

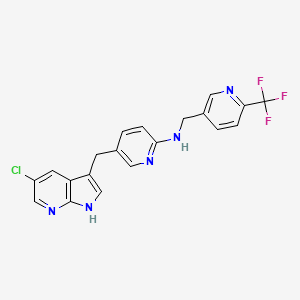

1. 5-((5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridin-3-yl)methyl)-n-((6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)methyl)pyridin-2-amine
2. Pexidartinib Hydrochloride
3. Plx3397
4. Turalio
1. 1029044-16-3
2. Plx3397
3. Plx-3397
4. Pexidartinib (plx3397)
5. Turalio
6. Cml-261
7. Pexidartinib [inn]
8. Pexidartinib [usan]
9. 5-((5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl)-n-((6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)methyl)pyridin-2-amine
10. Chembl3813873
11. 6783m2lv5x
12. 3-pyridinemethanamine, N-(5-((5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridin-3-yl)methyl)-2-pyridinyl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)-
13. 5-[(5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-n-[[6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl]methyl]pyridin-2-amine
14. 5-[(5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-n-{[6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl]methyl}pyridin-2-amine
15. 5-({5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl}methyl)-n-{[6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl]methyl}pyridin-2-amine
16. Pexidartinibum
17. Unii-6783m2lv5x
18. 5-((5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridin-3-yl)methyl)-n-((6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)methyl)pyridin-2-amine
19. Pexidartinib [mi]
20. Pexidartinib(plx3397)
21. Pexidartinib (usan/inn)
22. Pexidartinib [usan:inn]
23. Pexidartinib [who-dd]
24. Gtpl8710
25. Schembl1267310
26. Ex-a589
27. Chebi:145373
28. Dtxsid301026482
29. Hms3886d19
30. Bcp15183
31. Plx 3397
32. Bdbm50177716
33. Mfcd28900745
34. Nsc789300
35. Nsc793434
36. Nsc800843
37. S7818
38. Akos026750359
39. Zinc115705166
40. Ccg-268862
41. Db12978
42. Nsc-789300
43. Nsc-793434
44. Nsc-800843
45. Sb19178
46. Ncgc00480774-01
47. Ncgc00480774-06
48. Ac-30300
49. As-74915
50. Da-48267
51. Hy-16749
52. Ft-0699505
53. Plx 3397;plx3397;pl-x3397
54. D11270
55. A856116
56. J-690008
57. Q25100640
58. B0084-470807
59. 2(s)-amino-3-(4-{2-amino-6-[2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(3'-fluoro-biphenyl-4-yl)-ethoxy]-pyrimidin-4-yl}-phenyl)-propionic Acid Hydrochloride
60. 5-[(5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-n-[[6-(trifluoromethyl)-3-pyridyl]methyl]pyridin-2-amine
61. N-[5-[(5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-2-pyridinyl]-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3-pyridinemethanamine
62. N-[5-[(5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-2-pyridinyl]-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3-pyridinemethanamine;pexidartinib
| Molecular Weight | 417.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H15ClF3N5 |
| XLogP3 | 4.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 417.0968077 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 417.0968077 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 66.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 29 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 537 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Pexidartinib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT) associated with severe morbidity or functional limitations and not amenable to improvement with surgery.
Treatment of tenosynovial giant cell tumour. ,
Pexidartinib works by suppressing the growth of tenosynovial giant cell tumors. In clinical trials comprising of patients with symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumor, pexidartinib had a higher overall response rate, characterized by improved patient symptoms and functional outcomes, compared to placebo. Pexidartinib works by inhibiting the activation and signaling of tumor-permissive cytokines and receptor tyrosine kinases that play a central role in tumor cell proliferation and survival.
L01XE
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX - Other protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX15 - Pexidartinib
Absorption
Following administration of single doses in healthy subjects and multiple doses in patients, the mean Cmax was 8625 ng/mL and the mean AUC was 77465 ngxh/mL. The median Tmax was 2.5 hours and the time to reach the steady state was approximately 7 days. Administration of pexidartinib with a high fat meal resulted in an increased drug Cmax and AUC by 100%, with a delay in Tmax by 2.5 hours.
Route of Elimination
Pexidartinib is predominantly excreted via feces, where fecal excretion accounts for 65% of total pexidartinib elimination. Via this route of elimination, about 44% of the compound found in feces is recovered as unchanged parent drug. The renal elimination accounts for 27% of pexidartinib elimination, where more than 10% of the compound is found as the N-glucuronide metabolite.
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of pexidartinib is about 187 L. In rats, pexidartinib was shown to penetrate into the central nervous system.
Clearance
The apparent clearance is about 5.1 L/h.
Pexidartinib primarily undergoes oxidation mediated by hepatic CYP3A4 and glucuronidation by UGT1A4. Following UGT1A4-mediated glucuronidation, a major inactive N-glucuronide metabolite is formed with approximately 10% higher exposure than the parent drug after a single dose administration of pexidartinib. Based on the findings of _in vitro_ studies, CYP1A2 and CYP2C9 may also play a minor role in drug metabolism.
The elimination half-life is about 26.6 hours.
Tenosynovial giant cell tumor is a rare, non-malignant neoplasm that causes abnormal growth and damage to the synovium, bursae, or tendon sheaths. Recruitment of immune cells, specifically macrophages, is closely associated with the tumor mass formation in tenosynovial giant cell tumors. Macrophages drive tumor-promoting inflammation and play a central role in every stage of tumor progression. As the most abundant immune cells in the tumor microenvironment of solid tumors, macrophages promote processes that enhance tumor survival, such as angiogenesis, tumor cell invasion, and intravasation at the primary site. They also modulate the immune response to tumors to inhibit tumor clearance and directly engage with tumor cells to activate pro-survival signaling pathways. The recruitment, proliferation, and irreversible differentiation of macrophages are regulated by colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1), which is a cytokine that is often translocated and highly expressed in tenosynovial giant cell tumors. Elevated expression of CSF-1 and CSF-1 receptor (CSF1R) has also been implicated in various models of malignant cancers and tumors. Pexidartinib targets the CSF1/CSF1R pathway as a selective CSF1R inhibitor. It stimulates the autoinhibited state of the CSF1R by interacting with the juxtamembrane region of CSF1R, which is responsible for folding and inactivation of the kinase domain, and preventing the binding of CSF1 and ATP to the region. Without the binding of CSF1 to the receptor, CSF1R cannot undergo ligand-induced autophosphorylation. By inhibiting the CSF1R signaling pathway, pexidartinib works to inhibit tumor cell proliferation and downmodulate cells involved in the disease, such as macrophages. It was also shown to inhibit the CD117 or proto-oncogene receptor tyrosine kinase (cKIT), mutant fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), and platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR)-, which are all receptor tyrosine kinases that regulate critical cellular processes such as cell proliferation and survival.
