

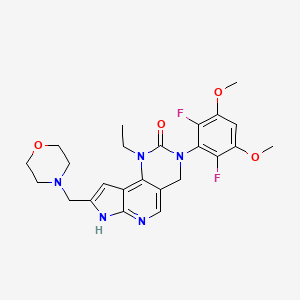

1. 2h-pyrrolo(3',2':5,6)pyrido(4,3-d)pyrimidin-2-one, 3-(2,6-difluoro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-ethyl-1,3,4,7-tetrahydro-8-(4-morpholinylmethyl)-
2. Incb-054828
3. Incb054828
4. Pemazyre
1. 1513857-77-6
2. Pemazyre
3. Incb054828
4. Pemigatinib [inn]
5. Fgfr Inhibitor Incb054828
6. Pemigatinib [usan]
7. Incb-054828
8. Y6bx7bl23k
9. Incb54828
10. Incb-54828
11. 1513857-77-6 (free Base)
12. 2h-pyrrolo(3',2':5,6)pyrido(4,3-d)pyrimidin-2-one, 3-(2,6-difluoro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-ethyl-1,3,4,7-tetrahydro-8-(4-morpholinylmethyl)-
13. 3-(2,6-difluoro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-ethyl-8-(morpholinomethyl)-1,3,4,6-tetrahydro-2h-pyrrolo[3',2':5,6]pyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidin-2-one
14. 3-(2,6-difluoro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-ethyl-8-[(morpholin-4-yl)methyl]-1,3,4,7-tetrahydro-2hpyrrolo[3',2':5,6]pyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidin-2-one
15. Pemazyre (tn)
16. 3-(2,6-difluoro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-ethyl-8-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-1,3,4,7-tetrahydro-2h-pyrrolo(3',2':5,6)pyrido(4,3-d)pyrimidin-2-one
17. 3-(2,6-difluoro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-ethyl-8-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-1,3,4,7-tetrahydro-2h-pyrrolo[3',2':5,6]pyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidin-2-one
18. Pemigatinib [mi]
19. Pemigatinib [jan]
20. Pemigatinib [usan:inn]
21. Unii-y6bx7bl23k
22. Pemigatinib [who-dd]
23. Pemigatinib (jan/usan/inn)
24. Gtpl9767
25. Pemigatinib (incb054828)
26. Chembl4297522
27. Schembl15556271
28. Pemigatinib [orange Book]
29. Bdbm301310
30. Dtxsid501027955
31. Incb 54828
32. Ex-a4049
33. Nsc816556
34. Us10131667, Example 126
35. At15587
36. Db15102
37. Incb054828incb054828
38. Nsc-816556
39. Ac-36489
40. As-78489
41. Example 126 [wo2014007951]
42. Hy-109099
43. Cs-0039499
44. D11417
45. A936247
46. 11-(2,6-difluoro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-13-ethyl-4-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-5,7,11,13-tetrazatricyclo[7.4.0.02,6]trideca-1,3,6,8-tetraen-12-one
47. 3-(2,6-difluoro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-ethyl-8-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-1,3,4,7-tetrahydro-2h-pyrrolo[3'',2'':5,6]pyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidin-2-one
48. 3-(2,6-difluoro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-ethyl-8-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-4,7-dihydropyrrolo[4,5]pyrido[1,2-d]pyrimidin-2-one
49. 3-(2,6-difluoro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-ethyl-8-(morpholinomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-1h-pyrrolo[3',2':5,6]pyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidin-2(7h)-one
| Molecular Weight | 487.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H27F2N5O4 |
| XLogP3 | 1.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 487.20311068 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 487.20311068 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 83.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 731 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Pemigatinib is indicated for the treatment of unresectable locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma in previously-treated adult patients with a fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) fusion or other rearrangement as detected by an FDA-approved test.
Pemazyre monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of adults with locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma with a fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) fusion or rearrangement that have progressed after at least one prior line of systemic therapy.
