

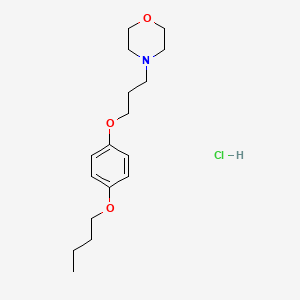

1. 4-(3-(4-butoxyphenoxy)propyl)morpholine
2. 4-(3-(p-butoxyphenoxy)propyl)morpholine
3. Balsabit
4. Fleet Pain Relief
5. Itch-x
6. Pramegel
7. Pramocaine
8. Pramocaine Hydrochloride
9. Pramox
10. Pramoxine
11. Prax
12. Proctofoam
13. Tronolane
14. Tronothane
1. 637-58-1
2. Pramoxine Hcl
3. Pramocaine Hydrochloride
4. Prax Lotion
5. Tronothane
6. Pramocaine (hydrochloride)
7. Morpholine, 4-[3-(4-butoxyphenoxy)propyl]-, Hydrochloride
8. 4-[3-(4-butoxyphenoxy)propyl]morpholine Hydrochloride
9. Nsc-25573
10. 4-(3-(4-butoxyphenoxy)propyl)morpholine Hydrochloride
11. Pramoxine Hydrochloride [usp]
12. Mls000028604
13. Tronolane
14. 88ayb867l5
15. 4-(3-(p-butoxyphenoxy)propyl)morpholine Hydrochloride
16. 4-[3-(4-butoxyphenoxy)propyl]morpholine;hydrochloride
17. 637-58-1 (hcl)
