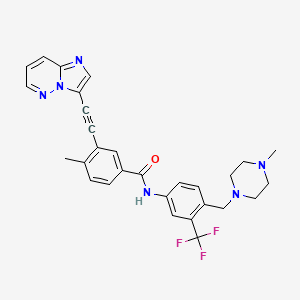

1. 3-(2-(imidazo(1,2-b)pyridazin-3-yl)ethynyl)-4-methyl-n-(4-((4-methylpiperazin-y-1-yl)methyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)benzamide
2. Ap 24534
3. Ap-24534
4. Ap24534
5. Iclusig
6. Ponatinib Hydrochloride
1. 943319-70-8
2. Ap24534
3. Ponatinib (ap24534)
4. Ap 24534
5. Ap-24534
6. 3-(imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-3-ylethynyl)-4-methyl-n-(4-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)benzamide
7. Chembl1171837
8. Chebi:78543
9. 943319-70-8 (free Base)
10. 4340891kfs
11. 3-(2-imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-3-ylethynyl)-4-methyl-n-[4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide
12. 3-(imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-3-ylethynyl)-4-methyl-n-{4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl}benzamide
13. 3-(2-imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-3-ylethynyl)-4-methyl-n-[4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide
14. Benzamide, 3-(2-imidazo(1,2-b)pyridazin-3-ylethynyl)-4-methyl-n-(4-((4-methyl-1- Piperazinyl)methyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-
15. 3-(2-(imidazo(1,2-b)pyridazin-3-yl)ethynyl)-4-methyl-n-(4-((4-methylpiperazin-1- Yl)methyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)benzamide
16. 3-(imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-3-ylethynyl)-4-methyl-n-(4-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)benzamide.
17. Ponatinib [usan]
18. Ponatinib [usan:inn]
19. Ponatinibum
20. Unii-4340891kfs
21. Hsdb 8184
22. 0li
23. 3-(2-(imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-3-yl)ethynyl)-4-methyl-n-(4-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)benzamide
24. 3-(imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-3-ylethynyl)-4-methyl-n-{4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl}benzam Ide
25. 3-[2-(imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-3-yl)ethynyl]-4-methyl-n-{4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl}benzamide
26. Ponatinib, Free Base
27. Ap24534,ponatinib
28. Ponatinib [inn]
29. Ponatinib [mi]
30. Ponatinib (usan/inn)
31. Ponatinib [vandf]
32. Ap24534 - Ponatinib
33. Ponatinib [who-dd]
34. Mls006010166
35. Schembl589260
36. Gtpl5890
37. Dtxsid50241426
38. Ex-a067
39. Bcpp000397
40. Hms3295i23
41. Hms3654h16
42. Bcp02037
43. Bdbm50322535
44. Mfcd17215203
45. Nsc758487
46. Nsc800855
47. Zinc36701290
48. Akos015995214
49. Am81261
50. Bcp9000307
51. Ccg-264900
52. Cs-0204
53. Db08901
54. Nsc-758487
55. Nsc-800855
56. Pb34916
57. Ncgc00263152-01
58. Ncgc00263152-02
59. Ncgc00263152-12
60. Ncgc00263152-14
61. Ac-26973
62. As-19133
63. Hy-12047
64. Smr004701274
65. Ft-0660376
66. S1490
67. Sw218091-2
68. A24930
69. D09950
70. Ab01565847_03
71. Q198728
72. Brd-k44227013-001-02-3
73. 3-(2-imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-3-ylethynyl)-4-methyl-n-[4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-benzamide
74. 3-(imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-3-ylethynyl)-4-methyl-n-{4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl}benzam
75. Benzamide, 3-(2-imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-3-ylethynyl)-4-methyl-n-[4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-
76. Ponatinib;3-(2-(imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-3-yl)ethynyl)-4-methyl-n-(4-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)benzamide
| Molecular Weight | 532.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C29H27F3N6O |
| XLogP3 | 4.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 532.21984399 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 532.21984399 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 65.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 39 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 910 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antineoplastic Agents; Protein Kinase Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Ponatinib. Online file (MeSH, 2014). Available from, as of March 4, 2014: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2014/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
Iclusig (ponatinib) is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the: Treatment of adult patients with T315I-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) (chronic phase, accelerated phase, or blast phase) and T315I-positive Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ALL). /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ICLUSIG (ponatinib hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (March 2014). Available from, as of March 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=807f988e-117b-4497-934d-73aa78baac71
Iclusig (ponatinib) is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the: Treatment of adult patients with chronic phase, accelerated phase, or blast phase chronic myeloid leukemia or Ph+ ALL for whom no other tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy is indicated. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ICLUSIG (ponatinib hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (March 2014). Available from, as of March 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=807f988e-117b-4497-934d-73aa78baac71