Pemigatinib is a small molecule kinase inhibitor that exerts anti-tumour activity through inhibition of fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs). With an IC50 of less than 2 nM, pemigatinib displays potent inhibition of FGFR1, FGFR2, and FGFR3. In mouse xenograft models of human tumours with FGFR1, FGFR2, or FGFR3 alterations, pemigatinib exhibited potent anti-tumour activity by suppressing the growth of xenografted tumour models. It also showed efficacy against a patient-derived xenograft model of cholangiocarcinoma that expressed an oncogenic FGFR2 Transformer-2 beta homolog (TRA2b) fusion protein. Pemigatinib also inhibited FGFR4 _in vitro_, however at a concentration approximately 100 times higher than those that inhibit FGFR1, 2, and 3.
L01EX20
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EN - Fibroblast growth factor receptor (fgfr) tyrosine kinase inhibitors
L01EN02 - Pemigatinib
Absorption
Following administration of a single oral dose of 13.5 mg pemigatinib, the median Tmax was 1.13 (0.50-6.00) hours. The steady state was reached within 4 days following repeated once daily dosing, with the median drug accumulation ratio of 1.63 (range 0.63 to 3.28). Steady-state concentration of pemigatinib increased in a dose-proportional manner over the dose range of 1 to 20 mg, which is about 0.07 to 1.5 times the recommended dose. The mean steady-state AUC and Cmax were 2620 nM x h (54% CV) and 236 nM, respectively.
Route of Elimination
Following oral administration of a single radiolabeled dose of 11 mg pemigatinib, about 82.4% of the dose was recovered in feces. Of this recovered drug, about 1.4% of the dose was unchanged parent compound. About 12.6% of the dose was recovered in urine, where 1% of the dose was unchanged.
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution was 235 L (60.8% CV) following a single oral dose of 13.5 mg pemigatinib.
Clearance
Following administration of a single oral dose of 13.5 mg pemigatinib, the geometric mean apparent clearance (CL/F) was 10.6 L/h (54% CV).
Pemigatinib is predominantly metabolized by the CYP3A4 enzyme _in vitro_. Its specific metabolic pathway and resulting metabolites have not yet been characterized.
Following administration of a single oral dose of 13.5 mg pemigatinib, the geometric mean elimination half-life (t) of pemigatinib was 15.4 (51.6% CV) hours.
Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) is a receptor tyrosine kinase involved in activating signalling pathways that promote cell proliferation, survival, and migration, as well as growth arrest and cellular differentiation. The initiation of the FGFR signalling pathway requires the binding of its natural ligand, fibroblast growth factor (FGF). Once FGF binds to the extracellular ligand-binding domain of the receptor, FGFRs dimerize and autophosphorylate the tyrosine residue in the intracellular tyrosine-kinase domain, leading to the activation of the tyrosine kinase. Downstream cascades involve phosphorylation of multiple intracellular signalling proteins, such as phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K)-AKT and RAS/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and phospholipase C, which activates the protein kinase C pathway. FGFR-mediated pathway ultimately promotes cell growth, differentiation, survival, angiogenesis, and organogenesis, depending on cell type. Expressed in different isoforms in various tissues and cell lines, FGFRs are not constitutively active in normal cells. However, FGFR1, FGFR2, or FGFR3 alterations in certain tumours can lead to constitutive FGFR activation and aberrant FGFR signalling, supporting the proliferation and survival of malignant cells. Pemigatinib inhibits FGFR1, FGFR2, and FGFR3, blocking their signalling pathways and decreasing cell viability in cancer cell lines with activating FGFR amplification and fusions that resulted in constitutive activation of FGFR signalling. Genetic alterations in FGFR1, FGFR2, and FGFR3 (such as amplification, missense, or fusion mutations in the coding region) leading to constitutive activation of FGFR signalling pathways are observed in various tumours. However, alterations in FGFR genes are demonstrated in selected patients and do not always imply oncogene development. Therefore, it is imperative that fusion or rearrangement of FGFRs are demonstrated through tests prior to initiation of drug therapy.
