
1. Aquamephyton
2. Konakion
3. Phyllohydroquinone
4. Phylloquinone
5. Phytomenadione
6. Phytonadione
7. Vitamin K 1
1. Phylloquinone
2. Phytonadione
3. 84-80-0
4. Phytomenadione
5. Phytylmenadione
6. 3-phytylmenadione
7. Aquamephyton
8. Konakion
9. Mephyton
10. Monodion
11. Phyllochinon
12. Synthex P
13. 2-methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthoquinone
14. Kinadion
15. Vitamink1
16. Mono-kay
17. Combinal K1
18. Kativ N
19. Alpha-phylloquinone
20. Trans-phylloquinone
21. K-ject
22. Fitomenadiona
23. Phyllochinonum
24. Phytomenadionum
25. Phytonadionum
26. Aqua Mephyton
27. Antihemorrhagic Vitamin
28. Vitamin K 1
29. Fitomenadione
30. Aqua-mephytin
31. Kephton
32. 79083-00-4
33. 2',3'-trans-vitamin K1
34. 2-methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthochinon
35. 11104-38-4
36. Vitamin K
37. Phylloquinone E-form
38. 2-methyl-3-[(2e,7r,11r)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-en-1-yl]naphthalene-1,4-dione
39. Chebi:18067
40. 2-methyl-3-[(e,7r,11r)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-enyl]naphthalene-1,4-dione
41. Nsc 270681
42. Nsc-270681
43. S5z3u87qhf
44. 2-methyl-3-(3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecenyl)-1,4-naphthalenedione
45. 1,4-naphthoquinone, 2-methyl-3-phytyl-
46. Phythyl-menadion
47. Mlf3d1712d
48. Phytonadione, (e)-(+/-)-
49. 1,4-naphthalenedione,2-methyl-3-[(2e,7r,11r)-3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecen-1-yl]-
50. Dsstox_cid_3472
51. 1,4-naphthalenedione, 2-methyl-3-(3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecenyl)-, (r-(r*,r*-(e)))-
52. 2-methyl-3-((7r,11r,e)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-en-1-yl)naphthalene-1,4-dione
53. Dsstox_rid_77041
54. Dsstox_gsid_23472
55. Vitamin K1-18o(mixture Of 1-18o And 4-18o)
56. Orakay
57. 1,4-naphthalenedione, 2-methyl-3-(3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecenyl)-
58. 2-methyl-3-[(2e)-3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecenyl]naphthoquinone
59. 2-methyl-3-phythyl-1,4-naphthochinon
60. Cas-84-80-0
61. Rel-2-methyl-3-((7r,11r,e)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-en-1-yl)naphthalene-1,4-dione
62. Phytonadione, K1
63. 1,4-naphthalenedione, 2-methyl-3-(3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecenyl)-, [r-[r*,r*-(e)]]-
64. Phyllochinon [german]
65. Fitomenadione [dcit]
66. Vitamin K1 (van)
67. Phytonadione [usp:jan]
68. Unii-s5z3u87qhf
69. Fitomenadiona [inn-spanish]
70. Phytomenadionum [inn-latin]
71. Kanavit
72. Neokay
73. A-phylloquinone
74. Konakion Mm
75. Konakion Mm Paed
76. Hsdb 3162
77. Vitamin K1 Oil
78. (e)-phytonadione
79. 2-methyl-3-((7r,11r,e)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-enyl)naphthalene-1,4-dione
80. Ncgc00159423-02
81. Trans-phytomenadione
82. Einecs 201-564-2
83. Einecs 234-330-3
84. Einecs 279-052-3
85. Mfcd00214063
86. Vitamin K1, 11
87. Vitamin K1 (generic)
88. Vitamin K1 ,(s)
89. Phytonadione [jan]
90. 2-methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthochinon [german]
91. Schembl3882
92. Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone)
93. Vitamin K1, Viscous Liquid
94. Chembl1550
95. Unii-mlf3d1712d
96. Phytonadione, (e)-
97. Phylloquinone, (e)-
98. Mls001074732
99. Bidd:gt0793
100. Phytomenadione, (e)-
101. Schembl351365
102. Vitamin K1 (e-phytonadione)
103. 2-methyl-3-[(2e)-3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecenyl]naphthoquinone #
104. Dtxsid8023472
105. Bdbm24782
106. [r-[r*,r*-(e)]]-2-methyl-3-(3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecenyl)-1,4-napthalenedione
107. [r-[r*,r*-(e)]]-2-methyl-3-(3-7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecenyl)-1,4-naphthalenedione
108. Phylloquinone E-form [mi]
109. Hms2094g09
110. Hms2270j10
111. Pharmakon1600-01505485
112. 10485-69-5
113. Hy-n0684
114. Zinc3831332
115. Tox21_111655
116. Bdbm50553259
117. Lmpr02030028
118. Nsc760373
119. S4698
120. 2-methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-napthoquinone
121. Akos015841892
122. Tox21_111655_1
123. Ccg-213568
124. Cs-6376
125. Db01022
126. Nsc-760373
127. (r*,r*-(e))-(1)-2-methyl-3-(3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-enyl)-1,4-naphthoquinone
128. Ncgc00159423-03
129. Phylloquinone (k1), Analytical Standard
130. Ac-34846
131. As-13734
132. Smr000112043
133. Sbi-0206926.p001
134. Trans-phytomenadione 100 Microg/ml In Ethanol
135. Ab00698065_04
136. 214v063
137. A840928
138. Q186093
139. Sr-05000001941
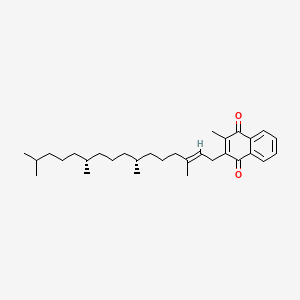
