

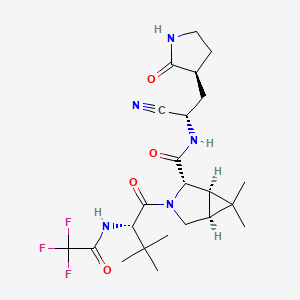

1. (1r,2s,5s)-n-((1s)-1-cyano-2-((3s)-2-oxopyrrolidin-3-yl)ethyl)-6,6-dimethyl-3-(3-methyl-n-(trifluoroacetyl)-l-valyl)-3-azabicyclo(3.1.0)hexane-2-carboxamide
2. Pf-07321332
3. Pf07321332
1. 2628280-40-8
2. 7r9a5p7h32
3. Paxlovid
4. Pf-07321332
5. Pf07321332
6. Nirmatrelvir [usan]
7. (1r,2s,5s)-n-[(1s)-1-cyano-2-[(3s)-2-oxopyrrolidin-3-yl]ethyl]-3-[(2s)-3,3-dimethyl-2-[(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)amino]butanoyl]-6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-2-carboxamide
8. (1r,2s,5s)-n-((1s)-1-cyano-2-((3s)-2-oxopyrrolidin-3-yl)ethyl)-6,6-dimethyl-3-(3-methyl-n-(trifluoroacetyl)-l-valyl)-3-azabicyclo(3.1.0)hexane-2-carboxamide
9. (1r,2s,5s)-n-[(1s)-1-cyano-2-[(3s)-2-oxopyrrolidin-3-yl]ethyl]-3-[(2s)-3,3-dimethyl-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetamido)butanoyl]-6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-2-carboxamide
10. (1r,2s,5s)-n-{(1s)-1-cyano-2-[(3s)-2-oxopyrrolidin-3-yl]ethyl}-3-[(2s)-3,3-dimethyl-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetamido)butanoyl]-6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-2-carboxamide
11. (1r,2s,5s)-n-{(1s)-1-cyano-2-[(3s)-2-oxopyrrolidin-3-yl]ethyl}-6,6-dimethyl-3-[3-methyl-n-(trifluoroacetyl)-l-valyl]-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-2-carboxamide
12. 3-azabicyclo(3.1.0)hexane-2-carboxamide, N-((1s)-1-cyano-2-((3s)-2-oxo-3-pyrrolidinyl)ethyl)-3-((2s)-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxo-2-((2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)amino)butyl)-6,6-dimethyl-, (1r,2s,5s)-
13. 3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-2-carboxamide, N-[(1s)-1-cyano-2-[(3s)-2-oxo-3-pyrrolidinyl]ethyl]-3-[(2s)-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxo-2-[(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)amino]butyl]-6,6-dimethyl-, (1r,2s,5s)-
14. Science.abl4784, 6
15. Nirmatrelvir [inn]
16. Nirmatrelvir [jan]
17. Nirmatrelvir [who-dd]
18. Unii-7r9a5p7h32
19. Pf07321332(nirmatrelvir)
20. Chembl4802135
21. Gtpl11503
22. Chebi:170007
23. Bdbm496902
24. Dtxsid501336829
25. Ex-a5024
26. Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir + Ritonavir)
27. Who 12161
28. At31194
29. Ac-35259
30. Example E61 [wo2021250648a1]
31. Paxlovid Component Pf-07321332
32. Hy-138687
33. 870124 More Info Pf-00835231
34. Cs-0166635
35. Pf 07321332
36. (1r,2s,5s)-n-((s)-1-cyano-2-((s)-2-oxopyrrolidin-3-yl)ethyl)-3-((s)-3,3-dimethyl-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetamido)butanoyl)-6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-2-carboxamide
37. (1s,3as,4ar)-n-[(1s)-1-cyano-2-[(3s)-2-oxotetrahydro-1h-pyrrol-3-yl]ethyl]-2-[(2s)-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxo-2-[(trifluoroacetyl)amino]butyl]-4,4-dimethyl-2,3,3a,4a-tetrahydro-1h-cyclopropa[1,2-c]pyrrole-1-carboxamide
| Molecular Weight | 499.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H32F3N5O4 |
| XLogP3 | 2.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 499.24063901 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 499.24063901 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 131 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 964 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 6 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Nirmatrelvir has received FDA emergency use authorization, in combination with [ritonavir], for the treatment of mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in adults and pediatric patients (12 years of age and older weighing at least 40 kg) with positive results of direct severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) viral testing, and who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death.
Paxlovid is indicated for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in adults who do not require supplemental oxygen and who are at increased risk for progressing to severe COVID 19 (see section 5. 1).
Nirmatrelvir is administered alongside ritonavir, a potent inhibitor of CYP3A enzymes, in order to inhibit its metabolism and increase plasma nirmatrelvir concentrations. While therapeutically beneficial, the use of ritonavir poses a significant risk of drug interaction due to its potent inhibition profile - patients and clinicians should consult the prescribing information for Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir and ritonavir) to evaluate any potential for drug interaction with existing medications prior to the initiation of Paxlovid.
Viral Protease Inhibitors
Compounds that specifically inhibit PROTEOLYTIC ENZYMES that are encoded by VIRUSES. (See all compounds classified as Viral Protease Inhibitors.)
Not yet assigned
Absorption
The median Tmax of nirmatrelvir, when given with ritonavir, is 3 hours. After a single oral dose of 300mg nirmatrelvir and 100mg ritonavir in healthy subjects, the Cmax and AUCinf of nirmatrelvir were 2.21 g/mL and 23.01 g*hr/mL, respectively.
Route of Elimination
The major route of nirmaltrevir elimination is via renal elimination, due in part to its coadministration with ritonavir which inhibits its metabolism. Following oral administration alongside ritonavir, approximately 49.6% of drug-related material was recovered in the feces and 35.3% was recovered in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The mean volume of distribution of nirmatrelvir, when given with ritonavir, is 104.7 liters.
Clearance
The mean oral clearance of nirmatrelvir, administered with ritonavir, is 8.99 L/h.
Nirmatrelvir is a substrate of CYP3A4, but undergoes minimal metabolism when administered alongside ritonavir.
The mean half-life of nirmatrelvir, administered alongside ritonavir, is 6.05 hours.
Nirmatrelvir is an inhibitor of a cysteine residue in the 3C-like protease (3CLPRO) of SARS-CoV-2. This cysteine is responsible to the activity of the 3CLPRO of SARS-CoV-2 and potentially other members of the coronavirus family. The 3CLPRO, also known as the main protease or non structural protein 5, is responsible for cleaving polyproteins 1a and 1ab. These polyproteins contain the 3CLPRO itself, a papain-like (PL) cysteine protease, and 14 other nonstructural proteins. Without the activity of the 3CLPRO, nonstructural proteins (including proteases) cannot be released to perform their functions, inhibiting viral replication.