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: VASCULAR OCCLUSION, HEART FAILURE, and HEPATOTOXICITY. Vascular Occlusion: Arterial and venous thrombosis and occlusions have occurred in at least 27% of Iclusig treated patients, including fatal myocardial infarction, stroke, stenosis of large arterial vessels of the brain, severe peripheral vascular disease, and the need for urgent revascularization procedures. Patients with and without cardiovascular risk factors, including patients age 50 years or younger, experienced these events. Monitor for evidence of thromboembolism and vascular occlusion. Interrupt or stop Iclusig immediately for vascular occlusion. A benefit-risk consideration should guide a decision to restart Iclusig therapy. Heart Failure: Heart failure, including fatalities, occurred in 8% of Iclusig-treated patients. Monitor cardiac function. Interrupt or stop Iclusig for new or worsening heart failure. Hepatotoxicity: Hepatotoxicity, liver failure and death have occurred in Iclusig-treated patients. Monitor hepatic function. Interrupt Iclusig if hepatotoxicity is suspected.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ICLUSIG (ponatinib hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (March 2014). Available from, as of March 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=807f988e-117b-4497-934d-73aa78baac71
Hepatotoxicity and acute hepatic failure with fatal outcome have been reported in patients receiving ponatinib; liver biopsies predominantly showed hepatocellular necrosis.6 Fulminant hepatic failure resulting in death following 1 week of therapy was reported in one ponatinib-treated patient in the premarketing clinical trial. Elevations in serum aminotransferase (ALT or AST) concentrations were reported in 56% of patients receiving ponatinib in the premarketing clinical trial; median time to onset of these elevations was 46 days.6 Severe hepatotoxicity has been reported in all the disease cohorts; however, fatal cases have only been reported in patients with blast phase chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) or Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) acute lymphocytic (lymphoblastic) leukemia (ALL).
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
Arterial thromboembolic events, sometimes serious or fatal, have been reported in patients receiving ponatinib. Specifically, cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and peripheral vascular thrombosis, including fatal myocardial infarction and stroke, have occurred during ponatinib therapy. In the premarketing clinical trial, arterial thromboembolic events of any grade were reported in 11% of patients receiving ponatinib. Serious arterial thrombosis occurred in 8% of ponatinib-treated patients, and approximately 4.7% of patients required a revascularization procedure. The most common arterial thromboembolic event was myocardial infarction (MI) or worsening coronary artery disease; approximately half of these patients developed congestive heart failure concurrent with or subsequent to the myocardial ischemic event. Serious cerebrovascular events, including hemorrhagic conversion of the initial ischemic event and stenosis of large arterial vessels of the brain (e.g., carotid, vertebral, middle cerebral artery), have been reported. In the premarketing clinical trial, 3 of 449 ponatinib-treated patients developed digital or distal extremity necrosis; amputation was required in 2 patients with concomitant diabetes mellitus and peripheral arterial disease. Most (88%) patients who experienced a serious arterial thromboembolic event had one or more cardiovascular risk factors (e.g., MI, coronary artery disease, angina, stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, cigarette smoking). If an arterial thromboembolic event occurs in a patient receiving ponatinib, interruption or discontinuance of therapy may be necessary. Venous thromboembolic events, including deep-vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, portal vein thrombosis, and retinal vein thrombosis, also have been reported in patients receiving ponatinib. Dosage modification or discontinuance of ponatinib therapy should be considered in patients who develop serious venous thromboembolism.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
Ponatinib may cause fetal harm; the drug has been shown to be embryotoxic and fetotoxic in animals. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Pregnancy should be avoided during therapy. If used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while receiving ponatinib, the patient should be apprised of the potential fetal hazard.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Ponatinib (22 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Ponatinib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with chronic phase, accelerated phase, or blast phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) that is resistant or intolerant to prior tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy or Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ALL) that is resistant or intolerant to prior tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy.
