
1. Apocillin
2. Beromycin
3. Beromycin, Penicillin
4. Berromycin, Penicillin
5. Betapen
6. Fenoxymethylpenicillin
7. Pen Vk
8. Penicillin Beromycin
9. Penicillin Berromycin
10. Penicillin V Potassium
11. Penicillin V Sodium
12. Penicillin Vk
13. Penicillin, Phenoxymethyl
14. Phenoxymethyl Penicillin
15. Phenoxymethylpenicillin
16. Potassium, Penicillin V
17. Sodium, Penicillin V
18. V Cillin K
19. V Sodium, Penicillin
20. V-cillin K
21. Vcillin K
22. Vegacillin
1. Phenoxymethylpenicillin
2. Penicillin Phenoxymethyl
3. Oracillin
4. 87-08-1
5. V-cillin
6. Phenomycilline
7. Fenospen
8. Vebecillin
9. Distaquaine V
10. Phenoxymethyl Penicillin
11. Beromycin
12. Phenoxymethylenepenicillinic Acid
13. Phenoximethylpenicillinum
14. Phenoxymethylpenicillinum
15. Fenoximetilpenicilina
16. Pen-v
17. Phenoxymethylpenicillinic Acid
18. Phenoxymethylpenicilline
19. Phenopenicillin
20. 6-phenoxyacetamidopenicillanic Acid
21. Meropenin
22. Fenossimetilpenicillina [dcit]
23. Phenoxomethylpenicillin
24. Penapar-vk
25. Phenocillin
26. Stabicillin
27. Fenacilin
28. Oratren
29. Apopen
30. Ospen
31. Fenoximetilpenicilina [inn-spanish]
32. Eskacillian V
33. V-tablopen
34. Pen-vee
35. Acipen V
36. Pen-oral
37. V-cyline
38. Penicillin-vk
39. V-cil
40. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(2-phenoxyacetyl)amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
41. Chebi:27446
42. Calcipen
43. Rocilin
44. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(phenoxyacetyl)amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
45. Eskacillin V
46. Crystapen V
47. V-cylina
48. Phenoxymethylpenicillin (inn)
49. Phenoxymethylpenicillin [inn]
50. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(2-phenoxyacetamido)-4-thia-1- Azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
51. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(2-phenoxyacetamido)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
52. Z61i075u2w
53. P-mega-tablinen
54. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(2-phenoxyacetamido)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
55. Pnv
56. Fenossimetilpenicillina
57. Penicillin V [usan]
58. Phenoxymethylpenicillin 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
59. Penicillanic Acid, 6-phenoxyacetamido-
60. Phenoxymethylpenicillinic Acid Potassium Salt
61. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-{[(phenyloxy)acetyl]amino}-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
62. Phenoxymethylpenicilline [inn-french]
63. Phenoxymethylpenicillinum [inn-latin]
64. Ccris 752
65. V-cillin (tn)
66. Penicillin V (usp)
67. Hsdb 6314
68. Phenoxomethylpenicillanyl
69. Phenoxymethylpenicillanyl
70. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(2-phenoxyacetamido)-
71. 132-98-9
72. Einecs 201-722-0
73. Brn 0096259
74. Penicillin V [usan:usp]
75. Unii-z61i075u2w
76. Penicillinv
77. Penicillin-v-potassium
78. 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-((phenyloxyacetyl)amino)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
79. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-((phenoxyacetyl)amino)-, (2s-(2alpha,5alpha,6beta))-
80. Pc Pen Vk
81. Spectrum_001007
82. Spectrum2_000495
83. Spectrum3_000543
84. Spectrum4_000472
85. Spectrum5_001409
86. Chembl615
87. Epitope Id:115011
88. Epitope Id:116056
89. Penicillin V [mi]
90. Penicillin V [hsdb]
91. Schembl49223
92. Bspbio_002185
93. Kbiogr_000944
94. Kbioss_001487
95. 4-27-00-05884 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
96. Mls001304105
97. Divk1c_000779
98. Spbio_000389
99. Penicillin V [usp-rs]
100. Dtxsid3023429
101. Schembl22099709
102. Chebi:53706
103. Gtpl10920
104. Hy-b0975a
105. Kbio1_000779
106. Kbio2_001487
107. Kbio2_004055
108. Kbio2_006623
109. Kbio3_001685
110. Ninds_000779
111. Glxc-25717
112. Penicillin V [orange Book]
113. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-((phenoxyacetyl)amino)-, (2s,5r,6r)-
114. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-((phenoxyacetyl)amino)-, (2s-(2.alpha.,5.alpha.,6.beta.))-
115. Zinc3831282
116. 2,2-dimethyl-6beta-[(phenoxyacetyl)amino]penam-3alpha-carboxylic Acid
117. Bdbm50370584
118. Penicillin V [usp Monograph]
119. 3,3-dimethyl-6beta-[(phenoxyacetyl)amino]penam-2alpha-carboxylic Acid (pin)
