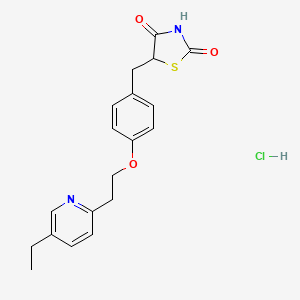

1. 5-(4-(2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridyl)ethoxy)benzyl)-2,4-thiazolidinedione
2. Actos
3. Ad 4833
4. Ad-4833
5. Ad4833
6. Pioglitazone
7. U 72107a
8. U-72107a
9. U72,107a
10. U72107a
1. 112529-15-4
2. Pioglitazone Hcl
3. Actos
4. Piomed
5. 5-(4-(2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethoxy)benzyl)thiazolidine-2,4-dione Hydrochloride
6. U-72107a
7. Pioglitazone (hydrochloride)
8. Ad 4833
9. U 72107a
10. Jqt35npk6c
11. U-72107e
12. Pioglitazone (as Hydrochloride)
13. Str-001
14. [5-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-2,4-] Thiazolidinedione Hydrochloride
15. Nsc-758876
16. Ncgc00095131-01
17. Pioditazone Hydrochloride
18. 5-[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridyl)ethoxy]benzyl]thiazolidine-2,4-dione Hydrochloride
19. Actos (tn)
20. Dsstox_cid_24203
21. Dsstox_rid_80116
22. Dsstox_gsid_44203
23. 5-[[4-[2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-dione;hydrochloride
24. 2,4-thiazolidinedione, 5-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-, Monohydrochloride
25. Smr000469167
26. Cas-112529-15-4
27. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride [usan]
28. Unii-jqt35npk6c
29. 5-(4-[2-(5-ethyl-pyridin-2-yl)-ethoxy]-benzyl)-thiazolidine-2,4-dione Hydrochloride
30. 5-[4-[2-(5-ethyl-pyridin-2-yl)-ethoxy]-benzyl]-thiazolidine-2,4-dione Hydrochloride
31. 5-{4-[2-(5-ethyl-pyridin-2-yl)-ethoxy]-benzyl}-thiazolidine-2,4-dione Hydrochloride
32. 2,4-thiazolidinedione, 5-((4-(2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy)phenyl)methyl)-, Monohydrochloride
33. Mfcd04975446
34. Poze
35. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride [usan:usp]
36. Pioglitazone Cloridrato
37. Pioglitazonehydrochloride
38. Cloridrato De Pioglitazona
39. Pioglitazone, Hydrochloride
40. Clorhidrato De Pioglitazona
41. Chlorhydrate De Pioglitazone
42. (+-)-5-(p-(2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridyl)ethoxy)benzyl)-2,4-thiazolidinedione Monohydrochloride
43. 5-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-2,4-thiazolidinedione Monohydrochloride
44. Chembl1715
45. Schembl21843
46. Mls001306462
47. Mls001401386
48. Spectrum1504401
49. Chebi:8229
50. Dtxsid3044203
51. Pioglitazone Hcl [vandf]
52. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride ,(s)
53. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride- Bio-x
54. Hms1922l05
55. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride (actos)
56. Act04238
57. Bcp22942
58. Tox21_111440
59. Tox21_300584
60. Ccg-39097
61. S2046
62. Akos015844016
63. Tox21_111440_1
64. Ac-1037
65. Ccg-100931
66. Ks-1186
67. Nc00181
68. Nsc 758876
69. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride (jp17/usp)
70. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride [mi]
71. Sb17324
72. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride [jan]
73. Ncgc00095131-02
74. Ncgc00163128-08
75. Ncgc00254492-01
76. 2,4-thiazolidinedione, 5-((4-(2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy)phenyl)methyl)-, Monohydrochloride, (+-)-
77. Aa-10090
78. Bp164272
79. Hy-14601
80. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride [mart.]
81. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride [vandf]
82. Bcp0726000151
83. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride [usp-rs]
84. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride [who-dd]
85. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride, >=98% (hplc)
86. Am20061770
87. Ft-0601607
88. P1901
89. Sw197561-4
90. D00945
91. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride [orange Book]
92. Oseni Component Pioglitazone Hydrochloride
93. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride [ep Monograph]
94. 025p468
95. A802593
96. Duetact Component Pioglitazone Hydrochloride
97. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride [usp Monograph]
98. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride Component Of Oseni
99. Q-201584
100. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
101. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride Component Of Duetact
102. Q27281642
103. Actoplus Met Component Pioglitazone Hydrochloride
104. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride Component Of Actoplus Met
105. 5-(4-(2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethoxy)benzyl)thiazolidine-2,4-dione Hcl
106. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
107. 5-((4-(2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy)phenyl)methyl)-2,4-thiazolidinedione, Hcl
108. 5-(4-[2-(5-ethyl-pyridin-2-yl)-ethoxy]-benzyl)-thiazolidine-2,4-dione Hcl
109. 5-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)-ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-2,4-thiazolidinedione Hydrochloride
110. 5-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-2,4-thiazolidinedione, Hydrochloride
111. 5-[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridyl)ethoxy]benzyl]-2,4-thiazolidinedione Hydrochloride
112. 5-{4-[2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethoxy]benzyl}-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-dione Hydrochloride
113. Pioglitazone For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
114. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
115. Pioglitazone Hydrochloride, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
116. (+/-)-5-(p-(2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridyl)ethoxy)benzyl)-2,4-thiazolidinedione Monohydrochloride
117. 127676-30-6
118. 2,4-thiazolidinedione, 5-((4-(2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy)phenyl)methyl)-, Hydrochloride (1:1)
119. 2,4-thiazolidinedione, 5-((4-(2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy)phenyl)methyl)-, Monohydrochloride, (+/-)-
| Molecular Weight | 392.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H21ClN2O3S |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 392.0961414 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 392.0961414 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 93.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 466 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Pioglitazone hydrochloride |
| Drug Label | ACTOS (pioglitazone hydrochloride) is an oral antidiabetic agent that acts primarily by decreasing insulin resistance. ACTOS is used in the management of type2 diabetes mellitus (also known as non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus [NIDDM] or adul... |
| Active Ingredient | Pioglitazone hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 15mg base; eq 30mg base; eq 45mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Synthon Pharms; Mylan Pharms; Accord Hlthcare; Aurobindo Pharma; Teva Pharms Usa; Torrent Pharms; Lupin; Sandoz; Watson Labs; Macleods Pharms; Zydus Pharms Usa; Dr Reddys Labs |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Pioglitazone hydrochloride |
| Drug Label | ACTOS (pioglitazone hydrochloride) is an oral antidiabetic agent that acts primarily by decreasing insulin resistance. ACTOS is used in the management of type2 diabetes mellitus (also known as non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus [NIDDM] or adul... |
| Active Ingredient | Pioglitazone hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 15mg base; eq 30mg base; eq 45mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Synthon Pharms; Mylan Pharms; Accord Hlthcare; Aurobindo Pharma; Teva Pharms Usa; Torrent Pharms; Lupin; Sandoz; Watson Labs; Macleods Pharms; Zydus Pharms Usa; Dr Reddys Labs |
Pioglitazone is indicated as second or third line treatment of type-2 diabetes mellitus as described below:
- as
* monotherapy: :
- in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) inadequately controlled by diet and exercise for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance.
- as
* dual oral therapy: in combination with:
- metformin, in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) with insufficient glycaemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy with metformin;
- a sulphonylurea, only in adult patients who show intolerance to metformin or for whom metformin is contraindicated, with insufficient glycaemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy with a sulphonylurea;
- as
* triple oral therapy: in combination with:
- metformin and a sulphonylurea, in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) with insufficient glycaemic control despite dual oral therapy.
Pioglitazone is also indicated for combination with insulin in type-2 diabetes mellitus adult patients with insufficient glycaemic control on insulin for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance.
After initiation of therapy with pioglitazone, patients should be reviewed after three to six months to assess adequacy of response to treatment (e. g. reduction in HbA1c). In patients who fail to show an adequate response, pioglitazone should be discontinued. In light of potential risks with prolonged therapy, prescribers should confirm at subsequent routine reviews that the benefit of pioglitazone is maintained.
