

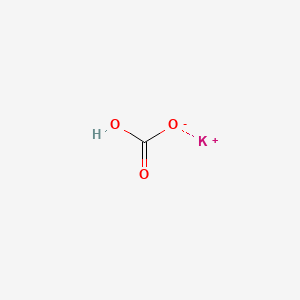

1. Khco3
2. Potassium Hydrocarbonate
1. 298-14-6
2. Potassium Hydrogen Carbonate
3. Potassium Hydrogencarbonate
4. Potassium Acid Carbonate
5. Monopotassium Carbonate
6. Carbonic Acid, Monopotassium Salt
7. Potassiumbicarbonate
8. Khco3
9. Potassium;hydrogen Carbonate
10. Armicarb
11. Kafylox
12. Kaligreen
13. Milstop
14. Purple K
15. Hm5z15lebn
16. Potassium Carbonate Solution
17. Potassium Bicarbonate [usp]
18. Chebi:81862
19. Ins-501(ii)
20. E-501(ii)
21. Mfcd00011402
22. Potassium Bicarbonate (usp)
23. Ccris 3510
24. Einecs 206-059-0
25. Unii-hm5z15lebn
26. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 073508
27. Potasium Bicarbonate
28. Potassium Bicabonate
29. Potassium Bicarbonat
30. Pbc
31. Einecs 241-378-9
32. K-vescent (tn)
33. Potassiumhydrogencarbonate
34. Potassium Hydogencarbonate
35. Potassium;hydron;carbonate
36. Ec 206-059-0
37. Potassium Hydrogen-carbonate
38. Schembl2420
39. Ins No.501(ii)
40. Chembl2106975
41. Dtxsid0021177
42. Potassium Bicarbonate, Acs Grade
43. Potassium Bicarbonate [ii]
44. Potassium Bicarbonate [mi]
45. Potassium Bicarbonate [fcc]
46. Potassium Bicarbonate [inci]
47. Potassium Bicarbonate [vandf]
48. Potassium Bicarbonate [mart.]
49. Akos009159056
50. Carbonic Acid, Potassium Salt (1:1)
51. Potassium Bicarbonate [usp-rs]
52. Potassium Bicarbonate [who-dd]
53. Db11098
54. E501
55. Potassium Carbonate Solution [fcc]
56. Ft-0645098
57. Potassium Bicarbonate [usp Monograph]
58. C18606
59. D02077
60. Potassium Bicarbonate, Trace Metals Grade 99.98%
61. Potassium Hydrogen Carbonate [ep Monograph]
62. Q410529
63. J-017655
| Molecular Weight | 100.115 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | CHKO3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 99.95627537 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 99.95627537 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 60.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 5 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 33.9 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Potassium bicarbonate is used as an antacid, electrolyte replenisher and potassium supplement. It can also be used as an excipient in drug formulations. An antacid is a medication used to neutralize gastric acid in a short timeframe after ingestion and the effect is soon overcome by meal-stimulated acid secretion.
Potassium is the principal intracellular cation in most body tissues. The concentration of potassium ions is essential to conduct nerve impulses in specialized tissues like brain, heart and skeletal muscle, as well as to maintain normal renal function, acid-base balance, and cellular metabolic functions. The use of compounds containing bicarbonate is showed to produce the release of CO2. This effect has been one of the problems of the use of potassium bicarbonate as it can cause eructation.
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A12 - Mineral supplements
A12B - Potassium
A12BA - Potassium
A12BA04 - Potassium hydrogencarbonate
Absorption
Potassium bicarbonate intake is done mainly in the small intestine in which approximately 90% of the potassium will be absorbed by passive diffusion.
Route of Elimination
Approximately 90% of the exogenous potassium consumed is lost in the urine while the other 10% is excreted in feces and a very small amount can be found in the sweat. The excreted potassium is freely filtered by the glomerulus of the kidney.
Some reports have shown that after absorption, most body potassium exchanges rapidly with a half-life of less than 7 hours.
The antacid potential of potassium bicarbonate is attained by increasing the gastrointestinal pH by neutralizing hydrochloric acid. The increase in pH results in suppression of the action of pepsin which is the enzyme that exacerbates ulceration due to the presence of acid.