120. Akos015969737
121. Db00417
122. Phenoxymethylpenicillin [mart.]
123. Idi1_000779
124. Phenoxymethylpenicillin [who-dd]
125. Phenoxymethylpenicillin [who-ip]
126. Phenoxymethyl Penicillinic Acid*free Acid
127. Smr000539431
128. Sbi-0051477.p003
129. Ab00514745
130. Cs-0013728
131. Phenoxymethylpenicillin [ep Monograph]
132. Phenoxymethylpenicillin For System Suitability
133. C08126
134. D05411
135. Phenoxymethylpenicillinum [who-ip Latin]
136. Q422215
137. W-109316
138. Brd-k43966364-237-02-2
139. Brd-k43966364-237-03-0
140. 6beta-phenoxyacetamido-2,2-dimethylpenam-3alpha-carboxylic Acid
141. Phenoxymethylpenicillin, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
142. Penicillin V, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
143. Phenoxymethylpenicillin, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
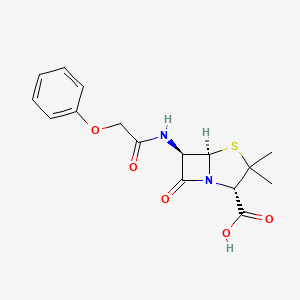
| Molecular Weight | 350.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H18N2O5S |
| XLogP3 | 2.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 350.09364285 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 350.09364285 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 121 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 547 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Penicillin-vk |
| Active Ingredient | Penicillin v potassium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; For solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 250mg base/5ml; eq 500mg base; eq 250mg base; eq 125mg base/5ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Penicillin-vk |
| Active Ingredient | Penicillin v potassium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; For solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 250mg base/5ml; eq 500mg base; eq 250mg base; eq 125mg base/5ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva |
Penicillins
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Penicillin V is used for the treatment of mild to moderately severe infections caused by organisms susceptible to low concentrations of the drug or for prophylaxis of certain streptococcal infections.
American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 85. Bethesda, MD: American Society Hospital Pharmacists, 1985. (Plus supplements A & B, 1985)., p. 8:12.16 153
Penicillin V /is/ indicated in the treatment of acute otitis media caused by susceptible organisms. /Included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 2149
Penicillin V /is/ indicated in the treatment of bacterial pharyngitis cuased by susceptible organisms. /Included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 2149
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for PENICILLIN V (21 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
The most important biological effect of penicillin, unrelated to hypersensitivity or to "toxic" reaction, is alteration of bacterial flora in areas of the body to which it gains access. Regardless of the route by which the drug is administered, but most strikingly when it is given by mouth, penicillin changes the composition of the microflora by eliminating sensitive microorganisms. ... In some persons ... suprainfection results from the changes in flora. /Penicillin/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1150
Fever and even vascular collapse and death may follow the use of penicillin in syphilis. This is one manifestation of the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction. It is thought to be due to hypersensitivity to antigens released during rapid and massive lysis of spirochetes. /Penicillin/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1150
Contraceptive failure and pregnancies attributed to the concurrent use of penicillins ... have been reported on a number of occasions. ... Mechanism /is/ not understood. It has been observed that ampicillin given to women in latter wk of pregnancy decreases urinary oestriol levels ... & phenoxymethylpenicillin behaves in a similar way ...