Pioglitazone is indicated in the treatment of type-2 diabetes mellitus as
* monotherapy: :
- in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) inadequately controlled by diet and exercise for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance.
Pioglitazone is also indicated for combination with insulin in type 2 diabetes mellitus adult patients with insufficient glycaemic control on insulin for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance.
After initiation of therapy with pioglitazone, patients should be reviewed after 3 to 6 months to assess adequacy of response to treatment (e. g. reduction in HbA1c). In patients who fail to show an adequate response, pioglitazone should be discontinued. In light of potential risks with prolonged therapy, prescribers should confirm at subsequent routine reviews that the benefit of pioglitazone is maintained.
Pioglitazone is indicated in the treatment of type-2 diabetes mellitus:
* as monotherapy:
- in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) inadequately controlled by diet and exercise for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance.
After initiation of therapy with pioglitazone, patients should be reviewed after 3 to 6 months to assess adequacy of response to treatment (e. g. reduction in HbA1c). In patients who fail to show an adequate response, pioglitazone should be discontinued. In light of potential risks with prolonged therapy, prescribers should confirm at subsequent routine reviews that the benefit of pioglitazone is maintained.
Pioglitazone is indicated as second or third line treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus as described below:
* as monotherapy:
- in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) inadequately controlled by diet and exercise for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance.
* as dual oral therapy in combination with:
- metformin, in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) with insufficient glycaemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy with metformin.
- a sulphonylurea, only in adult patients who show intolerance to metformin or for whom metformin is contraindicated, with insufficient glycaemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy with a sulphonylurea.
* as triple oral therapy in combination with:
- metformin and a sulphonylurea, in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) with insufficient glycaemic control despite dual oral therapy.
Pioglitazone is also indicated for combination with insulin in type 2 diabetes mellitus adult patients with insufficient glycaemic control on insulin for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance (see section 4. 4).
After initiation of therapy with pioglitazone, patients should be reviewed after 3 to 6 months to assess adequacy of response to treatment (e. g. reduction in HbA1c). In patients who fail to show an adequate response, pioglitazone should be discontinued. In light of potential risks with prolonged therapy, prescribers should confirm at subsequent routine reviews that the benefit of pioglitazone is maintained (see section 4. 4).
Pioglitazone is indicated in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus:
- as monotherapy
- in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) inadequately controlled by diet and exercise for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance
- as dual oral therapy in combination with
- metformin, in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) with insufficient glycaemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy with metformin
- a sulphonylurea, only in adult patients who show intolerance to metformin or for whom metformin is contraindicated, with insufficient glycaemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy with a sulphonylurea
- as triple oral therapy in combination with
- metformin and a sulphonylurea, in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) with insufficient glycaemic control despite dual oral therapy.
Pioglitazone is also indicated for combination with insulin in type 2 diabetes mellitus adult patients with insufficient glycaemic control on insulin for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance.
After initiation of therapy with pioglitazone, patients should be reviewed after 3 to 6 months to assess adequacy of response to treatment (e. g. reduction in HbA1c). In patients who fail to show an adequate response, pioglitazone should be discontinued. In light of potential risks with prolonged therapy, prescribers should confirm at subsequent routine reviews that the benefit of pioglitazone is maintained.
Pioglitazone is indicated as second or third line treatment of type-2 diabetes mellitus as described below:
- as monotherapy:
- in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) inadequately controlled by diet and exercise for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance;
- as dual oral therapy in combination with:
- metformin, in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) with insufficient glycaemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy with metformin;
- a sulphonylurea, only in adult patients who show intolerance to metformin or for whom metformin is contraindicated, with insufficient glycaemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy with a sulphonylurea;
- as triple oral therapy in combination with:
- metformin and a sulphonylurea, in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) with insufficient glycaemic control despite dual oral therapy.
Pioglitazone is also indicated for combination with insulin in type-2 diabetes mellitus adult patients with insufficient glycaemic control on insulin for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance.
After initiation of therapy with pioglitazone, patients should be reviewed after 3 to 6 months to assess adequacy of response to treatment (e. g. reduction in HbA1c). In patients who fail to show an adequate response, pioglitazone should be discontinued. In light of potential risks with prolonged therapy, prescribers should confirm at subsequent routine reviews that the benefit of pioglitazone is maintained.