FDA Label
Iclusig is indicated in adult patients with
- chronic phase, accelerated phase, or blast phase chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) who are resistant to dasatinib or nilotinib; who are intolerant to dasatinib or nilotinib and for whom subsequent treatment with imatinib is not clinically appropriate; or who have the T315I mutation
- Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Ph+ ALL) who are resistant to dasatinib; who are intolerant to dasatinib and for whom subsequent treatment with imatinib is not clinically appropriate; or who have the T315I mutation.
See sections 4. 2 Assessment of cardiovascular status prior to start of therapy and 4. 4 situations where an alternative treatment may be considered.
Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, Treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit PROTEIN KINASES. (See all compounds classified as Protein Kinase Inhibitors.)
L01EA05
L01XE24
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EA - Bcr-abl tyrosine kinase inhibitors
L01EA05 - Ponatinib
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of ponatinib is unknown. Peak concentrations of ponatinib are observed within 6 hours after Iclusig oral administration. Food does not affect absorption of food. The aqueous solubility of ponatinib is pH dependent, with higher pH resulting in lower solubility. When 45 mg of ponatinib is given to cancer patients, the pharmacokinetic parameters are as follows: Cmax = 73 ng/mL; AUC = 1253 nghr/mL;
Route of Elimination
Ponatinib is mainly eliminated via feces. Following a single oral dose of [14C]-labeled ponatinib, approximately 87% of the radioactive dose is recovered in the feces and approximately 5% in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
After oral administration of 45 mg ponatinib once daily for 28 days in cancer patients, the steady state volume of distribution is 1223 L. Ponatinib is a weak substrate for P-gp and ABCG2.
Ponatinib is greater than 99% bound to plasma proteins in vitro. The geometric mean (CV%) apparent steady state volume of distribution is 1223 liters (102%) following oral administration of Iclusig 45 mg once daily for 28 days in patients with cancer. Ponatinib is a weak substrate for both P-gp and ABCG2 [also known as BCRP] in vitro. Ponatinib is not a substrate for organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATP1B1, OATP1B3) and organic cation transporter 1 (OCT1) in vitro.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ICLUSIG (ponatinib hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (March 2014). Available from, as of March 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=807f988e-117b-4497-934d-73aa78baac71
Exposure increased by approximately 90% (median) (range: 20% to 440%) between the first dose and presumed steady state. Ponatinib is mainly eliminated via feces. Following a single oral dose of (14)C-labeled ponatinib, approximately 87% of the radioactive dose is recovered in the feces and approximately 5% in the urine.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ICLUSIG (ponatinib hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (March 2014). Available from, as of March 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=807f988e-117b-4497-934d-73aa78baac71
The absolute bioavailability of ponatinib is unknown. Peak concentrations of ponatinib are observed within 6 hours after Iclusig oral administration. Following ingestion of either a high-fat or low-fat meal by 22 healthy volunteers, plasma ponatinib exposures (AUC and Cmax) were not different when compared to fasting conditions. The aqueous solubility of ponatinib is pH dependent, with higher pH resulting in lower solubility.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ICLUSIG (ponatinib hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (March 2014). Available from, as of March 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=807f988e-117b-4497-934d-73aa78baac71
Ponatinib was equally distributed into RBCs and plasma, and did not show preferential partitioning into red blood cells in mouse, rat, monkey, or human blood. Drug derived radioactivity was found in the brain, the Tmax being 48 hours.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Iclusig (International non-proprietary name: Ponatinib p.21 (2013). Available from, as of March 13, 2014: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002695/WC500145648.pdf
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Ponatinib (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
At least 64% of a ponatinib dose undergoes phase I and phase II metabolism. CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent CYP2C8, CYP2D6 and CYP3A5 are involved in the phase I metabolism of ponatinib in vitro. Ponatinib is also metabolized by esterases and/or amidases.
