

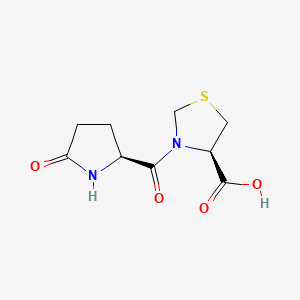

1. 3-((5-oxo-2-pyrrolidinyl)carbonyl)-4-thiazolidinecarboxylic Acid
2. 3-pyroglutamylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic Acid
3. 3-pyroglutamylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic Acid, (r-(r*,s*))-isomer
4. Adimod
5. Pgt-1a
1. 121808-62-6
2. (r)-3-((s)-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carbonyl)thiazolidine-4-carboxylic Acid
3. Pidotomod
4. Pidotimod [inn]
5. Pgt/1a
6. Pilimod
7. Nsc-759841
8. (r)-3-((s)-5-oxoprolyl)-4-thiazolidinecarboxylic Acid
9. Pidotimod (inn)
10. (4r)-3-[(2s)-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]-1,3-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic Acid
11. Ncgc00160516-01
12. Polimod
13. (4r)-3-{[(2s)-5-oxopyrrolidin-2-yl]carbonyl}-1,3-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic Acid
14. 785363r681
15. Pidotimodum
16. Pigitil
17. Pidotimodum [inn-latin]
18. 4-thiazolidinecarboxylic Acid, 3-[[(2s)-5-oxo-2-pyrrolidinyl]carbonyl]-, (4r)-
19. Smr000466390
20. Ccris 7271
21. Brn 6636310
22. Onaka
23. Thymodolic Acid
24. Axil
25. Timodolic Acid
26. Pilimod (tn)
27. Pidotimod - Bio-x
28. Unii-785363r681
29. Pidotimod [mi]
30. Pidotimod [mart.]
31. (r-(r*,s*))-3-((5-oxo-2-pyrrolidinyl)carbonyl)-4-thiazolidinecarboxylic Acid
32. Pidotimod [who-dd]
33. (4r)-3-[[(2s)-5-oxo-2-pyrrolidinyl]carbonyl]-4-thiazolidinecarboxylic Acid
34. (r)-3-((s)-(5-oxo-2-pyrrolidinyl)carbonyl)-thiazolidin-4-carbonsaeure [german]
35. Dsstox_cid_26199
36. Dsstox_rid_81430
37. Dsstox_gsid_46199
38. Mls000759528
39. Mls001032108
40. Mls001216453
41. Mls001423953
42. Schembl138407
43. Chembl1488165
44. Dtxsid0046199
45. Pidotimod, >=98% (hplc)
46. Chebi:94618
47. Hms2051c04
48. Hms2231m03
49. Hms3715h06
50. Pharmakon1600-01502322
51. Bcp05222
52. Hy-b0944
53. Zinc3781245
54. Tox21_111865
55. Mfcd00867583
56. Nsc759841
57. S3106
58. (r)-3-((s)-(5-oxo-2-pyrrolidinyl)carbonyl)-thiazolidin-4-carbonsaeure
59. Akos015896354
60. Ac-3493
61. Am90280
62. Ccg-100832
63. Db11364
64. Ks-5229
65. Nc00082
66. Nsc 759841
67. (r)-3-[[(s)-5-oxo-2-pyrrolidinyl]carbonyl]-1,3-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic Acid
68. 4-thiazolidinecarboxylic Acid, 3-((5-oxo-2-pyrrolidinyl)carbonyl)-, (r-(r*,s*))-
69. Ncgc00160516-03
70. Bp164260
71. Cas-121808-62-6
72. P2147
73. Sw197462-2
74. D07261
75. Ab00639966-08
76. Ab00639966_10
77. Ab00639966_11
78. 808p626
79. A804790
80. J-502193
81. Q3902720
82. (4r)-3-[(2s)-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]thiazolidine-4-carboxylic Acid;pidotimod
83. (4r)-3-[[(2s)-5-oxo-2-pyrrolidinyl]carbonyl]thiazolidine-4-carboxylic Acid
84. (4r)-3-[oxo-[(2s)-5-oxo-2-pyrrolidinyl]methyl]-4-thiazolidinecarboxylic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 244.27 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H12N2O4S |
| XLogP3 | -0.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 244.05177804 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 244.05177804 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 112 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 346 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For use as immunostimulant therapy for treatment of cell-mediated immunosuppression with respiratory or urinary infections.
Pidotimod modulates the immune system to induce an immune response against bacterial or viral pathogens
Adjuvants, Immunologic
Substances that augment, stimulate, activate, potentiate, or modulate the immune response at either the cellular or humoral level. The classical agents (Freund's adjuvant, BCG, Corynebacterium parvum, et al.) contain bacterial antigens. Some are endogenous (e.g., histamine, interferon, transfer factor, tuftsin, interleukin-1). Their mode of action is either non-specific, resulting in increased immune responsiveness to a wide variety of antigens, or antigen-specific, i.e., affecting a restricted type of immune response to a narrow group of antigens. The therapeutic efficacy of many biological response modifiers is related to their antigen-specific immunoadjuvanticity. (See all compounds classified as Adjuvants, Immunologic.)
Immunologic Factors
Biologically active substances whose activities affect or play a role in the functioning of the immune system. (See all compounds classified as Immunologic Factors.)
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L03 - Immunostimulants
L03A - Immunostimulants
L03AX - Other immunostimulants
L03AX05 - Pidotimod
Absorption
Bioavailability of 45%.
Route of Elimination
95% of intravenous dose is eliminated in the urine as the parent compound.
Half life of 4 h.
Pidotimod inhibits tumor necrosis factor (TNF-) induced increases in extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) phosphorylation. It also increases nuclear factor B (NFB) expression and translocation to the nucleus. It is these to modulatory effects on ERK and NFB signalling which are thought to produce the increase in toll-like receptor expression seen with pidotimod. Pidotimod increase maturation of dendritic cells responsible for presenting antigens to naive Th-cells. It also appears to result in a greater population these cells diiferentiating to Th1 cells which are believed to mediate the immune response to pathogens like bacteria and viruses. Lastly, pidotimod appears to increase antigen-specific antibody titer and cytotoxic response with antigen exposure. The precise mechanism and timeline of events leading to these effects is unknown.