliperidone following Invega administration is 28%. Administration of a 12 mg paliperidone extended-release tablet to healthy ambulatory subjects with a standard high-fat/high-caloric meal gave mean Cmax and AUC values of paliperidone that were increased by 60% and 54%, respectively, compared with administration under fasting conditions. Clinical trials establishing the safety and efficacy of Invega were carried out in subjects without regard to the timing of meals. While Invega can be taken without regard to food, the presence of food at the time of Invega administration may increase exposure to paliperidone. Based on a population analysis, the apparent volume of distribution of paliperidone is 487 L. The plasma protein binding of racemic paliperidone is 74%.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for INVEGA (paliperidone) tablet, extended release (June 2011). Available from, as of November 12, 2013: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=7b8e5b26-b9e4-4704-921b-3c3c0d159916
Following a single dose, the plasma concentrations of paliperidone gradually rise to reach peak plasma concentration (Cmax) approximately 24 hours after dosing. The pharmacokinetics of paliperidone following Invega administration are dose-proportional within the available dose range. The terminal elimination half-life of paliperidone is approximately 23 hours. Steady-state concentrations of paliperidone are attained within 4-5 days of dosing with Invega in most subjects. The mean steady-state peak:trough ratio for an Invega dose of 9 mg was 1.7 with a range of 1.2-3.1.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for INVEGA (paliperidone) tablet, extended release (June 2011). Available from, as of November 12, 2013: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=7b8e5b26-b9e4-4704-921b-3c3c0d159916
One week following administration of a single oral dose of 1 mg immediate-release (14)C-paliperidone to 5 healthy volunteers, 59% (range 51% - 67%) of the dose was excreted unchanged into urine, 32% (26% - 41%) of the dose was recovered as metabolites, and 6% - 12% of the dose was not recovered. Approximately 80% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in urine and 11% in the feces.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for INVEGA (paliperidone) tablet, extended release (June 2011). Available from, as of November 12, 2013: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=7b8e5b26-b9e4-4704-921b-3c3c0d159916
Paliperidone is excreted in human breast milk.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for INVEGA (paliperidone) tablet, extended release (June 2011). Available from, as of November 12, 2013: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=7b8e5b26-b9e4-4704-921b-3c3c0d159916
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Paliperidone (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Although in vitro studies suggested a role for CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 in the metabolism of paliperidone, in vivo results indicate that these isozymes play a limited role in the overall elimination of paliperidone. Four primary metabolic pathways have been identified in vivo, none of which could be shown to account for more than 10% of the dose: dealkylation, hydroxylation, dehydrogenation, and benzisoxazole scission. Paliperidone does not undergo extensive metabolism and a significant portion of its metabolism occurs in the kidneys.
Four primary metabolic pathways have been identified in vivo, none of which could be shown to account for more than 10% of the dose: dealkylation, hydroxylation, dehydrogenation, and benzisoxazole scission.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for INVEGA (paliperidone) tablet, extended release (June 2011). Available from, as of November 12, 2013: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=7b8e5b26-b9e4-4704-921b-3c3c0d159916
Although in vitro studies suggested a role for CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 in the metabolism of paliperidone, in vivo results indicate that these isozymes play a limited role in the overall elimination of paliperidone.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for INVEGA (paliperidone) tablet, extended release (June 2011). Available from, as of November 12, 2013: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=7b8e5b26-b9e4-4704-921b-3c3c0d159916
Paliperidone is a known human metabolite of risperidone.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The terminal elimination half-life of paliperidone is approximately 23 hours.
The median apparent half-life of paliperidone following Invega Sustenna single-dose administration over the dose range of 39 mg - 234 mg ranged from 25 days - 49 days. /Paliperidone palmitate/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for IINVEGA SUSTENNA (paliperidone palmitate) injection (October 2012). Available from, as of November 15, 2013: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=1af14e42-951d-414d-8564-5d5fce138554
The terminal elimination half-life of paliperidone is approximately 23 hours.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for INVEGA (paliperidone) tablet, extended release (June 2011). Available from, as of November 12, 2013: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=7b8e5b26-b9e4-4704-921b-3c3c0d159916
Paliperidone is the major active metabolite of risperidone. The mechanism of action of paliperidone, as with other drugs having efficacy in schizophrenia, is unknown, but it has been proposed that the drug's therapeutic activity in schizophrenia is mediated through a combination of central dopamine Type 2 (D2) and serotonin Type 2 (5HT2A) receptor antagonism.
The exact mechanism of paliperidone's antipsychotic action, like that of other antipsychotic agents, has not been fully elucidated, but may involve antagonism of central dopamine type 2 (D2) and serotonin type 2 (5-hydroxytryptamine [5-HT2A]) receptors.1 39 41 Antagonism at a1- and a2-adrenergic and histamine (H1) receptors may contribute to other therapeutic and adverse effects observed with the drug.1 2 39 Paliperidone possesses no affinity for cholinergic muscarinic and beta1- and beta2-adrenergic receptors.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013, p. 2506
Paliperidone is the major active metabolite of risperidone. The mechanism of action of paliperidone, as with other drugs having efficacy in schizophrenia, is unknown, but it has been proposed that the drug's therapeutic activity in schizophrenia is mediated through a combination of central dopamine Type 2 (D2) and serotonin Type 2 (5HT2A) receptor antagonism.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for INVEGA (paliperidone) tablet, extended release (June 2011). Available from, as of November 12, 2013: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=7b8e5b26-b9e4-4704-921b-3c3c0d159916
Paliperidone is an active metabolite of the second-generation atypical antipsychotic, risperidone recently approved for the treatment of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Because paliperidone differs from risperidone by only a single hydroxyl group, questions have been raised as to whether there are significant differences in the effects elicited between these two drugs. /The researchers/ compared the relative efficacies of paliperidone versus risperidone to regulate several cellular signalling pathways coupled to four selected GPCR targets that are important for either therapeutic or adverse effects: human dopamine D2 , human serotonin 2A receptor subtype (5-HT2A ), human serotonin 2C receptor subtype and human histamine H1 receptors. Whereas the relative efficacies of paliperidone and risperidone were the same for some responses, significant differences were found for several receptor-signalling systems, with paliperidone having greater or less relative efficacy than risperidone depending upon the receptor-response pair. Interestingly, for 5-HT2A -mediated recruitment of beta-arrestin, 5-HT2A -mediated sensitization of ERK, and dopamine D2 -mediated sensitization of adenylyl cyclase signalling, both paliperidone and risperidone behaved as agonists. These results suggest that the single hydroxyl group of paliperidone promotes receptor conformations that can differ from those of risperidone leading to differences in the spectrum of regulation of cellular signal transduction cascades. Such differences in signalling at the cellular level could lead to differences between paliperidone and risperidone in therapeutic efficacy or in the generation of adverse effects.
PMID:23826915 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3791992 Clarke WP et al; Br J Pharmacol 170 (3): 532-45 (2013)