

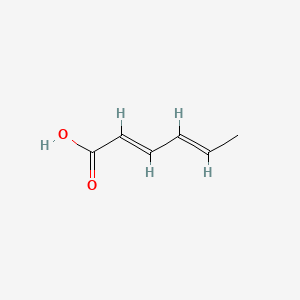

1. Acid, Hexadienoic
2. Acid, Propenylacrylic
3. Acid, Sorbic
4. Hexadienoic Acid
5. Potassium Sorbate
6. Propenylacrylic Acid
7. Sodium Sorbate
8. Sorbate, Potassium
9. Sorbate, Sodium
1. 110-44-1
2. 2,4-hexadienoic Acid
3. (2e,4e)-hexa-2,4-dienoic Acid
4. 2e,4e-hexadienoic Acid
5. Panosorb
6. Sorbistat
7. 2-propenylacrylic Acid
8. Hexadienoic Acid
9. Trans,trans-sorbic Acid
10. (e,e)-2,4-hexadienoic Acid
11. 2,4-hexadienoic Acid, (2e,4e)-
12. Hexa-2,4-dienoic Acid
13. 2,4-hexadienoic Acid, (e,e)-
14. Alpha-trans-gamma-trans-sorbic Acid
15. Preservastat
16. (e,e)-sorbic Acid
17. Trans,trans-2,4-hexadienoic Acid
18. Crotylidene Acetic Acid
19. Kyselina Sorbova
20. Acetic Acid, Crotylidene-
21. (2e,4e)-2,4-hexadienoic Acid
22. (e,e)-1,3-pentadiene-1-carboxylic Acid
23. 22500-92-1
24. Acetic Acid, (2-butenylidene)-
25. Trans-trans-2,4-hexadienoic Acid
26. Hexadienoic Acid, (e,e)
27. (2-butenylidene)acetic Acid
28. C6:2n-2,4
29. Sorbic Acid (nf)
30. Sorbic Acid [nf]
31. 1,3-pentadiene-1-carboxylic Acid
32. 1,3-pentadiene-1-carboxylic Acid, (e,e)-
33. E 200
34. Kyselina 1,3-pentadien-1-karboxylova
35. (2-butenylidene) Acetic Acid
36. Fema No. 3921
37. Chebi:38358
38. Ins-200
39. X045wj989b
40. Nsc-35405
41. Nsc-49103
42. Nsc-50268
43. 5309-56-8
44. Ncgc00091737-01
45. .alpha.-trans-.gamma.-trans-sorbic Acid
46. Dsstox_cid_1277
47. 2,4-hexadienoic Acid, (2e,4e)-, Homopolymer
48. Dsstox_rid_76053
49. Dsstox_gsid_21277
50. Hexadienic Acid
51. Caswell No. 801
52. Sorbic Acid [usan]
53. Acidum Sorbicum
54. Kyselina Sorbova [czech]
55. 34344-66-6
56. Cas-110-44-1
57. Sorbic Acid Solution
58. Ccris 5748
59. Hsdb 590
60. (2e)-2,4-hexadienoic Acid
61. Einecs 203-768-7
62. Sorbic Acid, (e,e)-
63. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 075901
64. Sorbinsaeure
65. Sorbinsaure
66. Sorbic-acid
67. Nsc49103
68. Unii-x045wj989b
69. Ai3-14851
70. E-sorbic Acid
71. Trans,trans-sa
72. Kyselina 1,3-pentadien-1-karboxylova [czech]
73. (e,e)-sorbic Acid; Sorbic Acid
74. Sorbic Acid Fcc
75. Hexa-2,4-dienoic Acid, (e,e)-
76. 2,4-hexadiensaeure
77. Mfcd00002703
78. Crotylidene-acetic Acid
79. Starbld0040592
80. Sorbic Acid [ii]
81. Sorbic Acid [mi]
82. Sorbic Acid [fcc]
83. Ec 203-768-7
84. Schembl1647
85. Sorbic Acid [hsdb]
86. Sorbic Acid [inci]
87. Sorbic Acid [vandf]
88. Sorbic Acid [mart.]
89. Sorbic Acid, >=99.0%
90. Mls002152937
91. (2-butenylidene)-acetic Acid
92. Sorbic Acid [usp-rs]
93. Sorbic Acid [who-dd]
94. (e,e)-sa
95. Chembl250212
96. (e,e)-hexa-2,4-dienoic Acid
97. Dtxsid3021277
98. Sorbic Acid, Analytical Standard
99. Chebi:35962
100. Fema 3921
101. Hms3039e13
102. Sorbic Acid [ep Monograph]
103. Sorbic Acid, Potassium Salt (van)
104. Hy-n0626
105. Str09707
106. Zinc1558385
107. Tox21_111164
108. Tox21_201719
109. Tox21_300182
110. 2,4-sa
111. Lmfa01030100
112. S4983
113. (2e,4e)-2,4-hexadienoic Acid #
114. Sorbic Acid 100 Microg/ml In Water
115. 2, 4-hexadienoic Acid Potassium Salt
116. Akos000119456
117. Ccg-266056
118. 2,4-hexadienoic Acid, (trans,trans)-
119. 2,4-hexadienoic Acid, >=99%, Fcc
120. Sorbic Acid 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
121. Ncgc00091737-02
122. Ncgc00091737-03
123. Ncgc00091737-05
124. Ncgc00253957-01
125. Ncgc00259268-01
126. E200
127. Smr001224532
128. Sorbic Acid 1000 Microg/ml In Methanol
129. Sorbic Acid, Tested According To Ph.eur.
130. Sorbic Acid, Saj First Grade, >=98.5%
131. Cs-0009618
132. S0053
133. Sorbic Acid 1000 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
134. Sorbic Acid, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 98%
135. (e,e)-2,4-hexadienoic Acid [fhfi]
136. Sorbic Acid, For Synthesis, 99.0-101.0%
137. Alpha-trans-laquo Gammaraquo -trans-sorbic Acid
138. D05892
139. E80726
140. Hexadienoic Acid1,3-pentadiene-1-carboxylic Acid
141. A829400
142. An-651/40229308
143. Q407131
144. J-002425
145. J-524281
146. F8886-8255
147. Sorbic Acid, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
148. Sorbic Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
149. Sorbic Acid, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 112.13 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H8O2 |
| XLogP3 | 1.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 112.052429494 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 112.052429494 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 37.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 8 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 123 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Food Preservatives