140. C31h46o2 (2-methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthoquinone)
141. Q-201934
142. Sr-05000001941-1
143. W-108488
144. 2-methyl-3-((7r,11r,e)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec
145. 84c51b31-3ce2-476b-be66-a84bdd46a513
146. Vitamin K1; 2-methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthoquinone
147. Phytomenadione, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
148. Phytonadione, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
149. 2-methyl-3-(3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecenyl)-1,4-naphthalened- Ione
150. Vitamin K1 Solution, 10 Mug/ml In Ethanol, Certified Reference Material
151. Vitamin K1, Bioxtra, >=99.0% (sum Of Isomers, Hplc), Mixtur Of Isomers
152. 1,4-naphthalenedione, 2-methyl-3-((2e,7r,11r)-3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecen-1-yl)-
153. 1,4-naphthalenedione, 2-methyl-3-((2e,7r,11r)-3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecenyl)-
154. Phytonadione, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
155. 1,4-naphthalenedione, 2-methyl-3-((2e,7r,11r)-3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecen-1-yl)-, Rel-
156. 2-methyl-3-((2e,7r,11r)-3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecenyl)-1,4-naphthalenedione
157. 2-methyl-3-[(2e,7r,11r)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-en-1-yl]-1,4-dihydronaphthalene-1,4-dione
158. 2-methyl-3-[(e,7r,11r)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-enyl]naphthalene-1,4-dione;vitamin K1
159. Vitamin K1-13c6 Solution, 5 Mug/ml In Ethanol, Certified Reference Material, Ampule Of 1 Ml
| Molecular Weight | 450.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C31H46O2 |
| XLogP3 | 10.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 14 |
| Exact Mass | 450.349780706 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 450.349780706 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 34.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 696 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Phytonadione |
| Drug Label | Phytonadione is a vitamin, which is a clear, yellow to amber, viscous, odorless or nearly odorless liquid. It is insoluble in water, soluble in chloroform and slightly soluble in ethanol. It has a molecular weight of 450.70.Phytonadione is 2-methyl-3... |
| Active Ingredient | Phytonadione |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 1mg/0.5ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Intl Medication |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Vitamin k1 |
| PubMed Health | Phytonadione |
| Drug Classes | Nutriceutical, Nutritive Agent |
| Drug Label | Phytonadione is a vitamin, which is a clear, yellow to amber, viscous, odorless or nearly odorless liquid. It is insoluble in water, soluble in chloroform and slightly soluble in ethanol. It has a molecular weight of 450.70.Phytonadione is 2-methyl-3... |
| Active Ingredient | Phytonadione |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 1mg/0.5ml; 10mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Phytonadione |
| Drug Label | Phytonadione is a vitamin, which is a clear, yellow to amber, viscous, odorless or nearly odorless liquid. It is insoluble in water, soluble in chloroform and slightly soluble in ethanol. It has a molecular weight of 450.70.Phytonadione is 2-methyl-3... |
| Active Ingredient | Phytonadione |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 1mg/0.5ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Intl Medication |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Vitamin k1 |
| PubMed Health | Phytonadione |
| Drug Classes | Nutriceutical, Nutritive Agent |
| Drug Label | Phytonadione is a vitamin, which is a clear, yellow to amber, viscous, odorless or nearly odorless liquid. It is insoluble in water, soluble in chloroform and slightly soluble in ethanol. It has a molecular weight of 450.70.Phytonadione is 2-methyl-3... |
| Active Ingredient | Phytonadione |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 1mg/0.5ml; 10mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira |
Antifibrinolytic Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
THE RATIONAL THERAPEUTIC USE OF VITAMIN K IS BASED ON ITS ABILITY TO CORRECT BLEEDING TENDENCY OR HEMORRHAGE ASSOC WITH ITS DEFICIENCY. A DEFICIENCY OF VITAMIN K & ITS ATTENDANT DEFICIENCY OF PROTHROMBIN & RELATED CLOTTING FACTORS CAN RESULT FROM INADEQUATE INTAKE, ABSORPTION, OR UTILIZATION OF VITAMIN, OR AS A CONSEQUENCE OF ACTION OF THE ACTION OF A VITAMIN K ANTAGONIST. /VITAMIN K/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1785