Pioglitazone is indicated in the treatment of type-2 diabetes mellitus:
- as
* monotherapy: :
- in patients (particularly overweight patients) inadequately controlled by diet and exercise for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance;
- as
* dual oral therapy: in combination with:
- metformin, in patients (particularly overweight patients) with insufficient glycaemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy with metformin;
- a sulphonylurea, only in patients who show intolerance to metformin or for whom metformin is contraindicated, with insufficient glycaemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy with a sulphonylurea;
- as
* triple oral therapy: in combination with:
- metformin and a sulphonylurea, in patients (particularly overweight patients) with insufficient glycaemic control despite dual oral therapy.
Pioglitazone is also indicated for combination with insulin in type-2 diabetes mellitus patients with insufficient glycaemic control on insulin for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance.
Pioglitazone is indicated as second or third line treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus as described below:
* as monotherapy:
- in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) inadequately controlled by diet and exercise for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance;
as
* dual oral therapy: in combination with
- metformin, in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) with insufficient glycaemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy with metformin;
- a sulphonylurea, only in adult patients who show intolerance to metformin or for whom metformin is contraindicated, with insufficient glycaemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy with a sulphonylurea;
as
* triple oral therapy: in combination with
- metformin and a sulphonylurea, in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) with insufficient glycaemic control despite dual oral therapy.
Pioglitazone is also indicated for combination with insulin in type 2 diabetes mellitus in adult patients with insufficient glycaemic control on insulin for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance.
After initiation of therapy with pioglitazone, patients should be reviewed after 3 to 6 months to assess adequacy of response to treatment (e. g. reduction in HbA1c). In patients who fail to show an adequate response, pioglitazone should be discontinued. In light of potential risks with prolonged therapy, prescribers should confirm at subsequent routine reviews that the benefit of pioglitazone is maintained.
Pioglitazone is indicated as second or third line treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus as described below:
as monotherapy
- in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) inadequately controlled by diet and exercise for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance;
as dual oral therapy in combination with
- a sulphonylurea, only in adult patients who show intolerance to metformin or for whom metformin is contraindicated, with insufficient glycaemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy with a sulphonylurea;
Pioglitazone is also indicated for combination with insulin in type 2 diabetes mellitus in adult patients with insufficient glycaemic control on insulin for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance.
After initiation of therapy with pioglitazone, patients should be reviewed after 3 to 6 months to assess adequacy of response to treatment (e. g. reduction in HbA1c). In patients who fail to show an adequate response, pioglitazone should be discontinued. In light of potential risks with prolonged therapy, prescribers should confirm at subsequent routine reviews that the benefit of pioglitazone is maintained.
Pioglitazone is indicated as second- or third-line treatment of type-2 diabetes mellitus as described below:
* as monotherapy: :
- in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) inadequately controlled by diet and exercise for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance;
* as dual oral therapy in combination with: :
- metformin, in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) with insufficient glycaemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy with metformin;
- a sulphonylurea, only in adult patients who show intolerance to metformin or for whom metformin is contraindicated, with insufficient glycaemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy with a sulphonylurea;
* as triple oral therapy in combination with: :
- metformin and a sulphonylurea, in adult patients (particularly overweight patients) with insufficient glycaemic control despite dual oral therapy.
Pioglitazone is also indicated for combination with insulin in type-2-diabetes-mellitus adult patients with insufficient glycaemic control on insulin for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance (see section 4. 4).
After initiation of therapy with pioglitazone, patients should be reviewed after three to six months to assess adequacy of response to treatment (e. g. reduction in HbA1c). In patients who fail to show an adequate response, pioglitazone should be discontinued. In light of potential risks with prolonged therapy, prescribers should confirm at subsequent routine reviews that the benefit of pioglitazone is maintained (see section 4. 4).
Hypoglycemic Agents
Substances which lower blood glucose levels. (See all compounds classified as Hypoglycemic Agents.)
A10BG03
A10BG03
A10BG03
A10BG03
A10BG03
A10BG03
A10BG03
A10BG03
A10BG03
A10BG03