18. Morpholine, 4-(3-(4-butoxyphenoxy)propyl)-, Hydrochloride
19. Smr000058670
20. Dsstox_cid_27757
21. Dsstox_rid_82534
22. Dsstox_gsid_47777
23. Pramoxine Hydrochloride (usp)
24. Tronothane Hydrochloride
25. Proctofoam-ns
26. Hsdb 7220
27. Ncgc00016529-01
28. Cas-637-58-1
29. Einecs 211-293-1
30. Nsc 25573
31. 4-[3-(p-butoxyphenoxy)propyl]morpholine Hydrochloride
32. Unii-88ayb867l5
33. Sr-01000000243
34. Pramoxine, Hcl
35. Tronothane (tn)
36. Prestwick_1044
37. P-butoxyphenyl Gamma-morpholinopropyl Ether Hydrochloride
38. Gamma-morpholinopropyl 4-n-butoxyphenyl Ether Hydrochloride
39. Opera_id_1593
40. Pramoxine Hcl [inci]
41. Mls002222295
42. Schembl180542
43. Spectrum1501139
44. Amy585
45. Chebi:8358
46. Chembl1201171
47. Dtxsid2047777
48. Morpholine, 4-(3-(p-butoxyphenoxy)propyl)-, Hydrochloride
49. Hms1570o13
50. Hms1921j07
51. Pharmakon1600-01501139
52. Hy-b1319
53. Nsc25573
54. Pramoxine Hydrochloride [mi]
55. Tox21_110477
56. Mfcd00054323
57. Nsc757847
58. S4092
59. Pramoxine Hydrochloride [hsdb]
60. Akos015895041
61. Tox21_110477_1
62. Ac-2094
63. Ccg-212937
64. Cs-4643
65. Nsc-757847
66. Pramoxine Hydrochloride [vandf]
67. Wln: T6n Dotj A3or Do4 &gh
68. Pramocaine Hydrochloride [mart.]
69. Pramoxine Hydrochloride [usp-rs]
70. Ncgc00016529-07
71. Ncgc00094907-01
72. Ncgc00094907-02
73. Ncgc00094907-03
74. Pramocaine Hydrochloride [who-dd]
75. As-12691
76. Db-054541
77. Ft-0603501
78. Pramoxine Hydrochloride [orange Book]
79. Sw197114-3
80. Vu0239834-5
81. D00739
82. D97624
83. Epifoam Component Pramoxine Hydrochloride
84. Pramoxine Hydrochloride [usp Monograph]
85. A834509
86. Pramosone Component Pramoxine Hydrochloride
87. Pramoxine Hydrochloride Component Of Epifoam
88. Pramoxine Hydrochloride, Analytical Standard, >=98%
89. Q-100732
90. Sr-01000000243-3
91. Pramoxine Hydrochloride Component Of Pramosone
92. Proctofoam Hc Component Pramoxine Hydrochloride
93. Q27269918
94. 4-[3-(4-butoxyphenoxy)propyl]morpholin-4-ium;chloride
95. Pramoxine Hydrochloride Component Of Proctofoam Hc
96. P-butoxyphenyl .gamma.-morpholinopropyl Ether Hydrochloride
97. .gamma.-morpholinopropyl 4-n-butoxyphenyl Ether Hydrochloride
98. 4-[3-(4-butoxyphenoxy)propyl]morpholine Hydrochloride (1:1)
99. Morpholine, 4-[3-(p-n-butoxyphenoxy )propyl]-, Hydrochloride
100. 4-n-butoxyphenyl.gamma.-morpholinopropyl Ether Hydrochloride
101. Morpholine, 4-[3-(4-butoxyphenoxy)propyl]-, Hydrochloride (1:1)
102. 4-[3-(4-butoxyphenoxy)propyl]morpholine Chloride;pramocaine Hydrochloride
103. Pramoxine Hydrochloride, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
104. Pramoxine Hydrochloride, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 329.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H28ClNO3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 329.1757714 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 329.1757714 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 30.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 248 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Anesthetic (local)
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 1376
Indicated for the symptomatic relief of: hemorrhoids, anorectal inflammation and anorectal pain. (these medications /including pramoxine/ are effective when applied to the anal, periana, or anorectal areas. However, they are not likely to relieve symptoms associated with conditions confined to the rectum, which lacks sensory nerve fibers.) /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 153
Pramoxine preparations are used topically for the temporary relief of pain and itching associated with dermatoses; rashes due to poison ivy, poison oak, poison sumac, insect bites; minor burns; anogenital pruritus or irritation; and fissures; or hemorrhoids. The drug should not be used for bronchoscopy or gastroscopy since it is not sufficiently potent to abolish the gag reflex.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2004 (Plus Supplements)., p. 3414
Local effects, such as burning or stinging, may occur following topical application of pramoxine. The drug has a low index of sensitization, and cross-sensitization with other local anesthetics is unlikely.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2004 (Plus Supplements)., p. 3414
Topical pramoxine preparations should not be used in or near the eyes or nose.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2004 (Plus Supplements)., p. 3414
The preparations should not be applied to extensive areas of skin and are not for prolonged use. The aerosol foam for rectal administration should not be used longer than 4 consecutive weeks.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2004 (Plus Supplements)., p. 3414
If pramoxine preparations are used for self-medication and the condition worsens or symptoms persist for prolonged periods (e.g., for more than 7 days) or clear and occur again within a few days, the drug should be discontinued and a physician consulted.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2004 (Plus Supplements)., p. 3414
If rectal bleeding occurs during use of pramoxine for pain and itching of hemorrhoids or if erythema, irritation, swelling, or pain occurs during use of pramoxine preparations, the drug should be discontinued and a physician consulted.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2004 (Plus Supplements)., p. 3414
Anesthetics, Local
Drugs that block nerve conduction when applied locally to nerve tissue in appropriate concentrations. They act on any part of the nervous system and on every type of nerve fiber. In contact with a nerve trunk, these anesthetics can cause both sensory and motor paralysis in the innervated area. Their action is completely reversible. (From Gilman AG, et. al., Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 8th ed) Nearly all local anesthetics act by reducing the tendency of voltage-dependent sodium channels to activate. (See all compounds classified as Anesthetics, Local.)
... These agents are readily absorbed through mucous membranes into the systemic circulation. The rate of absorption is influenced by the vascularity or rate of blood flow at the site of application, the total dosage (concentration and volume) administered, and the duration of exposure. ... /Local anesthetics/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 154
Local anesthetics block both the initiation and conduction of nerve impulses by decreasing the neuronal membrane's permeability to sodium ions. This reversibly stabilizes the membrane and inhibits depolarization, resulting in the failure of a propagated action potential and subsequent conduction blockade. /Local anesthetics/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 154