BLEEDING THAT ACCOMPANIES OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE OR BILIARY FISTULA RESPONDS PROMPTLY TO ADMINISTRATION OF VITAMIN K. ORAL PHYTONADIONE ADMIN WITH BILE SALTS IS BOTH SAFE AND EFFECTIVE AND SHOULD BE USED IN THE CARE OF THE JAUNDICED PATIENT, BOTH PREOPERATIVELY & POSTOPERATIVELY.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1785
IF FOR SOME REASON ORAL ADMIN IS NOT FEASIBLE /IN TREATMENT OF OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE OR BILIARY FISTULA/, A PARENTERAL PREPN SHOULD BE USED.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1785
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for PHYTONADIONE (22 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
IN PT WHO HAVE SEVERE HEPATIC DISEASE, ADMIN OF LARGE DOSES OF MENADIONE OR PHYLLOQUINONE MAY FURTHER DEPRESS FUNCTION OF LIVER.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1784
Maternal Medication usually Compatible with Breast-Feeding: K1 (vitamin): Reported Sign or Symptom in Infant or Effect on Lactation: None. /from Table 6/
Report of the American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Drugs in Pediatrics 93 (1): 141 (1994)
A rare hypersensitivity-like reaction, which has occasionally resulted in death, has been reported after intravenous administration of phytonadione, especially when administration is rapid.
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 2957
In newborns, especially premature infants, mendiol sodium diphosphate has been associated with hemolytic anemia, hyperbilirubinemia, and kernicterus because of immature hepatic function in these infants. There is less risk with phytonadione, unless high doses are given.
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 2957
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PHYTONADIONE (21 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Oral phylloquinone is indicated to treat prothrombin deficiency caused by coumarin or indanedione derivatives; and hypoprothrombinemia secondary to antibacterial therapy, salicylates, or obstructive jaundice or biliary fistulas with concomitant bile salt administration. Parenteral (intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous) phylloquinone is indicated to treat coagulation disorders due to faulty formation of coagulation factors II, VII, IX, and X caused by vitamin K deficiency or some interference with vitamin K activity. These indications include the above indications as well as hypoprothrombinemia secondary to sprue, ulcerative colitis, celiac disease, intestinal resection, pancreatic cystic fibrosis, or regional enteritis; or hypoprothrombinemia caused by interference with vitamin k metabolism.
Phylloquinone is a vitamin K indicated in the treatment of coagulation disorders due to faulty formation of coagulation factors II, VII, IX, and X caused by deficiency or interference in the activity of vitamin K. It has a long duration of action as vitamin K is cycled in the body, and a wide therapeutic index as large doses can be tolerated. Patients should have their prothrombin time monitored during therapy and healthcare professionals should be aware of the increased risk of hypersensitivity reactions with parenteral administration.
Antifibrinolytic Agents
Agents that prevent fibrinolysis or lysis of a blood clot or thrombus. Several endogenous antiplasmins are known. The drugs are used to control massive hemorrhage and in other coagulation disorders. (See all compounds classified as Antifibrinolytic Agents.)
Vitamins
Organic substances that are required in small amounts for maintenance and growth, but which cannot be manufactured by the human body. (See all compounds classified as Vitamins.)
B02BA01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B02 - Antihemorrhagics
B02B - Vitamin k and other hemostatics
B02BA - Vitamin k
B02BA01 - Phytomenadione
Absorption
A 4 g oral dose of phylloquinone is 13% 9% bioavailable, with a Tmax of 4.7 0.8 hours. 1.5 0.8 nmol is found in the plasma compartment, and 3.6 3.4 nmol is found in the second compartment. A 10 mg intramuscular phylloquinone dose is 89.2% 25.4% bioavailable. The same dose reaches a mean Cmax of 67 30 ng/mL, with a mean Tmax of 9.2 6.6 hours, and an AUC of 1700 500 h\*ng/mL. A 10 mg intravenous phylloquinone dose has a mean AUC of 1950 450 h\*ng/mL.
Route of Elimination
Intravenous phylloquinone is 36% eliminated in the feces in 5 days and 22% recovered in urine in 3 days.