Stockley, I.H. Drug Interactions. Boston: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1981., p. 272
Individual with phenylketonuria (ie, homozygous genetic deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase) and other individuals who must restrict their intake of phenylalanine should be warned that Warner Chilcott's penicillin V potassium powder for oral soln contains aspartame ... which is metabolized in the GI tract to phenylalanine following oral administration.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 255
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PENICILLIN V (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Indicated for the treatment of mild to moderately severe infections due to penicillin G-sensitive microorganisms, with the use of bacteriological studies (including sensitivity tests) and clinical response. Phenoxymethylpenicillin may be used for the treatment of: - mild to moderate infections of the upper respiratory tract, scarlet fever, and mild erysipelas caused by Streptococcus without bacteremia - mild to moderately severe infections of the respiratory tract caused by Pneumococcus - mild infections of the skin and soft tissues caused by penicillin G-sensitive Staphylococcus - mild to moderately severe infections of the oropharynx caused by Fusospirochetosis, including Vincents gingivitis and pharyngitis, usually respond to oral penicillin therapy **Off-label** Indicated for use as prophylaxis against bacterial endocarditis in patients with congenital heart disease or rheumatic or other acquired valvular heart disease when they undergo dental procedures and surgical procedures of the upper respiratory tract.
FDA Label
Phenoxymethylpenicillin works against penicillin-sensitive microorganisms with bactericidal effects. It targets the bacteria during its active multiplication stage by interfering with bacterial cell wall peptidoglycan synthesis. _In vitro_, phenoxymethylpenicillin was shown to be active against staphylococci (except penicillinase-producing strains), streptococci (groups A, C, G, H, L and M), and pneumococci, as well as _Corynebacterium diphtheriae_, _Bacillus anthracis_, Clostridia, _Actinomyces bovis_, _Streptobacillus moniliformis_, _Listeria monocytogenes_, _Leptospira_, _Neisseria gonorrhoeae_, and _Treponema pallidum_.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
J01CE02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01C - Beta-lactam antibacterials, penicillins
J01CE - Beta-lactamase sensitive penicillins
J01CE02 - Phenoxymethylpenicillin
Absorption
Upon oral administration, phenoxymethylpenicillin is rapidly but incompletely absorbed. The bioavailability of phenoxymethylpenicillin ranges from 25 to 60%. Compared to the free acid form of the drug, the calcium or potassium salts of phenoxymethylpenicillin displays better absorption profiles. It is reported that fasting state enhances the drug absorption. The peak plasma concentrations of 200 to 700 ng/mL are achieved in 2 hours following an oral dose of 125 mg. Following an oral dose of 500 mg, the peak plasma concentrations of 3 to 5 g/mL are reached in 30 to 60 minutes post-dose.
Route of Elimination
While the drug is rapidly excreted, only 25% of the total dose is detected in the urine. Renal excretion may be delayed in neonates, young infants, and patients with renal impairment.
Volume of Distribution
Following intravenous administration, the volume of distribution at steady state was 35.4 L. Small amounts of the drug can be found in various tissues, with the highest amount found in the kidneys, with lesser amounts in the liver, skin, and intes tines. Phenoxymethylpenicillin was found in the cerebrospinal fluid. Phenoxymethylpenicillin was detectable in the placenta and human breast milk.
A dose of 1,000,000 units of the acid gives peak plasma levels of about 2 to 3 ug/ml ...