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Atomoxetine. Online file (MeSH, 2016). Available from, as of May 3, 2016: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2016/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
The ocular bioavailability of timolol increased in sorbic acid solution due to ion pair formation. Its octanol/water partition coefficient also increased, suggesting the formation of a more lipophilic complex. The concentration of timolol in rabbit aqueous humor was determined after instillation of timolol ophthalmic solution containing sorbic acid. When the molar ratio of sorbic acid to timolol was two or higher, the concentration of timolol in the aqueous humor was higher than with timolol alone. In the presence of sorbic acid the maximal aqueous humor concentration and the area under the curve were more than two-fold higher than those of Timoptol, a timolol maleate ophthalmic solution, and similar in value to TIMOPTIC-XE, a gel-forming ophthalmic solution. To investigate the transcorneal absorption mechanism, in vitro permeation profiles across the intact and de-epithelialyzed cornea were analyzed on the basis of the bilayer diffusion model. The partition coefficient in the epithelium was about twice as high in the presence of sorbic acid than with timolol alone, although the diffusion coefficient in the epithelium did not change. We conclude that the improved ocular bioavailability in the presence of sorbic acid is due to increased partitioning of timolol in the corneal epithelium.
PMID:15019072 Higashiyama M et al; Int J Pharm 272 (1-2): 91-8 (2004)
Topical medicaments and cosmetics containing sorbic acid should be avoided. There has been no evidence of flare-ups of eczema from ingestion of foods containing sorbic acid. Therefore, avoiding foods with sorbic acid is unnecessary.
Marks, J.G. Jr., DeLeo V.A., Contact and Occupational Dermatology. St. Louis, MO: Mosby Year Book 1992., p. 120
Food Preservatives
Substances capable of inhibiting, retarding or arresting the process of fermentation, acidification or other deterioration of foods. (See all compounds classified as Food Preservatives.)
Following oral administration of radiolabelled sorbic acid, ... the total recovery of radioactivity was approx. 100% of the low and high doses. The major route of metabolism of sorbic acid was via expired CO2 with approx. 85% of the admininstered radioactivity being recovered as CO2 within 4-10 hours post administration. From the rate and extent of this metabolism, it may be concluded that sorbic acid is rapidly and quantitatively absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract.
European Chemicals Agency (ECHA); Registered Substances, Hexa-2,4-dienoic acid (CAS Number: 110-44-1) (EC Number: 203-768-7) (Last updated: December 27, 2015). Available from, as of May 2, 2016: https://echa.europa.eu/
Metabolism of sorbic acid in rats is identical to that of normally occurring fatty acids. Under normal conditions of intake, sorbic acid is almost completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water. Traces (0.1% of dose) may be converted by oxidation to trans,trans-muconic acid.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V5 812
1,4-Dinitro-2-methylpyrrole, a mutagenic product formed by the interaction of two common food additives, sorbic acid and sodium nitrite, was transformed to 1-nitro-2-methyl-4-aminopyrrole by human fecal mixtures and various intestinal bacterial strains.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V5 812
Following oral administration of radiolabelled sorbic acid, ... the total recovery of radioactivity was approx. 100% of the low and high doses. The major route of metabolism of sorbic acid was via expired CO2 with approx. 85% of the administered radioactivity being recovered as CO2 within 4-10 hours p.a. From the rate and extent of this metabolism, it may be concluded that sorbic acid is rapidly and quantitatively absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract.
European Chemicals Agency (ECHA); Registered Substances, Hexa-2,4-dienoic acid (CAS Number: 110-44-1) (EC Number: 203-768-7) (Last updated: December 27, 2015). Available from, as of May 2, 2016: https://echa.europa.eu/