Volume of Distribution
The steady state volume of distribution of phylloquinone is 20 6 L in subjects who are also taking phenprocoumon therapy.
Clearance
Intravenous phylloquinone is 90% cleared in 2 hours, and 99% cleared in 8 hours. A 10 mg intravenous dose of phylloquinone has a mean clearance of 91 24 mL/min.
Little is known about the excretion of vitamin K. High fecal concentrations of vitamin K probably result from bacterial synthesis in the intestine.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 3566
Although the drug may be concentrated in the liver for a short time after absorption, only small amounts of phytonadione are stored in body tissues.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 3566
Phytonadione is absorbed from the GI tract only in the presence of bile salts. Radioisotope studies show that absorption occurs via intestinal lymph. There is some evidence that absorption of phytonadione across the GI mucosa is a saturable, energy-dependent process that occurs in the proximal small intestine.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 3566
Fat-soluble vit...k...absorbed from skin... /vit k/
Hayes, W.J., Jr., E.R. Laws Jr., (eds.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology Volume 1. General Principles. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc., 1991., p. 139
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for PHYTONADIONE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Phylloquinone's phytyl side chain is omega hydroxylated by CYP4F2. The side chain is then cleaved to 5 or 7 carbons long, and then glucuronidated prior to elimination. Vitamin Ks in general undergo a cycle of reduction to vitamin K hydroquinone by vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR), oxidation to vitamin K epoxide by gamma-glutamyl carboxylase, and converted back to vitamin K by VKOR.
...In experimental animals...phylloquinone...can be converted to more potent menaquinone series. Whether this can occur in man and of what significance these transformations are to action of phylloquinone...are still unknown.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1593
In animals treated with warfarin, major fraction of phylloquinone is metabolized to phylloquinone oxide.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1593
Phytonadione is rapidly metabolized to more polar metabolites, which are excreted in the bile and urine. The major urinary metabolites result from shortening of the side chain to five or seven carbon atoms, yielding carboxylic acids that are conjugated with glucuronate prior to excretion. Treatment with a coumarin-type anticoagulant results in a marked increase in the amount of phytonadione-2,3-epoxide in the liver and blood. Such treatment also increases the urinary excretion of phytonadione metabolites, primarily degradative products of phytonadione-2,3-epoxide. The biliary metabolites of phytonadione have not been identified.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1784
The liver plays an exclusive role in the metabolic transformations leading to the elimination of vitamin K from the body. After intravenous doses of 45 ug to 1 mg (3)H-phylloquinone, about 20% of the radiolabel was excreted in the urine within three days, and 35-50% was excreted as metabolites in the feces via the bile.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V76 461-2 (2000)
Intravenous phylloquinone has an initial half life of 22 minutes, followed by a half life of 125 minutes.
Vitamin K is a cofactor of gamma-carboxylase. Gamma carboxylase attaches carboxylic acid functional groups to glutamate, allowing precursors of factors II, VII, IX, and X to bind calcium ions. Binding of calcium ions converts these clotting factors to their active form, which are then secreted from hepatocytes into the blood, restoring normal clotting function. Vitamin K may also carboxylate matrix proteins in chondrocytes, inhibiting calcification of joints, and may increase type II collagen. The role of vitamin K in osteroarthritis, bone density, and vascular calcification is currently under investigation.
Vit k is necessary for formation of prothrombinogen & other blood clotting factors in liver. During clotting, circulating prothrombin is required for production of thrombin; in turn, thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin, network of which constitutes clot. /vit k/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 943
In normal animals and man, phyltonadione ... /is/ virtually devoid of pharmacodynamic activity. In Animals and man deficient in vitamin k, the pharmacological action of vitamin k is identical to its normal physiological function, that is, to promote hepatic biosynthesis of prothrombin (factor ii), proconvertin (factor vii), plasma thromboplastin component (ptc, christmas factor, factor ix), and Stuart factor (factor x).
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1783
On the basis of studies of microsomal metabolism in vitro and studies in rats and mice in vivo, /it was suggested/ that vitamin K may be mutagenic by affecting the mixed-function oxidase system which metabolizes benzo(a)pyrene. Phylloquinone at a high concentration (200 umol/l) inhibited the conversion of benzo(a)pyrene to its more polar metabolites, ... . Paradoxically, at a lower concentration of phylloquinone (25 umol/l), ... the metabolism of benzo(a)pyrene was increased. In this system, therefore, .... phylloquinone could either potentiate or inhibit it, depending on the concentration. This overall weaker inhibitory effect of phylloquinone could be due to the low solubility of this lipophilic compound, but it is difficult to explain the mechanism of the enhanced metabolism of benzo(a)pyrene at lower concentrations of phylloquinone.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V76 472 (2000)