

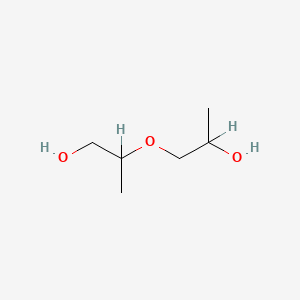

1. 2-(2-hydroxypropoxy)-1-propanol
1. 2-(2-hydroxypropoxy)-1-propanol
2. 106-62-7
3. 25322-69-4
4. 1-propanol, 2-(2-hydroxypropoxy)-
5. Polyoxypropylene Glycol
6. 2-(2-hydroxypropoxy)propanol
7. Methyloxirane Homopolymer
8. Alpha-hydro-omega-hydroxypoly(oxypropylene)
9. Polypropylene Glycol (m W 1,200-3,000)
10. Wny0h4g53q
11. Polyoxypropylene
12. Emkapyl
13. Lineartop E
14. Niax Ppg
15. Desmophen 360c
16. Polyglycol P 400
17. Niax Ppg 425
18. Jeffox Ppg 400
19. Polyglycol P-2000
20. Polyglycol P-4000
21. Voranol P 1010
22. Laprol 2002
23. Niax Ppg 1025
24. Niax Ppg 3025
25. Polyglycol Type P250
26. Polyglycol Type P400
27. Polyglycol Type P750
28. Napter E 8075
29. Niax Polyol Ppg 4025
30. Polyglycol Type P1200
31. Polyglycol Type P2000
32. Polyglycol Type P3000
33. Propylene Oxide Homopolymer
34. Laprol 702
35. Poly(propylene Glycol)
36. Unii-wny0h4g53q
37. Propylene Oxide, Propylene Glycol Polymer
38. Polypropylene Oxide
39. Poly(propylene Glycol) Macromolecule
40. Einecs 203-416-2
41. Poly Propylene Glycol
42. Alpha-hydro-omega-hydroxypoly(oxy(methyl-1,2-ethanediyl))
43. Ppg?
44. Schembl15111
45. Chebi:53262
46. Dtxsid30861722
47. 2-methyl-3-oxahexane-1,5-diol
48. Chebi:179442
49. Akos015899603
50. Bs-23535
51. Ft-0696553
52. F71159
53. 106h627
54. Alpha-hydro-omega-hydroxypoly[oxy(1-methylethylene)]
55. Q26863457
| Molecular Weight | 134.17 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H14O3 |
| XLogP3 | -0.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 134.094294304 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 134.094294304 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 49.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 9 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 65.3 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
3. 3 = moderately toxic: probable oral lethal dose (human) 0.5-5 g/kg, between 1 oz and 1 pint (or 1 lb) for 70 kg person (150 lb).
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-120
Lower mol wt /PPG's (200-1200) ... are absorbed through the skin to some extent, /but/ skin penetration ... not ... serious industrial hazard ... These ... are not like low mol wt polyethylene glycols in their physiologic activity; they are rapidly absorbed from the GI tract ...
Patty, F. (ed.). Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology: Volume II: Toxicology. 2nd ed. New York: Interscience Publishers, 1963., p. 1523
Acute skin absorption tests ... have indicated that the materials are all poorly absorbed through the skin.
Patty, F. (ed.). Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology: Volume II: Toxicology. 2nd ed. New York: Interscience Publishers, 1963., p. 1525
/Male rats maintained for 100 days on diet containing 1.0% of P750/ ... postulated that material is readily metabolized or eliminated when absorbed in small doses; this probably accounts for its lack of apparent physiological effect.
Patty, F. (ed.). Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology: Volume II: Toxicology. 2nd ed. New York: Interscience Publishers, 1963., p. 1525