In vivo, ponatinib was hydrolysed by non-specific esterases or amidases at the amide bond to an acid and aniline. AP24600 was the major metabolite in rat and human plasma but was a trace level metabolite in monkey plasma. In rat, monkey and human plasma, the amide hydrolysis metabolite AP24600 was 263%, < 1% and 58.4% of the ponatinib levels. In rats, the metabolism of ponatinib was mainly to the N-desmethyl metabolite AP24567, which was excreted in feces, and AP24600 (and its downstream metabolites) which was excreted in urine. In monkey feces drug-related radioactivity was present mostly as the parent compound or as N-desmethyl ponatinib (M42), hydroxy ponatinib (M31), a double lactam at piperazine moiety (M35) and N-oxide ponatinib (M36). In human feces, ponatinib accounted for 23.7% of the radioactivity and there was extensive metabolism of ponatinib. Other metabolites identified in human feces were hydroxy ponatinib, N-desmethyl ponatinib, and several minor metabolites resulting from two or more modifications.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Iclusig (International non-proprietary name: Ponatinib p.21 (2013). Available from, as of March 13, 2014: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002695/WC500145648.pdf
At least 64% of a ponatinib dose undergoes phase I and phase II metabolism. CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent CYP2C8, CYP2D6 and CYP3A5 are involved in the phase I metabolism of ponatinib in vitro. Ponatinib is also metabolized by esterases and/or amidases.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ICLUSIG (ponatinib hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (March 2014). Available from, as of March 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=807f988e-117b-4497-934d-73aa78baac71
After oral administration of 45 mg ponatinib once daily for 28 days in cancer patients, the terminal elimination half-life is 24 hours (range of 12 - 66 hours).
The terminal half-life of ponatinib in plasma after an IV dose was 9.7 hr in the rat and 5.3 hr in the monkey.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Iclusig (International non-proprietary name: Ponatinib p.21 (2013). Available from, as of March 13, 2014: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002695/WC500145648.pdf
The geometric mean (range) terminal elimination half-life of ponatinib was approximately 24 (12 to 66) hours following Iclusig 45 mg oral administration once daily for 28 days in patients with cancer.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ICLUSIG (ponatinib hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (March 2014). Available from, as of March 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=807f988e-117b-4497-934d-73aa78baac71
Ponatinib is a multi-target kinase inhibitor. Its primary cellular target is the Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase protein which is constitutively active and promotes the progression of CML. This protein arises from the fused Bcr and Abl gene- what is commonly known as the Philadelphia chromosome. Ponatinib is unique in that it is especially useful in the treatment of resistant CML because it inhibits the tyrosine kinase activity of Abl and T315I mutant kinases. The T315I mutation confers resistance in cells as it prevents other Bcr-Abl inhibitors from binding to the Abl kinase. Other targets that ponatinib inhibits are members of the VEGFR, PDGFR, FGFR, EPH receptors and SRC families of kinases, and KIT, RET, TIE2, and FLT3. A decrease in tumour size expressing native or T315I mutant BCR-ABL have been observed in rats.