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1142
Approx 60-73% of an oral dose of penicillin V or penicillin V potassium is absorbed from the GI tract in healthy, fasting adults. Following oral administration of a single dose of penicillin V or penicillin V potassium in fasting children or adults, peak serum concn of penicillin V are generally attained within 30-60 min. Peak serum penicillin V concn are attained sooner and are slightly higher following administration of the potassium salt than the free acid.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 254
Following oral administration of a single 125-mg tablet of penicillin V potassium in healthy, fasting adults in one study, serum penicillin V concn averaged 1.2, 1.2, 0.5, and 0.1 ug/ml @ 30 min, 1 hr, 2 hr, and 4 hr, respectively, after the dose. Oral administration of a single 250-mg tablet of the drug in healthy, fasting adults results in serum penicillin V concn averaging 2.1-2.8, 2.3-2.7, 0.8-0.9, and 0.1-0.2 ug/ml @ 30 min, 1 hr, 2 hr, and 4 hr, respectively, after the dose. Following oral administration of a single 500-mg tablet of penicillin V potassium in healthy, fasting adults, serum penicillin V concn average 4.7-5, 4.9-6.3, 2.3-3, and 0.04-0.1 ug/ml @ 30 min, 1 hr, 2 hr, and 6 hr, respectively, after the dose.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 254
Variable results have been obtained in studies evaluating the effect of food on GI absorption of penicillin V and penicillin V potassium. In most studies, presence of food in the GI tract resulted in lower and delayed peak serum concn of penicillin V, although the total amt of drug absorbed was unaffected. However, results of several studies in children 2 mo to 5 yr of age indicate that both the peak serum concn and the area under the serum concn-time curve (AUC) are decreased when penicillin V potassium is administered with or immediately prior to milk or food.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 255
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for PENICILLIN V (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
About 35-70% of an oral dose is metabolized to penicilloic acid, an inactive metabolite. Small amounts of 6-aminopenicillanic acid have been recovered in the urine of patients on penicillin G. A small percentage of the drug appears to be hydroxylated into one or more active metabolites, which are also excreted via urine.
Approximately 35-70% of an oral dose of penicillin V or penicillin V potassium is metabolized to penicilloic acid which is microbiologically inactive. Small amt of 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA) have also been found in urine of patients receiving penicillin V. In addition, the drug appears to be hydroxylated to a small extent to one or more microbiologically active metabolites which are also excreted in urine.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 255
Upon oral administration, the half-life is about 30 minutes. It can last up to 4 hours in patients with renal impairment.
The serum half-life of penicillin V in adults with normal renal function is reportedly 0.5 hr.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 255
Phenoxymethylpenicillin inhibits the biosynthesis of cell wall mucopeptide by binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, which are critical in the cell wall synthesis and maintenance, as well as cell division. This disrupts the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. This subsequently leads to cell lysis.
Penicillins and breakdown products of penicillins act as haptens after their covalent reaction with proteins. The most important antigenic intermediate of penicillin appears to be the penicilloyl moiety, which is formed when the beta-lactam ring is opened. This is considered to be the major (predominant) determinant of penicillin allergy. /Penicillins/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1148
Penicillin is known to interfere with synthesis of N-acetylmuramic acid mucopeptides and teichoic acids which are part of cell-wall material. ... Under favorable conditions penicillin exerts direct bactericidal action, & successful penicillin therapy may be relatively independent of immunity mechanisms of the host. /Penicillins/
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1135
The penicillins and their metabolites are potent immunogens because of their ability to combine with proteins and act as haptens for acute antibody-mediated reactions. The most frequent (about 95 percent) or "major" determinant of penicillin allergy is the penicilloyl determinant produced by opening the beta-lactam ring of the penicillin. This allows linkage of the penicillin to protein at the amide group. "Minor" determinants (less frequent) are the other metabolites formed, including native penicillin and penicilloic acids. /Penicillins/
Haddad, L.M., Clinical Management of Poisoning and Drug Overdose. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Co., 1990., p. 953
Bactericidal; inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis. Action is dependent on the ability of penicillins to reach and bind penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located on the inner membrane of the bacterial cell wall. Penicillin-binding proteins (which include transpeptidases, carboxypeptidases, and endopeptidases) are enzymes that are involved in the terminal stages of assembling the bacterial cell wall and in reshaping the cell wall during growth and division. Penicillins bind to, and inactivate, penicillin-binding proteins, resulting in the weakening of the bacterial cell wall and lysis. /Penicillins/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 2150