Ponatinib is a kinase inhibitor. Ponatinib inhibited the in vitro tyrosine kinase activity of ABL and T315I mutant ABL with IC50 concentrations of 0.4 and 2.0 nM, respectively. Ponatinib inhibited the in vitro activity of additional kinases with IC50 concentrations between 0.1 and 20 nM, including members of the VEGFR, PDGFR, FGFR, EPH receptors and SRC families of kinases, and KIT, RET, TIE2, and FLT3. Ponatinib inhibited the in vitro viability of cells expressing native or mutant BCR-ABL, including T315I. In mice, treatment with ponatinib reduced the size of tumors expressing native or T315I mutant BCR-ABL when compared to controls.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ICLUSIG (ponatinib hydrochloride) tablet, film coated (March 2014). Available from, as of March 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=807f988e-117b-4497-934d-73aa78baac71
Gain-of-function mutations of membrane receptor tyrosine kinase KIT especially gate-keeper D816V point mutation in KIT render kinase auto-activation, disease progression, and poor prognosis. D816V KIT is found in -80% of the patients of systemic mastocytosis (SM), and is resistant to the first and the second generations of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). The purpose of this investigation was aimed at exploring whether ponatinib (AP24534), a novel effective TKI against T315I Bcr-Abl was active against D816V KIT. /The researchers/ discovered that ponatinib abrogated the phosphorylation of KIT harboring either V560G (sensitive to imatinib) or D816V mutation (resistant to imatinib) and the downstream signaling transduction. Ponatinib inhibited the growth of D816V KIT expressing cells in culture and nude mouse xenografted tumor. Ponatinib triggered apoptosis by inducing the release of cytochrome c and AIF, downregulation of Mcl-1. Furthermore, ponatinib abrogated the phosphorylation of beta-catenin at site Y654, suppressed the translocation of beta-catenin, inhibited the transcription and DNA binding of TCF and the expression of its targets (e.g. Axin2, c-Myc, and cyclin D1). Moreover, ponatinib was highly active against xenografted D816V KIT tumors in nude mice and significantly prolonged the survival of mice with aggressive SM or mast cell leukemia by impeding the expansion and infiltration of mast cells with imatinib-resistant D814Y KIT. ...
PMID:24552773 Jin B et al; Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Feb 19. (Epub ahead of print)
The BCR-ABL inhibitor imatinib has revolutionized the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. However, drug resistance caused by kinase domain mutations has necessitated the development of new mutation-resistant inhibitors, most recently against the T315I gatekeeper residue mutation. Ponatinib (AP24534) inhibits both native and mutant BCR-ABL, including T315I, acting as a pan-BCR-ABL inhibitor. Here, we undertook a combined crystallographic and structure-activity relationship analysis on ponatinib to understand this unique profile. While the ethynyl linker is a key inhibitor functionality that interacts with the gatekeeper, virtually all other components of ponatinib play an essential role in its T315I inhibitory activity. The extensive network of optimized molecular contacts found in the DFG-out binding mode leads to high potency and renders binding less susceptible to disruption by single point mutations. The inhibitory mechanism exemplified by ponatinib may have broad relevance to designing inhibitors against other kinases with mutated gatekeeper residues.
PMID:21118377 Zhou T et al; Chem Biol Drug Des 77 (1): 1-11 (2011)
Ponatinib is a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor with potent activity against BCR-ABL with mutations, including T315I, and also against fms-like tyrosine kinase 3. We tested interactions between ponatinib at pharmacologically relevant concentrations of 50 to 200 nmol/L and the MDR-associated ATP-binding cassette (ABC) proteins ABCB1, ABCC1, and ABCG2. Ponatinib enhanced uptake of substrates of ABCG2 and ABCB1, but not ABCC1, in cells overexpressing these proteins, with a greater effect on ABCG2 than on ABCB1. Ponatinib potently inhibited [(125)I]-IAAP binding to ABCG2 and ABCB1, indicating binding to their drug substrate sites, with IC(50) values of 0.04 and 0.63 umol/L, respectively. Ponatinib stimulated ABCG2 ATPase activity in a concentration-dependent manner and stimulated ABCB1 ATPase activity at low concentrations, consistent with it being a substrate of both proteins at pharmacologically relevant concentrations. The ponatinib IC(50) values of BCR-ABL-expressing K562 cells transfected with ABCB1 and ABCG2 were approximately the same as and 2-fold higher than that of K562, respectively, consistent with ponatinib being a substrate of both proteins, but inhibiting its own transport, and resistance was also attenuated to a small degree by ponatinib-induced downregulation of ABCB1 and ABCG2 cell-surface expression on resistant K562 cells. Ponatinib at pharmacologically relevant concentrations produced synergistic cytotoxicity with ABCB1 and ABCG2 substrate chemotherapy drugs and enhanced apoptosis induced by these drugs, including daunorubicin, mitoxantrone, topotecan, and flavopiridol, in cells overexpressing these transport proteins. Combinations of ponatinib and chemotherapy drugs warrant further testing.
PMID:22778153 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3683995 Sen R et al; Mol Cancer Ther 11 (9): 2033-44 (2012)